![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
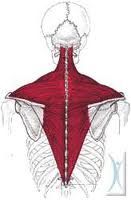
What are the two most superficial muscles of the back?
|
Trapezius
Latissimus Dorsi |
|
|
|
What shape is the trapezius?
|
Triangular
|
|
|
|
Are the trapezius and latissmus dorsi true back muscles
|
No.
Why? |
They are not true back muscles because they do not move the spine.
|
|
Trapezius
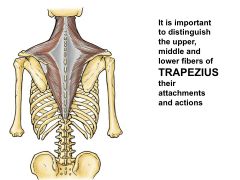
Name the regions |
Superior or Descending
Middle or Transverse Inferior or Ascending |
|
|
Trapezius
General Actions |
Generally - Elevates, Retracts and Rotates, Scapula
With shoulders fixed: Bilaterlal Contraction: Extends neck Unilateral Contraction: The head will either do ipsilateral flexion(Clinical Anatomy) |
|
|
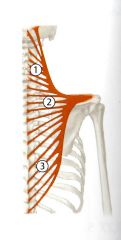
What is the Action of the superior trapezius?
|
Superior - Scapular Elevation (shrugging) (Prof),
Elevate scapula obliquely;with inferior trapezius rotate glenoid cavity superiorly; tilts head ipsilaterally and rotates it contralaterally. Entire trapezius muscle steadies scapula against thorax (Thiemes Atlas) |
|
|
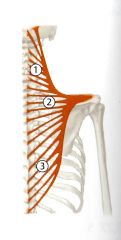
Trapezius
What is the Superior Trapezius ORIGIN and INSERTION? |
Origin - Medial third of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone, external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C1-C7 .
Insertion - lateral 1/3 of the Clavicle |
|
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Superior Trapezius?
|
Innervation -
Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) C3 & C4 nerves (pain and proprioception) |
|
|
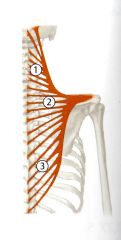
What is the Action of the middle trapezius?
|
Scapular Retraction (ad duction) (Prof)
Draws Scapula Medially (Thieme Atlas) Entire muscle is steadies scapula on thorax |
|
|
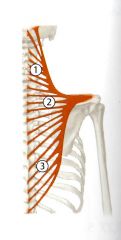
What is the Origin and Insertion of the Middle (Transverse) Trapezius?
|
ORIGIN:
Aponeurosis at T1 -T4 spinous processes INSERTION Acromion |
|
|
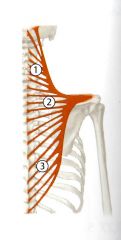
What is the Innervation of the middle trapezius?
|
Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI), C3 - C4 of the cervical plexus (pain and proprioception)
|
|
|
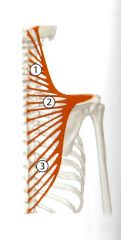
What is the Action of the Inferior (Ascending) Trapezius?
|
1) Retracts and depresses Scapula medially against resistance (Thiemes Atlas and Prof)
2) Rotate Scapula superiorly with superior trapezius Entire muscle is steadies scapula on thorax |
|
|
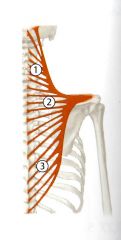
What is the Origin and Insertion of the Inferior (Ascending) trapezius?
|
Origin: Spinous Process of T5 - T12
Insertion: Spine of the Scapula (Thieme) |
|
|
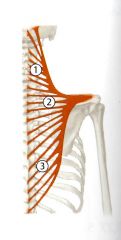
What is the Innervation of the Inferior (Ascending) Trapezius?
|
Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI)
C3-C4 nerves of the cervical plexus (pain and proprioception) |
|
|
|
Are the trapezius and latissmus dorsi true back muscles
|
No.
Why? |
They are not true back muscles because they do not move the spine.
|
|
|
What is inferior to the trapezius?
|
Latissimus Dorsi
|
|
|
|
What shape is the trapezius?
|
Triangular
|
|
|
|
What is the Action of the latissimus dorsi?
|
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus; raises the body toward arms during climbing (Clinical)
Respiration (cough muscle) (Thieme) |
|
|
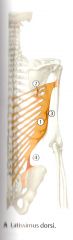
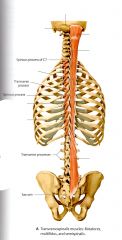
What are the 5 Origins of the Latissimus Dorsi?
|
Vertebral Part:
1) a. Spinous Process of T7* - T12 b. Thoracolumbar Fascia 2) Scapular Part - Inferior Angle 3) Costal Part - 9th to 12th rib 4) Illiac Part - Posterior 1/3 of the Illiac Crest |
T7 is transverse to the inferior angle of the scapula
|
|
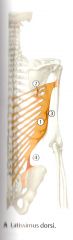
What is the Insertion of the Latissimus Dorsi?
|
Floor of the Intertubercular Sulcus (groove) of humerus (Clinical)
|
|
|
|
What is the Innervation of the latissimus dorsi?
|
Thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
|
|
|
|
What does the latissimus dorsi surround, encase, provide structural support for?
|
Paraspinal Muscles (Intrinsic muscles or deep back muscles).
|
|
|
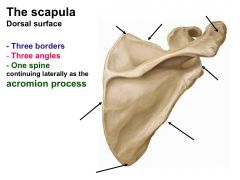
What are the parts of the scapula?
