![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
independent channels that collect excess tissue fluid from body tissues and return it to blood circulatory system
|
Lymph vascular system
|
|
|
|
Efferent vessels
|
Arteries
|
|
|
|
the convergence of capillaries
|
The Veins
|
|
|
|
vessels that are more than 0.1 mm in diameter (large arterioles, muscular and elastic arteries, and muscular veins)
|
macrovasculature
|
|
|
|
(arterioles, capillaries, and postcapillary venules)
|
microvasculature
|
|
|
|
of three basic structural constituents:
Tissue Components of the Vascular Wall |
endothelium
muscular tissue connective tissue |
|
|
|
Tissue Components of the Vascular Wall
|
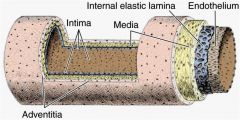
A. Tunica intima
B. Tunica media C. Tunica adventitia |
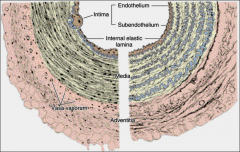
|
|
|
List the layers
|
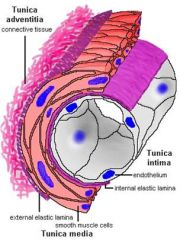
|
|
|
|
A. Tunica intima
3ct |
1. endothelium & basal
lamina 2. subendothelium (very thin loose C.T.) 3. internal elastic membrane (optional). |
|
|
|
B. Tunica media
|
smooth muscle fibers
elastic fibers lamellae collagen fibers (type III) proteoglycans |
|
|
|
C. Tunica adventitia
|
Loose CT
Vasa vasorum: More frequent in veins than in arteries Innervation unmyelinated sympathetic nerve fibers (vasomotor) |
|
|
|
C. Tunica adventitia
Innervation: |
- unmyelinated sympathetic nerve fibers (vasomotor) supply the muscles
-(norepinephrine) resulting in vasoconstriction. |
|
|
|
C. Tunica adv
entitia Innervation: *Arteries in skeletal muscles also receive = |
cholinergic nerve supply.
|
|
|
|
C. Tunica adventitia
Innervation: Smooth muscle fibers relax (vasodilation) when sympathetic stimulation decreases |
.
|
|
|
|
small vessels are seen in adventitia and outer parts of media of larger vessels. They provide nourishment to the thick layers
Smooth muscle fibers relax (vasodilation) |
Vasa vasorum
T/F More frequent in veins than in arteries |
|
|
|
Classification of arteries:
|
Elastic arteries:
Muscular arteries: Arterioles |
|
|
|
Classification of arteries:
Elastic arteries: |
conducting vessels,
include aorta and its main branches |
|
|
|
Classification of arteries:
Muscular arteries: |
main distributing
vessels, e.g. radial artery. |
|
|
|
Classification of arteries:
Arterioles |
the terminal branches of
the arterial tree supply the capillary bed |
|
|
|
The amount of elastic tissue decreases as the vessels become smaller and the smooth muscle component assumes greater prominence.
Classification of arteries: info |
.. Tunica intima
|
|
|
|
Tunica intima thicker than that of muscular arteries
What kind of arteries = |
Elastic Arteries
|
|
|
|
Elastic Arteries
Tunica intima . Endothelium type is |
simple squamous.
|
|
|
|
Elastic Arteries 1. Tunica intima
Rod –like cytoplasmic inclusions are observed in the E.M. of arterial endothelium. |
Weibel-Palade bodies
which contain factor VIII related antigen (von-Willebrand factor), interleukin 8, P-selectin and endothelin. |
|
|
|
Elastic Arteries
2. Tunica media describe = |
thickness increases with age
no distinct external elastic membrane. |
|
|
|
Elastic Arteries
3. Tunica adventitia |
Loose CT
fibroblasts collagen bundles oriented longitudinally some elastic fibers. |
|
|
|
Elastic Arteries
3. Tunica adventitia Are Fibroblasts & macrophages seen in this layer. |
Yes
are frequently observed along with the nerves. = |
|
|
|
Muscular arteries layers
3ct |
1. Tunica intima:
2. Tunica media 3. Tunica adventitia: |
|
|
|
Arteriole
Layers & description 3ct |
1.Tunica intima:
Endothelium lying on a thin basal lamina A very thin subendothelial connective tissue consisting of reticular and elastic fibers. Internal elastic lamina is thin and fenestrated and absent from terminal arterioles. Tunica media 1- 5 layers of smooth muscle fibers and some elastic fibrils. No definite external elastic lamina is present Tunica adventitia Thinner than the media, loose C.T. with longitudinally oriented collagen and elastic fibers. |
|
|
|
Transitional and Specialized Arteries
Caliber |
Caliber
Intermediate Intermediate caliber: Popliteal & tibial have walls that resemble larger arteries Large Large caliber arteries: e.g. external iliac have walls that resemble muscular arteries Transitional region between elastic and muscular arteries are called arteries of mixed type (e.g.: external carotid, axillary and common iliac arteries). ++ |
|
|
|
Special Arteries:
2ct |
Umbilical artery
Penile arteries ++ |
|
|
|
Carotid bodies:
Sensory organs of arteries |
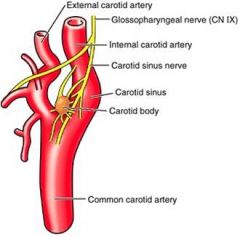
***Chemoreceptor sensitive to low oxygen tension, high carbon dioxide concentration and low pH of arterial blood
|
|
|
|
Sensory organs of arteries
|
Sections of a carotid body, which is a highly vascularized structure sensitive to hypoxia. Its main cells have dense-core granules containing catecholamines that are surrounded by glia-like sustentacular cells.
|
|
|
|
***
_____ ________ Appears as a dilation of the lower end of the internal carotid, and functions as a ._______ = |
carotid sinus
***baroreceptor |
|

