![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Blood Agar Plates (BAP) tests the ability of an organism to produce hemolysins, enzymes that damage/lyse red blood cells Oxidise test will show colonies on these plates. Which could be Neisseria species. reagent: tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine |
|

|
Sulfur Indole Motility Media H2S production (turns agar black) tests the ability of an organism to do several things: reduce sulfur, produce indole and swim through the agar (be motile). |
|

|
Mannitol Salt Agar It's selective & differential & inhibits other MO's. It's selective for Staphylococcus & differential for different species for Staphylococcus Contains mannitol, 7.5% NaCl, and phenol red. |
|
|
Which organism will turn MSA yellow? |
Staphylococcus aureus. A coagulase test is used to confirm this organism. |
|

|
Coagulase test
This test differentiates Sa from other coagulase negative(clear) Sa (it's the SA in MRSA) |
|

|
Simmon’s Citrate Agar
defined medium used to determine if an organism can use citrate as its sole carbon source |
|

|
MacConkey agar selective & differential. The selective ingredients are the bile salts and the dye, crystal violet which inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria. The differential ingredient is lactose. Fermentation of this sugar results in an acidic pH and causes the pH indicator, neutral red, to turn a bright pinky-red color |
|
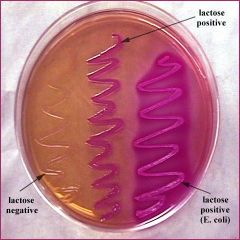
MacConkey Plate (fecal swab) |
* Selective- bile salts kill G+ organisms
* Differential- based on lactose fermentation |
|

organisms capable of lactose fermentation such as____ , form bright pinky-red colonies |
Escherichia coli |
|

MacConkey agar is commonly used to differentiate between the _____ |
Enterobacteriaceae |
|
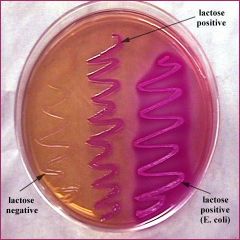
MacConkey Plate Results |
* -NEG=cream= Lac- (Potentially pathogenic for salmonella Ex. Salmonella typhi causing typhoid fever) |
|

