![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
selective toxicity
|
the ability of an antimicrobial (drug) to harm a pathogen without harming the host
|
|
|
What does TI stand for and what does it mean?
|
therapeutic index - the ratio between the toxic dose and the therapeutic dose of a drug; used as a measure of the relative safety of the drug for a particular treatment
|
|
|
What do each of the numbers stand for in the therapeutic index?
|
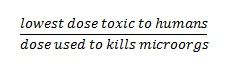
|
|
|
For a drug, do we want a high TI or a low TI?
|
For a drug, we want a high TI.
|
|
|
high TI (therapeutic index)
|
very safe; can be taken internally
|
|
|
low TI (therapeutic index)
|
could be dangerous; generally used for topical application
|
|
|
What is the difference between bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal?
|
Bacteriostatic only slows the growth of bacteria.
Bacteriocidal actually kills bacteria. |
|
|
broad spectrum antibiotic
|
effective against many different bacteria; commonly used first when specific pathogen is unknown
|
|
|
narrow spectrum antibiotic
|
effective against specific bacteria; commonly used after specific pathogen is known
|
|
|
List the 3 ways drugs can interact.
|
Synergistic
Antagonistic Additive |
|
|
synergistic
|
one drug enhances effects of another
|
|
|
antagonistic
|
one drug interferes w/ the action of the other
|
|
|
additive
|
drugs have NO effect on each other
|
|
|
List the 3 drugs discussed in class that act by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
|
Bacitracin
Vancomycin Beta-lactam (β-lactam) drugs |
|
|
How does bacitracin inhibit cell wall synthesis?
|
Prevents transport of components to the outside of cell; cell wall cannot be made w/o these components
|
|
|
How does vancomycin inhibit cell wall synthesis?
|
Prevents cross-linking by binding to the ends of peptide side chains; only works on gram (+) bacteria
|
|
|
How do beta-lactam (β-lactam) drugs inhibit cell wall synthesis?
|
They are competitive inhibitors of PBPs and thus prevent bridges from forming between adjacent strands of peptidoglycan
|
|
|
What is the only kind of bacteria that vancomycin works on? Why?
|
Gram (+) bacteria because it has a thicker cell wall.
|
|
|
PBP
|
penicillin binding protein - form peptide bridges between adjacent strands of peptidoglycan
|
|
|
Identify these drugs as either having a high TI or a low TI.
Bacitracin Vancomycin Beta-lactam (β-lactam) drugs |
Bacitracin = Low TI
Vancomycin = Low TI Beta-lactam drugs (β-lactam) = High TI |
|
|
Why do most drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis have a high TI?
|
These drugs have a high TI because they attack cell walls and human cells do not have a cell wall.
|
|
|
TRUE/FALSE
Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis only work on actively growing cells. |
TRUE
They cannot affect bacteria that have already been made. |
|
|
Do PBPs (penicillin binding proteins) bind to penicillin?
|
No. The name was given and never changed when the actual function was discovered.
|
|
|
Which is safer for humans: drugs that inhibit cell synthesis or drugs that inhibit protein synthesis via the ribosome? Why?
|
Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis are safer for humans because human cells don't have a cell wall, thus drugs cannot interfere with human cells.
|
|
|
What is done to beta-lactam (β-lactam) drugs when bacteria become resistant to them?
|
The beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring stays the same, but the side chains are modified to fight the resistant bacteria.
|
|
|
Identify the 5 drugs that inhibit protein synthesis.
|
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines Macrolides Chloraphenical Antisense nucleic acids *** All are bacteriocidal *** |
|
|
Drugs that inhibit protein synthesis attack the cell structure ________.
|
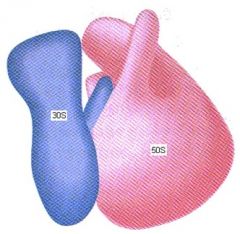
Ribosome, small (30S) and large subunit (50S) [This is a ribosome in bacteria.]
|
|
|
translocation
|
movement of mRNA through the ribosome
|
|
|
How do aminoglycosides inhibit protein synthesis?
|
Aminoglycosides change the shape of the 30S subunit so that it can't read mRNA properly. This produces incorrect amino acids.
|
|
|
What is unique about aminoglycosides compared to the other drugs that inhibit protein synthesis?
|
It is the only drug that kills bacteria (bacteriocidal).
|
|
|
Do aminoglycosides have a low TI or a high TI?
|
Low TI
|
|
|
List 2 drugs that are classified as aminiglycosides.
|
Streptomycin
Neomycin |
|
|
How do tetracyclines inhibit protein synthesis?
|
It prevents the attachment of tRNA to the ribosome, so that you cannot make the next amino acid.
