![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the properties of life?
|
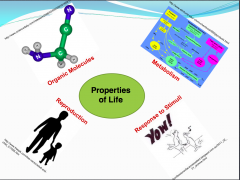
1. Organic Molecules, definite structure
2. Use of raw materials for structure 3. Ability to reproduce structure 4. Ability to respond to stimuli |
|
What is anatomy?
|
Study of the structure of body parts and their relationships with one another.
|
|
What is physiology?
|
Study of the function of the body's structural machinery.
|
|
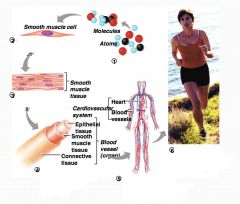
What are the levels of structural organisation?
|
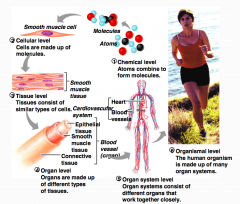
1. Chemical - atoms combined to form molecules
2. Cellular - made of molecules 3. Tissue - similar types of cells 4. Organ - different types of tissue 5. Organ System - different organs working together 6. Organismal - various organ systems |
|
What are some organ systems studied in this subject?
|
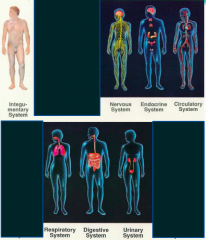
- Integumentary system
- Nervous system - Endocrine system - Circulatory system - Respiratory system - Digestive system - Urinary system |
|
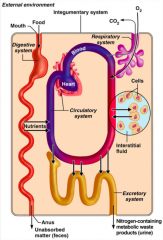
What does the gastrointestinal system in terms of organ system interrelationships?
|
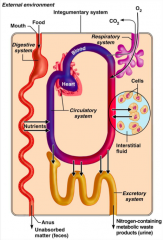
The gastrointestinal system digests and metabolises food.
|
|
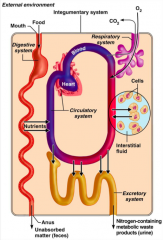
What does the circulatory system do in terms of organ system interrelationships?
|
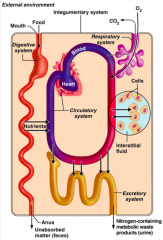
Blood, which is part of the circulatory system, distributes nutrients and oxygen.
|
|
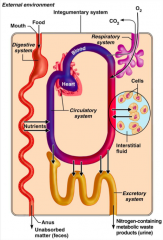
What do the urinary and respiratory systems do in terms of organ system interrelationships?
|
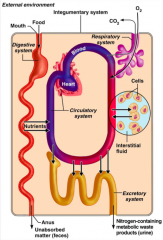
The urinary and respiratory systems eliminate metabolic wastes.
|
|
|
What are the survival needs?
|
- Nutrients
- Oxygen - Water - Normal body temperature - Atmospheric pressure |
|
|
Why do we need nutrients to survive?
|
Needed for energy and cell building.
|
|
|
Why do we need oxygen to survive?
|
Necessary for metabolic reactions.
|
|
|
Why is water needed for survival?
|
Provides the necessary environment for chemical reactions.
|
|
|
Why do we need a normal body temperature to survive?
|
Necessary for chemical reactions to occur at life-sustaining rates.
|
|
|
Why do we need correct atmospheric pressure to survive?
|
Required for proper breathing and gas exchange in the lungs.
|
|
|
What is homeostasis?
|
Ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in an ever-changing outside world.
|
|
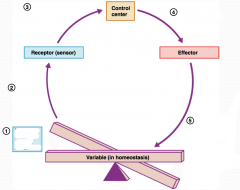
What is step 1 in the Homeostatic Control Mechanism?
|
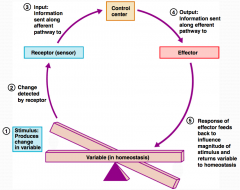
Stimulus produces change in a variable.
|
|
What is step 2 in the Homeostatic Control Mechanism?