3 Angles 3 Borders 2 Surfaces 2 Processes 1 Spine |
3 ANGLES
1) Superior Angle 2) Inferior Angle 3) Lateral Angle (Head of the Scapula)* 3 BORDERS 1) Superior Boder 2) Medial (Vetebral) Border 3) Lateral (Axillary) Border 2 SURFACES 1 & 2)) Anterior and Posterior Surface 2 PROCESSES 1) Acromion Process* 2) Coracoid Process 1 SPINE which continues laterally to the Acromion Process |
Acromion articulates with the clavicle in shoulder movement
The humerus articulates at the lateral angle |
|
|
What are two useful landmarks of the scapula?
|
1) The root of the spine is in the same transverse plane as T3 Spinous Process.
2) The inferior angle lies in the same plane as T7 spinous process.* |
T7 spinous process is an origin for the vertebral part of latissimus dorsi. (T7-T12 and the thoracolumbar fascia)
|
|
|
What are the 3 scapulothoracic movements?
|
1) Scapular elevation and depression (shrugging)
2) Scapular Protraction (ab-duction*) and Retraction (ad-duction) 3) Scapular Rotation - around an axis - to reposition lateral angle that participates in shoulder movement that is from vertical to horizontal. Also, to flex or abduct the shoulder. |
To abduct = to take away
Add to the body - adduction |
|
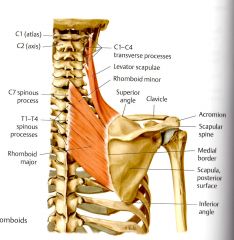
What are the three muscles that are revealed when the trapezius is reflected?
|
1) Levator Scapulae
2) Rhomboids Minor 3) Rhomboids Major |
|
|
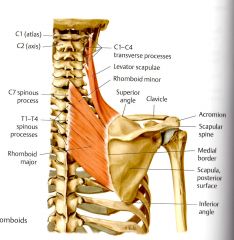
What is the ACTION of the Levator Scapulae?
|
Elevates the scapula medially while moving the inferior angle medially, inclines the neck ipsilaterally (Thieme) and tilts the glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating the scapula (Clinical)
|
|
|
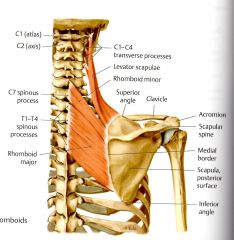
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION for Levator Scapulae?
|
ORIGIN:
Transverse Processes of C1 - C4 INSERTION: Superior Angle of the Scapula |
|
|
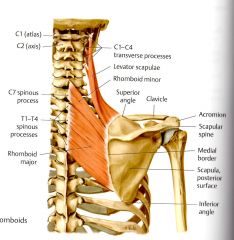
What is the INNERVATION of the Levator Scapulae?
|
Dorsal Scapular Nerve C4 & C5*
|
Innveration of Levator Scapulae, and Rhomboids major and minor are the same.
|
|
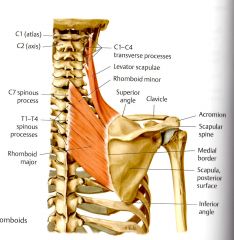
What is the ACTION of the Rhomboid Minor?
|
Steadies, Retracts, and Elevates the Scapula medially (Thieme and Clinical). Also, fix the scapula to the thoracic wall. (Clinical)
|
|
|
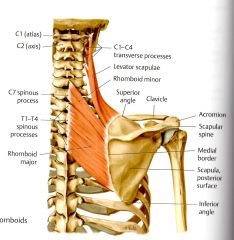
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION for Rhomboid Minor?
|
ORIGIN:
Spinous Process of C6, C7 (Thieme) INSERTION: Superior to the spine on the medial (vertebral) border (Thieme) |
|
|
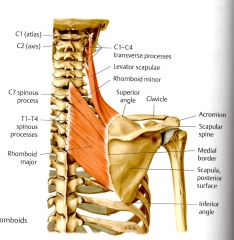
What is the INNERVATION of Rhomboid Minor?
|
Dorsal Scapular Nerve C4 & C5*
|
Innveration of Levator Scapulae, and Rhomboids major and minor are the same.
