![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Helminth Phyla and Classes
|
1) Phylum Nemathelminthes (Roundworms)
a. Class Nematomorpha - horsehair worms b. Class Nematoda 2) Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) a. Class Trematoda - flukes b. Class Cestoda - tapeworms 3) Phylum Acanthocephala (Thorny-headed worms) |
|
|
Describe Phylum Nemathelminthes - Class Nematoda
|
1. Free living or parasitic
2. Spindle-shaped; taper at both ends 3. Body not segmented 4. Body cavity and digestive tract present 5. No proboscis 6. Separate sexes |
|
|
Describe Phylum Platyhelminthes - Class Cestoda
|
1. All species are parasitic
2. Sexes NOT separate: individual tapeworm has male and female organs 3. Flat; ribbon or band-shaped 4. Segmented body 5. No body cavity 6. Not digestive tract 7. No proboscis |
|
|
Describe Phylum Platyhelminthes - Class Trematoda
|
1. All species parasitic
2. Sexes NOT separate 3. Flat; oval or leaf shaped 4. Body not segmented 5. No body cavity 6. Digestive tract present but no anus 7. No proboscis |
|
|
Phylum Acanthocephala
|
1. All species are parasitic
2. Separate sexes 3. Tapering posterior end 4. Body not segmented 5. Body cavity present 6. No digestive tract 7. Proboscis present |
|
|
Phylum Nemathelminthes - Class Nematomorpha
|
1. Larvae parasitic in insects
2. Adults free living in fresh water: mate, lay eggs in water or moist soil 3. Hatched larvae penetrate insect and mature 4. Emerge when insect in contact with water 5. Gordian or horsehair worms |
|
|
Describe a Nematode's body wall.
|
Comprised of cuticle, hypodermis and muscle cells.
1. Cuticle - tough, thick protective outer covering produced by hypodermal cells. a. Resistant to host digestive enzymes. b. Functions as a hydrostatic skeleton c. Metabolically active and antigenic. 2. |
|
|
Describe Nematodas
|
1. Muscle cells underlie hypodermis - provide locomotion by longitudinal contraction
2. Body cavity - a pseudocoelom because it has no cell lining; contains fluid that is highly allergenic or toxic to host; fluid pressure provides turgor and keeps body straight. |
|
|
Digestive tract of Nematoda
|
1. Simple straight tube
2. Mouth (stoma) +/- external modifications 3. Esophagus - muscular and glandular parts 4. Intestine - female ends in rectum and male ends in cloaca along with vas deferenes 5. Anus - rectum or cloaca leads to anus that opens to outside of body |
|
|
Describe Nematoda Metabolism
|
1. Majority are facultative anaerobes - store glycogen and depends on host for carbohydrates
2. Host supplies all of food: examples are blood, lymph, pre-digested ingesta, etc.. |
|
|
Describe Nemotoda Reproductive system
|
Dioecious (spearate sexes) - highly developed; females often produce large numbers of eggs (1,000/day)
Level of egg development within female varies with species of nematode a. Oviparous b. Ovoviviparous c. Viviparous Often marked sexual dimorphism a. Females generally larger than males b. Males have a curled tail or A BURSA COPULATRIX c. Bursa is an appendage at posterior end |
|
|
Class Nematoda - Male Organs
|
Single tube with differentiated regions
Coiled testis --> vas deferens --> enlarged seminal vesicle --> muscular ejaculatory duct --> cloaca Accessory organs Spicules, gubernaculum, bursa Used in copulation |
|
|
Class Nematoda - Female Organs
|
Ovary --> oviduct --> uterus --> muscular ovejector --> vulva
Usually 2 sets of female organs (didelphic) Location of vulva: anterior, middle or posterior of body Eggs of most nematode species differ in morphology |
|
|
Definition of Viviparous.
|
Eggs hatch in uterus; female gives birth to larvae.
|
|
|
Definition of Ovoviviparous.
|
Female lays an egg that contains a larva.
|
|
|
Definition of Oviparous.
|
Female lays egg with an undeveloped embryo.
|
|
|
Basic nematode life cycle
|
Egg --> 5 larval stages --> adult male or female.
L1-L2: usually free living stages L3: usually infective stage to host L3-L5: adult are parasitic stages |
|
|
Describe the larval development.
|
Larvae usually undergo ECDYSIS (MOLT) between stages
L3 (some species) retain L2 cuticle = SHEATHED LARVAE which protects larvae from drying out and prevents larvae from feeding |
|
|
Subclasses (Orders) of Class Nematoda
|
1. Subclass Secernentea
a. Strongylida - 4 superfamilies b. Rhabditida c. Ascardida - 3 superfamilies d. Oxyurida e. Spirurida - 6 superfamilies 2. Subclass Adenophorea a. Enoplida - 2 superfamilies |
|
|
Features of Order Strongylida
|
1. Copulatory bursa in males of all superfamilies
2. Large buccal capsule in hookworms and true strongyles - used for attachment and sucking blood 3. No buccal capsule in trichostrongyles and lung worms 4. Larval stages migrate in host tissues |
|
|
Characteristics of strongyle type eggs
|
Smooth-surfaced, ellipsoidal shells
Contain an embryo in a MORULA stage when laid and passed out with the feces |
|
|
4 supefamilies of the Order Strongylida
|
1. Ancylostomatoidea - hookworms
2. Strongyloidea - true strongyles 3. Trichostrongyloidea - trichostrongyles 4. Metastrongyloidea - metastrongyles or lung worms |
|