|
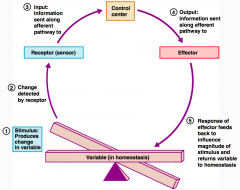
Change is detected by receptor.
|
|
What is step 3 in the Homeostatic Control Mechanism?
|
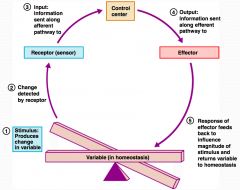
Input information is sent along the afferent pathway to the control center.
|
|
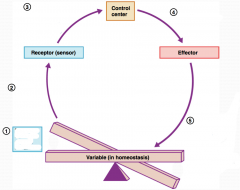
What is step 4 in the Homeostatic Control Mechanism?
|
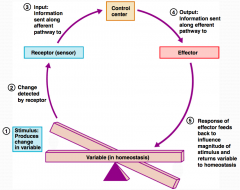
Information is outputted by the control center and sent along the efferent pathway to the effector.
|
|
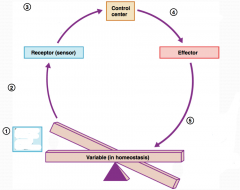
What is step 5 in the Homeostatic Control Mechanism?
|
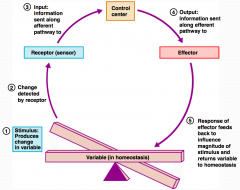
Response of effector feeds back to influence the magnitude of the stimulus and returns variable to homeostasis.
|
|
Describe the anatomical position.
|
Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body.
|
|
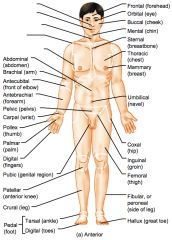
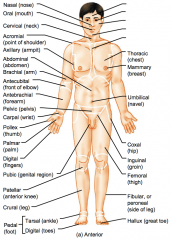
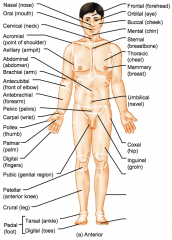
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
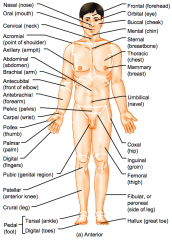
Nasal (nose)
Oral (mouth) Cervical (neck) Acromial (point of shoulder) Axillary (armpit) |
|
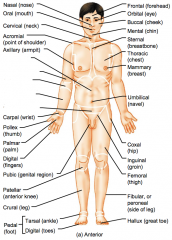
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
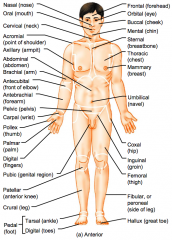
Abdominal (abdomen)
Brachial (arm) Antecubital (front of elbow) Antebrachial (forearm) Pelvic (pelvis) |
|
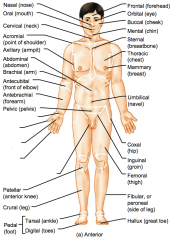
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
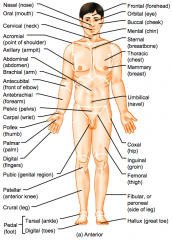
Carpal (wrist)
Pollex (thumb) Palmar (palm) Digital (fingers) Pubic (genital region) |
|
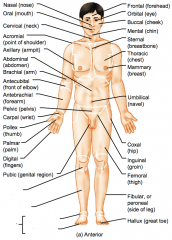
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
Patellar (anterior knee)
Crural (leg) Pedal (foot) Tarsal (ankle) Digital (toes) |
|
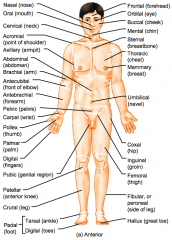
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
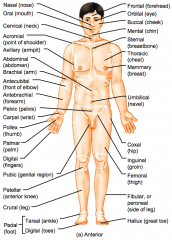
Frontal (forehead)
Orbital (eye) Buccal (cheek) Mental (chin) Sternal (breastbone) |
|
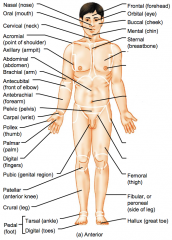
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
Thoracic (chest)
Mammary (breast) Umbilical (navel) Coxal (hip) Inguinal (groin) |
|
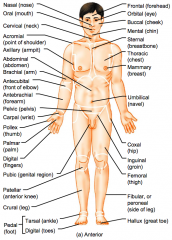
Name the hidden regional anterior view terms.
