![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition of optic center.
|
The point on the lens that light can pass through without bending. (no refraction/ no prismatic effect)
Point of no refraction. Page 102 |
|
|
Definition of the geometric center.
|
The center of the eyewitness becomes the point on the datum line halfway between the two vertical and horizontal lines. Where the horizontal and vertical lines intersect.
Page 248 |
|
|
Definition of "A", "B", "ED", and "DBL".
|
A: widest horizontal measure of the box
B: widest vertical measure of the box ED: (effective diameter) widest measurement in any direction DBL: least distance between lenses Page 250-251 |
|
|
What does prism do?
|
It deviates the light towards its base. It disperses the white light into component colors. It displaces the object towards its apex.
Page 101 |
|
|
What is the definition of a 1^ prism?
|
The power of a prism that can deviate the light 1 cm at the distance of 1 m.
1= 1cm/1m Page 101 |
|
|
What are the canceling and adding prisms?
|
Canceling:
Base In and Base Out Base Up and Base Up Base Down and Base Down Adding: Base Up and Base Down Base In and Base In Base Out and Base Out Page 105 |
|
|
What is GCD?
|
The distance between two geometrical centers on a frame.
A+DBL=GCD/FPD Page 250 |
|
|
What is MPD?
|
The distance between the optical centers in a completed pair of glasses.
Page 250 |
|
|
The eyes ___ mm and move down ___ to read.
|
The eyes <3to 6> mm and move down <10 to 12> to read.
|
|
|
What is mechanical center?
|
The center of the metal block, on a blocked lens, creates a center that the edger will cut the lens around.
|
|
|
The average PPD for adults is ____.
|
The average PPD for adults is <50 to 75 mm>.
Page 239 |
|
|
FPD is 72. "A" measurement is 52. How much is DBL?
|
DBL=20mm
A+DBL=FPD 52+DBL=72 DBL=72-52 DBL=20mm |
|
|
What is the MBS formula?
|
2xlargest decentration+ED=MBS
*MBS=minimum blank size |
|
|
What are the horizontal and vertical decentration formulas?
|
Horizontal Decentration:
(FPD-PPD)/2 FPD>PPD = move in Vertical Decentration: OCHT-(B/2) OCHT>B/2 = move up |
|
|
The "A" measurement is 50, the DBL is 20, the PPD is 60 and the OCHT is 28. The frame is a round frame. How much would you decenter the lenses and what is the MBS?
|
5 mm in
3 mm up 60 mm MBS FPD=A+DBL FPD=50+20=70 (70-60)/2= 5mm in 28-(50/2)= 3 mm up (2x5)+50= 60 mm MBS |
|
|
An order form has the following information: DBL 18, B 48, ED 48, PPD 68. The lab technician forgot to take the A measurement. What would you do? How would you calculate the MBS and decentration?
|
1 mm out
50 mm MBS A=B=ED in the case of a round frame. FPD=48+18=66 mm (66-68)/2= 1 mm out (2x1)+48= 50 mm MBS |
|
|
What is the layout blocker used for?
|
Blocking the lenses using the calculated decentration.
Page 255 |
|
|
The standard setting for an edger is ___.
|
The standard setting for an edger is <36.5>.
|
|
|
How would you write the PDPD and PNPD?
|
PDPD for distance and PNPD for reading.
Binocularly: # / # First number is PDPD which is larger. Second number is PNPD which is smaller usually by 4 mm. Monocularly: # / # Right side is the first number and left side is the second number. Can be written this way for PDPD or PNPD. |
|
|
How do you take PPD?
|
Sit 16 inches away from patient, line ruler with center of the patient's right pupil and left pupillary border. Read the distance.
