![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which elements do lipids contain?
|
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen |
|
|
Are lipids polar or non-polar?
|
Non-polar, insoluble in water so dissolve in other organic solvents) |
|
|
What are triglycerides? |
Combination of on GLYCEROL molecule and 3 FATTY ACID molecules |
|
|
What changes when a triglyceride is formed?
|
Glycerol remains the same, fatty acids change |
|
|
How is a fatty acid formed? |
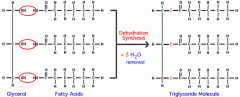
|
|
|
Which reaction allows fatty acids and glycerol to join?
|
Condensation reaction, |
|
|
What are the bonds within a triglyceride called?
|
Ester Bonds (between glycerol and fatty acids) |
|
|
What is a phospholipid? |
A special type of lipid |
|
|
Which is the hydrophilic end of a phospholipid?
|
Polar Head; interacts with water, lots of O atoms so interacts, glycerol head |
|
|
Which is the hydrophobic end of a phospholipid? |
Non-polar tails, doesn't interact with water, no O atoms so cant interact
|
|
|
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
|
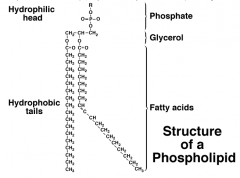
|
|
|
What are waxes?
|
E.g plants (leaf's cuticle), animals (insects exoskeleton) |
|
|
What are the properties of a saturated lipid?
|
~Single C-C bond ~all carbons linked to maximum hydrogen bonds ~Straight zig-zag ~Molecules readily align= SOLID ~Remain solid at body temp., useful in storage of mammals ~Animal lipids contain saturated fatty acids |
|
|
What are the properties of an unsaturated lipid? |
~Chain gets a kink ~Can't align properly, don't solidify ~Plant lipids: oils, unsaturated ~1C=C bond present= Mono-unsaturated ~more than 1C=C bond= Poly-unsaturated |
|
|
What are the roles of phospholipids? |
=Biological membranes =Electrical insulation (myelin sheath on axons) |
|
|
What are the roles of triglycerides?
|
=Thermal insulation; stored under skins, insulate against heat loss and heat gain =Protection: fat stored around delicate organs protects from physical damage =Metabolic water; produces a lot |
|
|
What is the test for fats and oils?
|
*sample tested is mixed with ETHANOL *dissolves lipids present *Shaken with volume of water *Dissolved lipids come out (INSOLUBLE) * Form an emulsion (makes cloudy white sample) |
|
|
What are globular proteins? |
~compact ~spherical molecules ~makes soluble in water ~many different functions ~Haemoglobin: consists of 4 folded polypeptide chains, centre of each is an iron-containing group (HAEM group) |
|
|
What are fibrous proteins? |
~long, thin molecules ~shape= insoluble in water, (structural function) ~in parallel structures, chains and sheets ~strong and tough ~cross-linkages; forms LONG fibres (keratin) ~e.g COLLAGEN; provides strength and toughness, needed in TENDONS ~single fibre (tropocollagen), consists of 3 POLYPEPTIDE chains TWISTEd AROUND EACH OTHER, linked with hydrogen bonds, very STABLE |
|
|
What is the primary structure of proteins? |
~order of linear amino acids ~up to 20 different types of amino acids ~joined in any number; different combinations ~determined by base sequence; one strand of the DNA |
|
|
What is the secondary structure of proteins? |
~shape formed due to hydrogen bonding between O of -CO groups, -H of -NH groups ~peptide bonds formed ~causes to be twisted into 3D shape (alpha helix) ~hydrogen bonds included |
|
|
What is the tertiary structure of proteins? |
~can be folded and twisted ~COMPLEX, COMPACT 3D STRUCTURE ~shape maintained by: Hydrogen bonds Ionic bonds Disulfide bonds Hydrophobic interactions =globular proteins in structure |
|
|
What is the quaternary structure? |
~polypeptides in combination ~(insulin=2 chains) ~non-protein groups & form large, complex molecules (e.g haemoglobin) |
|
|
What is the health risk of saturated fats? |
-Heart Disease: cause= fatty deposits in coronary arteries & high blood pressure -Food absorbed in SMALL INTESTINE; lipids and proteins make LIPOPROTEINS (travel in blood) ~High in saturated, LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN, build up and cause harm' ATHEROMA, gets deposited in arteries, restricts blood flow & O2 delivery to heart (Angina/Heart Attack) |