|
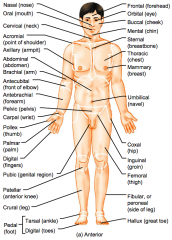
Femoral (thigh)
Fibular or perineal (side of leg) Hallux (great toe) |
|
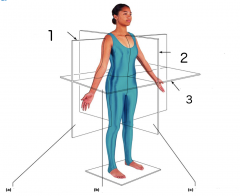
Name each of the body planes.
|
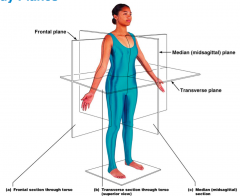
1. Frontal Plane
2. Median (midsagittal) plane 3. Transverse plane a. Frontal section through torso b. Transverse section through torso (superior view) c. Median (midsagittal) section |
|
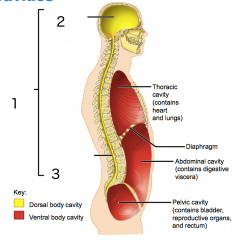
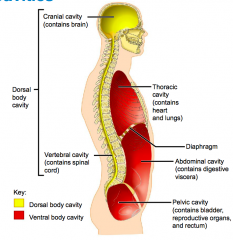
Name each of the hidden lateral view body cavities.
|
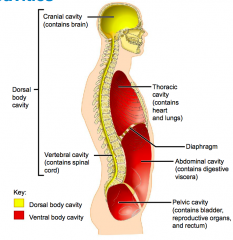
1. Dorsal body cavity
2. Cranial cavity (contains brain) 3. Vertebral cavity (contains spinal cord) |
|
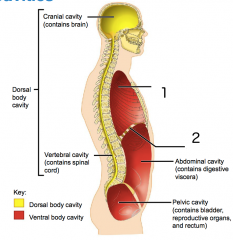
Name each of the hidden lateral view body cavities.
|
1. Thoracic cavity (contains heart and lungs)
2. Diaphragm |
|
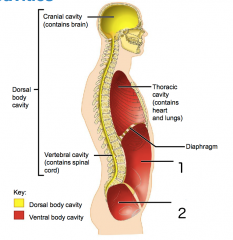
Name each of the hidden lateral view body cavities.
|
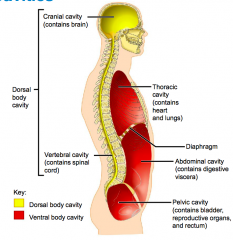
1. Abdominal cavity (contains digestive viscera)
2. Pelvic cavity (contains bladder, reproductive organs and rectum) |
|
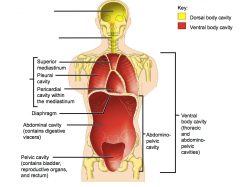
Name each of the hidden anterior view body cavities.
|
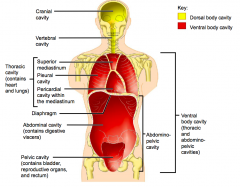
Cranial cavity
Vertebral cavity Thoracic cavity (contains lungs and heart) |
|
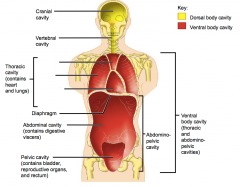
Name each of the hidden anterior view body cavities.
|
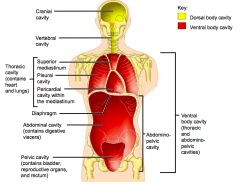
Superior mediastinum
Pleural cavity Pericardial cavity within the mediastinum |
|
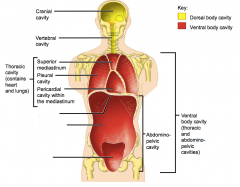
Name each of the hidden anterior view body cavities.