What is this?
|
Nemathelminthes: nematode or roundworm (Parascaris equorum)
|
|

What is this?
|
Platyhelminthes: trematode or fluke (Fasciola hepatica)
|
|

What is this?
|
Acanthocephala
|
|
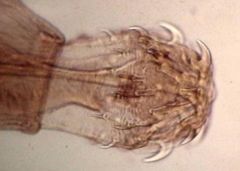
What is happening to this kind of worm?
|
Probsocis of an acanthocephalan
|
|

What is this?
|
Nematomorpha - Horsehair worm (Gordius)
|
|
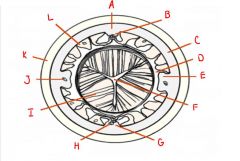
What is each letter?
|
A = Dorsal cord
B = Dorsal nerve C = Hypodermis D = Body cavity E = Lateral cord F = Esophageal lumen G = Ventral cord H = Ventral nerve I = Muscle fibers J = Excretory canal K = Cuticle L = Somatic muscle |
|
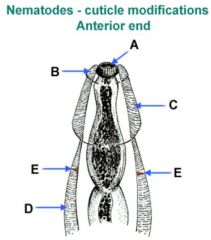
Label letters
|
A = Leaf crown
B = Cephalic vesicles C = Cervical vesicles D = Cervical alae E = Cervical papillae |
|
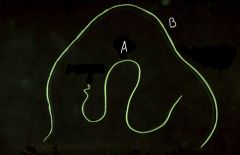
Which is male and which is female? How can you tell? What are these?
|
A = Male (coiled tail)
B = Female (longer) Dirofilaria immitis - Heartworm of dogs |
|
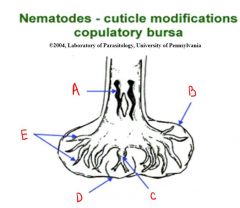
Label letters.
|
A = Spicule
B = Lateral lobe C = Dorsal ray D = Dorsal lobe E = Bursal rays |
|
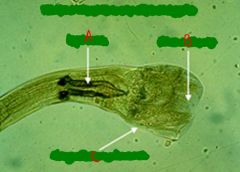
What is this? Label letters.
|
Tail end of male Strongyle
A = Spicule B = Bursal ray C = Copulatory bursa |
|
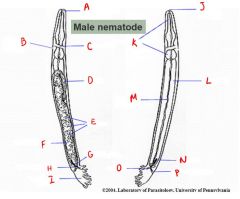
Label letters.
|
A = Buccal cavity
B = Excretory pore C = Nerve ring D = Testis E = Sperm F = Vas deferens G = Rectal gland H = Gubernaculum I = Copulatory bursa J = Mouth opening K = Esophagus L = Intestine M = Lumen of intestine N = Spicule O = Cloaca P = Dilator muscle |
|
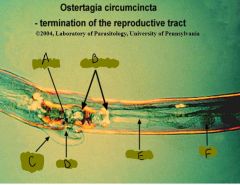
Label letters.
|
A = Vagina
B = Ovejector C = Vulva flap D = Vulva E = Uterus F = Egg |
|
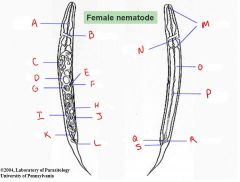
Label the letters.
|
A = Lumen of esophagus
B = Nerve ring C = Ovary D = Uterus E = Vagina F = Vulva G = Egg H = Uterus I = Ovary J = Egg K = Rectum L = Anus M = Esophagus N = Excretory pore O = Intestine P = Lumen of intestine Q = Rectum R = Rectal gland S = Anus |
|
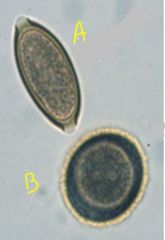
Label letters.
|
A = Trichicaris
B = Toxocara |