Pupilometer or PD stick |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
A 56, B 50, DBL 18, ED 58 PPD 68/64 |
3 mm in
64 mm MBS FPD=56+18=74 mm (74-68)/2= 3 mm in (2x3)+58= 64 mm MBS |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
55/20, B 52, ED 56, PPD 70/65 OCHT 28 |
2.5 mm in
61 mm MBS FPD=55+20=75 mm (75-70)/2= 2.5 mm in 28-(52/2)= 2 mm up (2x2.5)+56= 61 mm MBS |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
45/20, B 50, ED 51, PPD 65, OCHT 25 |
51 mm MBS
FPD=45+20=65 mm (65-65)/2= 0 25-(50/2)= 0 (2x0)+51= 51 mm MBS |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
48/18, B 50, ED 52, PPD 68 |
1 mm out
54 mm MBS FPD=48+18=66 mm (66-68)/2= 1 mm out (2x1)+52= 54 mm MBS |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
A 51, B 48, ED 54, DBL 19, PPD 68/64, OCHT 20 |
1 mm in
4 mm down 62 mm MBS FPD= 51+19= 70 mm (70-68)/2= 1 mm in 20-(48/2)= 4 mm down (2x4)+54= 62 mm MBS |
|
|
Select decentration and the MBS for the following spectacle:
45/15, B 42, ED 50 PPD 58 OCHT 21 |
1 mm in
52 mm MBS FPD=45+15=60 mm (60-58)/2= 1 mm in 21-(42/2)= 0 (2x1)+50= 52 mm MBS |
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question: 1^prism will deviate the light 2cm at __m. |
2cm / 1^= 2m
|
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question: 4^prism will deviate a light 4 cm __m. |
4cm / 4^= 1m
|
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question: __^prism will deviate a light 8cm at 0.50m. |
8cm / 0.50m= 16^
|
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question:__^prism will deviate a light 2cm at 1m. |
2cm / 1m= 2^
|
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question: 2^prism will deviate a light __cm at 2m. |
2^ x 2m= 4cm
|
|
|
By using the prism formula,
1^=1cm / 1m, answer the following question: 3^prism will deviate a light __cm at 3m. |
3^ x 3m= 9cm
|
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
A 4.00 diopter lens decentered 2 mm creates __^prism. |
(4x2) / 10= 0.8^
|
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
A 10.00 D lens decentered 3 mm creates __^prism. |
(10x3) / 10= 3^
|
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
Looking 8mm below the optical center of a -6.00 D lens will create __^ base __. |
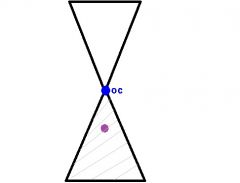
(6x8) / 10 = 4.8^
Base Down |
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
Looking 10mm below the optical center a +4.00 D lens will create __^ prism base ___. |
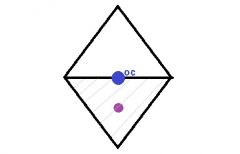
(4x10) / 10= 4^
Base up |
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
Looking 8mm above the optical center of a +10.00 D lens will induce __^ prism base___. |
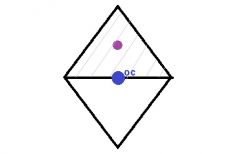
(8x10) / 10= 8^
Base down |
|
|
By using the Prentice's Rule, answer the following question:
Looking 5mm above optical center of a -8.00 D lens will induce __^prism base ___. |
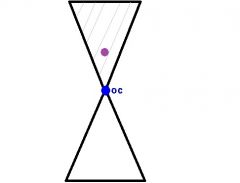
(8x5) / 10 = 4^
Base up |
|
|
Transpose the following lens:
-4.00+1.00x098 |
-3.00-1.00x008
|
|
|
Write the RX in plus form:
-2.00@140 -1.00@050 |
-2.00+1.00x140
|
|
|
Write the RX of this lens:
(+4.00) (plano) 90 |
+4.00-4.00x090
|
|
|
What are the true powers if this lens:
-5.50+2.50x055 |
-5.50@055 -3.00@145
|
|
|
What is the power at the axis of this lens:
-1.00-2.00x145 |
-1.00@145
|
|
|
What is the power at the horizontal meridian of this lens:
+1.00-0.50x090 |
+0.50@180
|
|
|
What is the power at the vertical meridian of this lens:
-2.00-3.00x180 |
-5.00@090
|
|
|
If the true powers of a lens at 180 is -5.00, and the other power is -2.00, what is the Rx of this lens?
|
-5.00+3.00x180
|
|
|
The sphere lines of the lensometer reads -1.00, the cylinder lines read +1.00, and the axis drum is on 90. What is the Rx of this lens?
|
-1.00+2.00x090
|
|
|
Sphere lines of a lensometer is focused on the +2.00, the cylinder lines is on +4.00, and the axis drum is on 120. Write the Rx of this lens in minus form.
|
+4.00-2.00x030
|
|
|
A patient is looking through 2BU prism in OD and 2BU prism in OS. How much is the imbalance?
|
0 prism imbalance
|
|
|
How much is the imbalance if a patient looks though 4BI and 2BI prisms?
|
6 prism imbalance
|
|
|
How much is the imbalance if a patient looks through 1BD and 2BU prisms?
|
3 prism imbalance
|
|
|
How much is the imbalance if a patient looks through 3BI and 2BO prisms?
|
1 prism imbalance
|
|
|
How much is the imbalance if a patient looks through 2BO and 2BO prisms?
|
4 prism imbalance
|