|
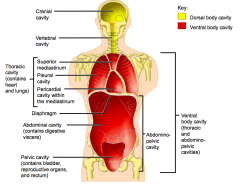
Diaphragm
Abdominal cavity (contains digestive viscera) Pelvic cavity (contains bladder, reproductive organs and rectum) |
|
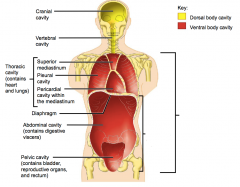
Name each of the hidden anterior view body cavities.
|
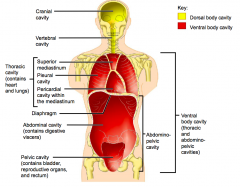
Abdominopelvic cavity
Ventral body cavity (thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities) |
|
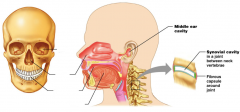
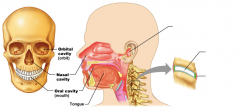
Name each of the hidden smaller body cavities.
|
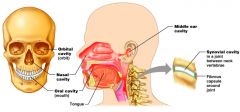
Orbital cavity (orbit)
Nasal cavity Oral cavity (mouth) Tongue |
|
Name each of the hidden smaller body cavities.
|
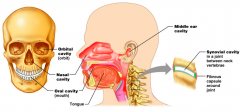
Middle ear cavity
Synovial cavity (in a joint between neck vertebrae) Fibrous capsule around joint |
|
Name each of the hidden abdominopelvic regions.
|
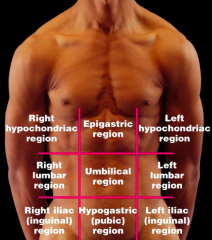
Right hypochondriac region
Right lumbar region Right iliac (inguinal) region |
|
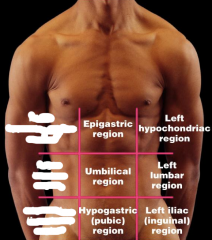
Name each of the hidden abdominopelvic regions.
|
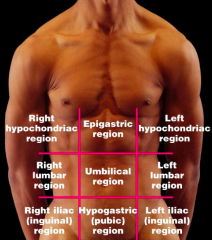
Epigastric region
Umbilical region Hypograstric (pubic) region |
|
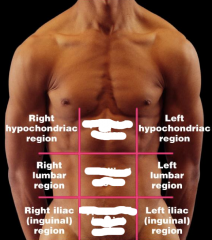
Name each of the hidden abdominopelvic regions.
|
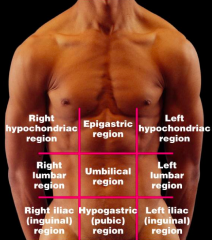
Left hypochondriac region
Left lumbar region Left iliac (inguinal) region |
|
|
Name each of the abdominopelvic quadrants starting from the stop left going clockwise.
|
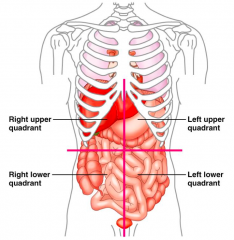
Right upper quadrant
Left upper quadrant Left lower quadrant Right lower quadrant |
|
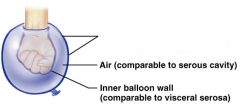
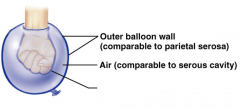
Name the hidden part of the serous membrane relationship.
|
Parietal serosa - outer balloon wall
|
|
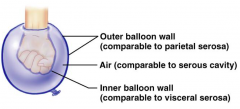
Name the hidden part of the serous membrane relationship.
|
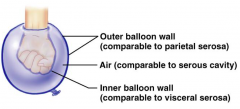
Serous cavity - air
|
|
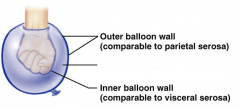
Name the hidden part of the serous membrane relationship.
