![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Malaria is spread by what microb?
|
parasitic protozoa, apicomplexa, plasmodium spp.
|
|
|
After blood meal, what are the 9 stages of life cycle of Plasmodium.
|
1)Sporozoites in saliva
2) sporozoites become merozoites in liver 3) merozoites become trophozoits that penetrate erythrocytes. 4) trophozoits enter schizogony produce more merozoites; most merozoites infect more erythrocytes...some become male and female gametocytes 5) female gametocytes injested by another mosquito. 6) gametocytes freed from erythrocytes in digestive trace; become gametes. Male gametes fertilize female gametes; produce zygote 7) zygote differentiates into an ookinete; penetrates gut wall of mosquit becomes oocyst 8) 10-20 days later, oocyst ruptures releasing sporozoites to salivary glands. 9) cycles starts again. |
|
|
Plasmodium spp. spreads what disease, what part of the world, mode of transmission, host organisms.
|
Malaria
tropics, subtropics Anopheles mosquitos Humans |
|
|
Classification of Animal Parasites
|
Helminths
|
|
|
Helminths are broke down to two subcategories...
|
Platyhelminths and Nematodes
|
|
|
Tapeworms are in what categories.
|
Animal Parasites, Helminths, Platyhelminths, cestodes.
|
|
|
Helminths, Platyhelminths are broke down to which subcategories
|
Cestodes and Trematodes
|
|
|
Tapeworms are part of what.
|
Animal Parasites, Helminths, Platyhelminths Cestodes
|
|
|
Flukes are part of what?
|
Animal Parasites, Helminths, Platyhelminths, Trematodes
|
|
|
Roundwormds are in what categories?
|
Animal Parasites, Helminths, Nematodes.
|
|
|
Example of Cestode that we studied, and what it's commonly known as?
|
Taenia Saginata; beef tapeworm.
|
|
|
Common name for Beef Tapeworm?
|
Taenia Saginata
|
|
|
Taenia Saginata graphical distrubtion of?, mode of transmission, and length of adult worms?
|
Worldwide /c local endemic areas, consumption of undercooked meat, and from 5 to 25 m. (15 to 75 feet)
|
|
|
Example of Trematodes that we studied?
|
Schistosoma Japonicum
|
|
|
Schistosoma japonicum primar infection or disease, graphical distrubtion of? mode of tranmission, and length of adult worms?
|
Schistosomiasis, fresh (contaminated) water, Asian/Africa, direct penetration of the skin, 7-20 mm.
|
|
|
Taenia Saginata
|
Beef Tapeworm
transmitted via consumption of undercooked meat s/s; usually mild nausea, diarrhea, abd. pain, and head. |
|
|
Scolex
|
small attachment organ that possesses suckers and/or hooks used to attach the worm to host tissues; taenia saginata
|
|
|
Proglottids
|
body segments behind scolex of Cestodes. Proglottids are not self fertilizing, however a tapeworm may be self fertile.
|
|
|
Gravid
|
full of fertilized eggs. Proglottids near or at the end of the chain of a tapeworm/cestode
|
|
|
Entamoeba histolytica
amoebic dysentera (amebiasis) infection occures host ingests cysts fecal/oral contamination areas with poor sanitation cysts able to withstand acidic environment of the stomach - |
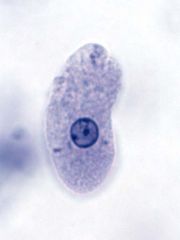
who:
what: when: how: where: why: |
|
|
DEFINITIVE HOST
|
the host in which the sexual reproduction of a parasite takes place
|
|
|
INTERMEDIATE HOST
|
The host occupied by juvenile stages of a parasite prior to the definitive host and in which asexual reproduction often occurs.
|
|
|
4 types of PROTOZOANS
|
sarcodines, mastigophorans, ciliates apicomplexa
|
|
|
SARCODINES are known as?
|
pseudopods: amoebae
|
|
|
MASTIGOPHORANS are known as?
|
flagellates
|
|
|
CILIATES are known for which mode of locamotion?
|
Cilia
|
|
|
APICOMPLEXA are known for which disease and which form of locamotion?
|
milaria and they ungulate
|
|
|
Which sarcodine did we study, what disease does it cause, how is it contaminate, and in what form/stage does it contaminate its host?
|
Entamoeba histolytica; amebic dysentery, fecal/oral contamination, contaminates as a cyst.
|
|
|
Which mastigophoran did we study, what disease does it cause, how does it contaminate, and in what form/stage does it contaminate its host?
|
Giardia intestinalis, giardiasis - more common water-bourne GI disease (dysentery),fecal/oral contaimination, contaiminates as cysts.
|
|
|
Which ciliate did we study, what disease does it cause, how does it contaminate, and in what form/stage does it contaminate its host?
|
Balantidium coli, balantidiasis (dysentery), fecal/oral, contaimination via cysts.
|