Protein synthesis does not occur. |
|
|
How do macrolides inhibit protein synthesis?
|
Binds to 50S subunit and prevents translocation
|
|
|
List a drug that is classified as a macrolide.
|
Erythromycin
|
|
|
Is erythromycin bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal?
|
Bacteriocidal
|
|
|
How does chloraphenical inhibit protein synthesis?
|
It prevents peptide bond formation.
|
|
|
Does chlorphenical have a high TI or a low TI? Why?
|
It has a low TI because human cells make peptide bonds also.
|
|
|
How do antisense nucleic acids inhibit protein synthesis?
|
Small segments of RNA or single stranded DNA bind to specific mRNA as a complimentary sequence, thus making it double stranded.
Double stranded mRNA cannot go through ribosome. |
|
|
antisense
|
sequence complimentary to another
|
|
|
TRUE / FALSE
All drugs that inhibit protein synthesis are bacteriocidal. |
TRUE
They all kill the bacteria. |
|
|
List the 2 drugs that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis.
|
Fluoroquinolones
Rifamycins |
|
|
Are drugs that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal?
|
They are bacteriocidal.
|
|
|
How do fluoroquinolones inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
|
They inhibit topoisomerase so that DNA cannot be made.
|
|
|
topoisomerase
|
an enzyme that helps to maintain the correct conformation of DNA in the cell nucleus
[Teacher said it is an enzyme that relieves stress from DNA during DNA replication. I thought that was gyrase.] |
|
|
How do rifamycins inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
|
They inhibit RNA polymerase, thus inhibiting transcription.
|
|
|
List the drug that inhibits metabolic pathways.
|
Sulfa
|
|
|
How does sulfa inhibit metabolic pathways?
|
It acts as a competitive inhibitor against PABA, thus blocking the formation of folic acid.
|
|
|
Why do bacteria need to make folic acid?
|
Bacteria use it as a precursor to making DNA/RNA.
|
|
|
Why do bacteria need PABA?
|
PABA is required to make folic acid.
|
|
|
Can humans make folic acid?
|
No.
|
|
|
Does using a drug create resistance to it? (3)
|
No. Bacteria spontaneously mutate on their own.
Using a drug only increases the amount of resistant bacteria. Drug resistance will happen no matter what due to the process of natural selection. |
|
|
________ commonly contain the drug-resistant gene.
|
Plasmids commonly contain the drug-resistant gene.
|
|
|
How do plasmids transfer the drug-resistant gene? (2)
|
To their offspring
Conjugation (or similar) |
|
|
What are the most common type of plasmids?
|
R-plasmids
|
|
|
The ________________ is where plasmid replication begins.
|
origin of replication
|
|
|
List the 4 mechanisms of resistance that bacteria can do.
|
Drugs inactivated by enzymes
Alteration of shape (mutation) Decrease drug uptake Increase elimination of drugs |
|
|
List the 2 ways drugs can be inactivated by bacterial enzymes.
|
Beta-lactamase destroys the beta-lactam ring, thus rendering the drug useless.
Chloraphenicol acetyltransferase destroys chloraphenicol. |
|
|
List the 2 ways drugs can be mutated (alteration of shape) by bacteria.
|
Changing shape of PBPs inhibits beta-lactam drugs.
Changing shape of ribosome inhibits any drug that binds to the ribosome. |
|
|
Is the ribosome shape change small or large? Why?
|
The ribosome shape change is only small b/c bacteria do not want to affect overall ribosome function.
|
|
|
How does bacteria decrease drug uptake?
|
Decreases the number of membrane-bound proteins involved in transport
|
|
|
How does bacteria increase drug elimination?
|
Increases the # of pumps in the membrane to transport molecules out of the cell
|
|
|
List the 3 ways antiviral drugs function.
|
Viral uncoating
Nucleic acid synthesis errors Assembly and release |
|
|
How do antiviral drugs carry out viral uncoating?
|
It prevents the release of nucleic acids from protein coat.
|
|
|
List 3 examples of antiviral drugs that carry out viral uncoating.
|
Amantadine
Rimantidine Pleconaril |
|
|
How do antiviral drugs promote nucleic acid synthesis errors? (3)
|
These drugs mimic 1 of the 4 bases and causes an error in the final product.
Virus mistakenly uses the drug instead of its own base. This is based on error rate of viral polymerases, which DO NOT proofread DNA. |
|
|
How do antiviral drugs carry out assembly and release?
|
Inhibits protease so that proteins cannot be cut, thus forming a single amino acid chain
|
|
|
protease
|
an enzyme that cuts or cleaves proteins
|
|
|
Why do viruses use protease?
|
They need it to cut proteins b/c they are polycistronic organisms.
|
|
|
polycistronic organisms
|
organisms that have mRNA that encodes for multiple, different polypeptides
|
|
|
Why do most antifungal, antiprotozoan, and antihelminthic drugs have a low TI?
|
It is because they are eukaryotes and so are humans.
|
|
|
What component do antifungals target?
|
Ergosterol
|
|
|
How do antihelminthic drugs function?
|
They target the neuromuscular functions of the parasitic worm so that the it is paralyzed and cannot move.
|