|
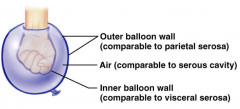
Visceral serosa - inner balloon wall
|
|
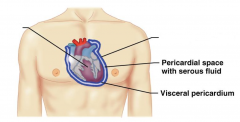
Name the hidden parts of the heart serosa.
|
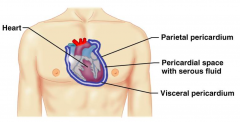
Heart
Parietal pericardium |
|
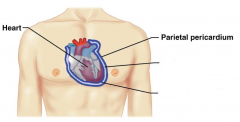
Name the hidden parts of the heart serosa.
|
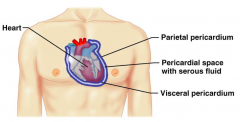
Pericardial space with serous fluid
Visceral pericardium |
|
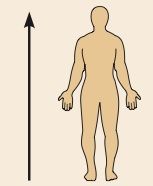
Superior
|
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
|
|
Inferior
|
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
|
|
Anterior
|
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of; Ventral
|
|
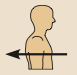
Posterior
|
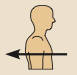
Toward or at the back of the body; behind; Dorsal
|
|
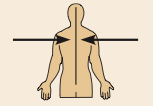
Medial
|
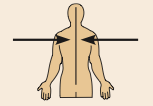
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
|
|
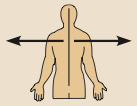
Lateral
|
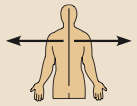
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
|
|
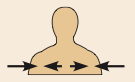
Intermediate
|
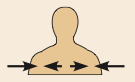
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
|
|
Proximal
|
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
|
Distal
|
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
|
Superficial
|
Toward or at the body surface
|
|

Deep
|

Away from the body surface; more internal
|
|
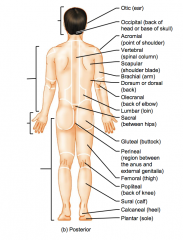
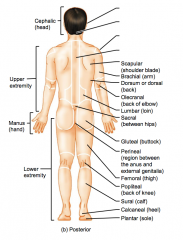
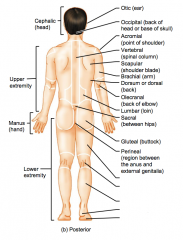
Name the hidden parts of the posterior region terms.
|
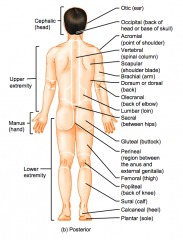
Cephalic (head)
Upper extremity Manus (hand) Lower Extremity |
|
Name the hidden parts of the posterior region terms.
|
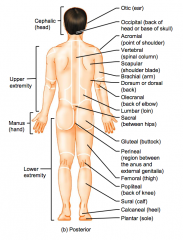
Otic (ear)
Occipital (back of head or base of the skull) Acromial (point of the shoulder) Vertebral (spinal column) |
|
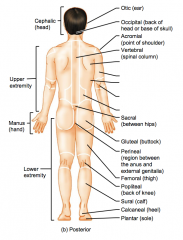
Name the hidden parts of the posterior region terms.
|
Scapular (shoulder blade)
Brachial (arm) Dorsum or dorsal (back) Olecranal (back of elbow) |
|
|
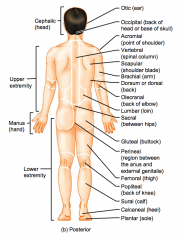
Name the hidden parts of the posterior region terms.
|
Lumbar (loin)
Sacral (between hips) Gluteal (buttock) Perineal (region between the anus and the external genitalia) |
|
Name the hidden parts of the posterior region terms.
|
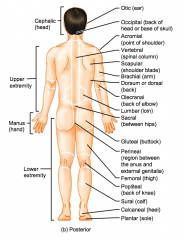
Femoral (thigh)
Popliteal (back of knee) Sural (calf) Calcaneal (heel) Plantar (sole) |