|
Urease test This test is used to identify bacteria capable of hydrolyzing urea using the enzyme urease |
|
|
Pure Culture Technique |
* Streak aseptically w/ quadrant technique to isolate colonies |
|
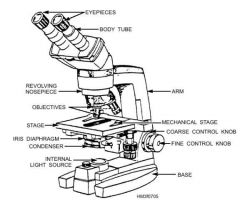
Compound Microscope- parts and functions |
* Base- Stability of scope * Adjustment knobs- focus specimen or ↑/↓ stage * Arm-connects base to lens system * Rheostat- light intensity control (set @ 4 1/2) * Obj lens & Oculars- magnify specimen * Light- illuminates specimen * ABBE condenser- focus light * Diaphragm- controls amount of light |
|
|
Resolving Power |
LAB MANUAL says determines the size of the smallest object that can be seen clearly under specified conditions.
The ability of a microscope to distinguish one point object from a nearby point object |
|
|
Reagent definitions |
1. Primary stain: Stains cell |
|
|
Gram Stain Function |
determine cell wall structure & possible treatments |
|
|
Gram Stain Technique |
1. Transfer aseptically, dry, and heat fix 2. -crystal violet 60sec, rinse H20 (adheres to peptidoglycan) 3. Mordant-gram's iodine 60sec, rinse H20 (seals 1°) 4. Decolorizer- ETOH 15 sec, rinse H20 (Remove some/all of crystal violet dye) 5. 2°- Safranin 30 sec, rinse H20 (recolors) blot dry |
|
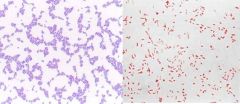
Gram Stain Results |
Gram Positive=Purple |
|
|
Endospore Stain Technique |
* Transfer aseptically, dry, and heat fix |
|
|
Endospore Stain Disease, Genus & Species |
* Tetanus
* Clostridium tetani |
|
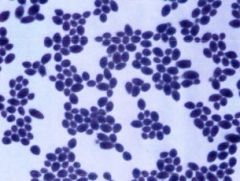
Fungi Identification- |
* unicellular
* warmer temps * large, not perfectly round * Usually viewed under 40x |
|
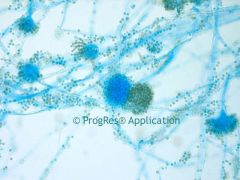
Fungi Identification- Molds |
* Multicellular
* cooler temps * have conidia or spores and a root system of hyphae * Usually viewed under 40x |
|
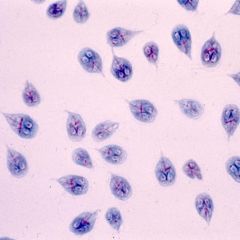
Protozoa Identification |
* Very small
* Usually viewed under 100x |
|
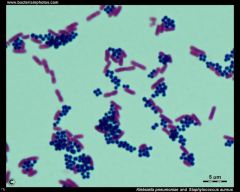
Bacterial Identification |
* Very small
* Usually cocci or rods |
|
|
Effects of Physical Agents on bacteria |
Heat (Based on growth in tube from None to thick+++) |
|
|
Effects of Physical Agents on bacteria UV |
UV light (Based on amount of growth on plate) |
|
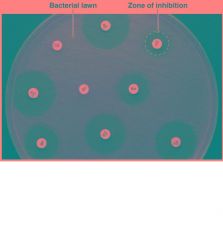
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test |
Based on how large the zone of growth/inhibition measured in mm
categorized as S = susceptible, I = intermediate, R = resistant uses a Kirby Bauer Plate |
|
|
Acid Fast Stain Technique AFB |
* Transfer aseptically, dry, and heat fix
* Place over boiling H20 w/ filter paper * 1°-Carbolfuschin on paper for 5min * Mordant- Steam during that 5min * Decolorizer- Acid rinse 2x 15 sec * 2°- Methyl Blue 60 sec, rinse H20, blot dry |
|
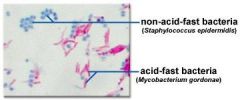
Acid-Fast Stain Results |
* Acid-fast= magenta (pinkish-purple) |
|
|
Acid-fast disease, genus & species |
-Tuberculosis |
|
|
selective vs differential medium |
S: allows only certain species of microorganisms grow, prevents growth of some organisms D: causes diff. organisms to produce diff. results |
|
|
Sheep blood agar plate (SBA)-(Throat culture) |
-Differential based on its ability of hemolysis (lysis of RBC) |
|
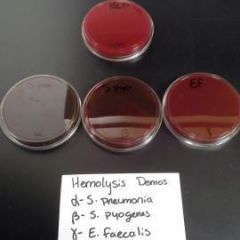
SBA plate results |
1. SHEEP BLOOD AGAR |
|
|
SBA Plate Disease, Genus & species |
-Strep pyogenes |
|
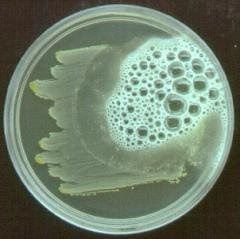
Oxidase Test- (Further test on throat swab) |
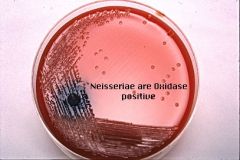
* Tests γ (gamma) hemolytic colony for oxidase & Neisseria spp. using oxidase reagent
* -NEG= cream color= NO oxidase= NOT Neisseria spp. * +POS= Pink/Purple/Black= +Oxidase= Neisseria spp. |
|
|
Oxidase Reagent |
dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine hydrocloride |
|
|
Manitol Salts Agar Plate (MSA) (Skin Swab) |
* Selective- Kills G- organisms, but grows G+
* Differential- Manitol fermenting organisms (Those w/ manitolasase) will change color of plate |
|
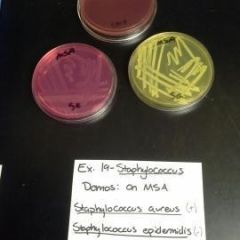
MSA Plate Results & Disease, Genus, & species |
* -NEG= Pink= No manitolase= Staph epidermidus
* +POS= Yellow= Manitolase= Staph aureus (Possibly pathogenic for MRSA) |
|
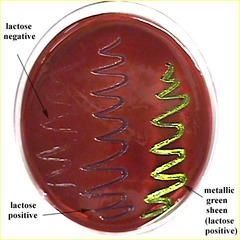
EMB Plate- Eosin methylene blue (fecal swab) |
* Selective- bile salts kill G+ organisms
* Differential- Based on lactose fermentation |
|
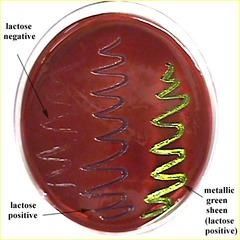
EMB plate results |
* -NEG=cream= Lac- (Potentially pathogenic for salmonella Ex. Salmonella typhi causing typhoid fever) |
|

TSI |
* Measures1. Acid/Alkaline
|
|

Methyl Red tube Reactions |
* -Neg= Yellow
* +Pos= Red * Voges-Paskauer- *Opposite Results* |
|
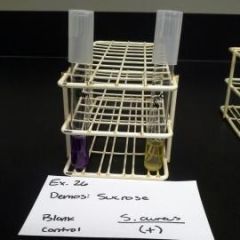
Glucose, Sucrose, & Lactose Tube Results |
* -NEG- Purple |
|

Catalase Test |
Neg-No bubbles |
|

Starch Plate Results |
* -NEG- Black Zone
|
|

DNA Plate Results |
* -NEG- Foggy Zone
* +POS- Clear/Green Zone |
|

SIM Tube Results |
Sulfur (H2S) |
|
|
Plate Counts |
* <30 colonies = TFTC "too few to count" |
|
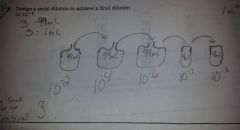
Dilution Notes |
* 1.0→9.0= 10¯¹
* 1.0→99= 10‾² * 0.1→9.9= 10¯² * If plate 1.0mL no need to change exponent, IF 0.1mL add 10‾¹ PLATE = 9cm * Always record in scientific notation with positive exponent!! |
|
|
Acidic Stains |
Nigrosin, Congo Red & India Ink all carry a NEGATIVE charge which will repell from Neg. charge bacteria |
|
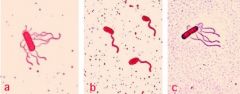
What stucture is this?
|
Flagella |
|
|
explain the characteristics used to classify bacteria according to Bergey's Manual |
major resource that covers all known prokaryotes based mostly on characteristics such as Gram stain and metabolic reactions. that is called phenetic.
2nd edition uses -phylogenetic:(evolutionary) history and relationships of the thousands of known species |
|
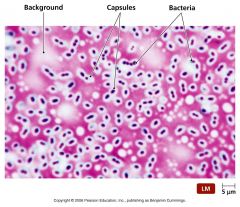
|
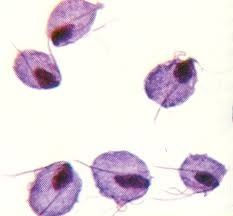
Tricomona |
|
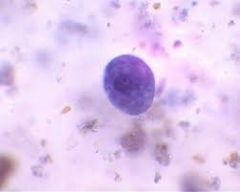
Trophozoite |
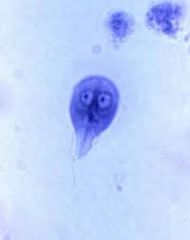
Giardia (has 2 eyes looking) |
|
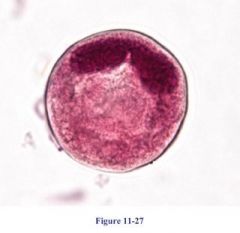
Balantidium cyst |
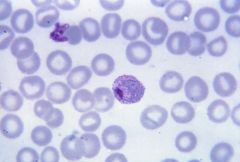
Plasmadium |