|
|
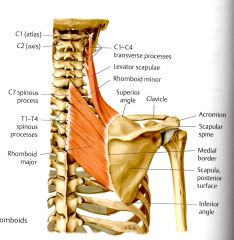
What is the ACTION of the Rhomboid Major?
|
Steadies, Retracts and elevates the scapula medially (Thiemes and Clinical) and fixes scapula to the thoracic wall (Clinical)
|
|
|
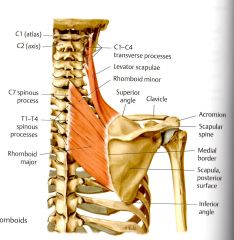
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION for Rhomboid Major?
|
Spinous Process of T1 - T4 (Thieme)
|
|
|
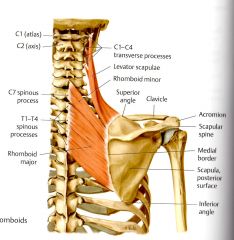
What is the INNERVATION of the Rhomboid Major?
|
Dorsal Scapular Nerve C4 & C5*
|
Innervation of Levator Scapulae, and Rhomboids major and minor are the same.
|
|
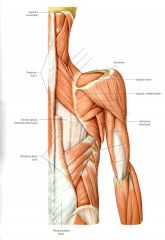
What are the 5 back muscles of the Intermediate Layer until lecture 060112?
|
1) Levator Scapula
2) Rhomboid Minor 3) Rhomboid Major 4) Serratus Posterior Superior 5) Serratus Posteror inferior |
|
|
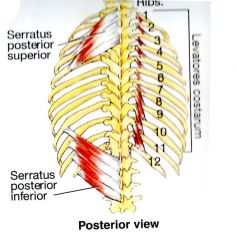
What is the ACTION of the Serratus Posterior Inferior?
|
a respiratory muscle used for forced expiration by depressing the ribs
|
|
|
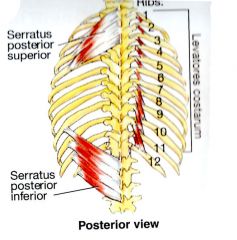
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Serratus Posterior Inferior?
|
ORIGIN:
Spinous Process of T11-L2 INSERTION: Inferior Borders of 8th-12th ribs near the angles. |
|
|
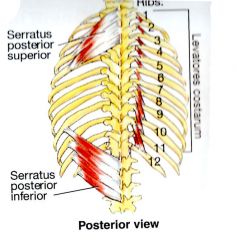
What is the INNERVATION of the Serratus Posterior Inferior?
|
Anterior (ventral) primary rami of spinal nerves T9-T12 (Thieme)
|
|
|
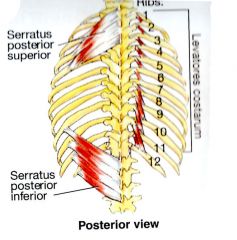
What is the ACTION of the Serratus Posterior Superior?
|
A respiratory muscle used for inhalation by elevating the ribs
|
|
|
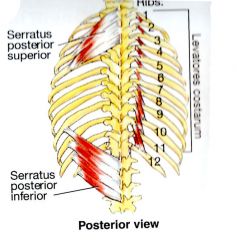
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Serratus Posterior Superior?
|
ORIGIN:
Nuchal Ligament, spinous process of C7-T3 INSERTION: Ribs 2 - 4 (superior borders) |
|
|
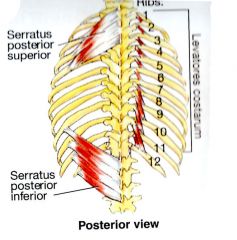
What is the INNERVATION of the Serratus Posterior Superior?
|
2nd - 5th intercostal nerves
|
|
|
|
What layer of back muscles actually move the spine?
What are they called? |
Deep Muscles
Intrinsic or Paraspinal Back Muscles |
Lie in vertical parallel columns along the spine
|
|
|
What are their primary purpose?
What nerves are they generally innervated by? |
Postural Muscles resisting the pull of gravity and are critical to bipedal motion.
Dorsal Rami of the spinal nerves |
|
|
|
The intrinsic/paraspinal muscles arise from _____ and sometimes referred to as _______
|
epicures of the embryonic somites
epaxial muscles |
|
|
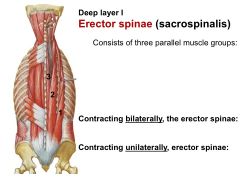
What are the three erector spinae (sacrospinalis)?
|
1) Iliocostalis
2) Longissimus 3) Spinalis |
|
|
|
What are the three subdivisions of the iliocostalis?
|
1) Iliocostalis lumborum
2) Iliocostalis thoracis 3) Iliocostalis cervicis |
|
|
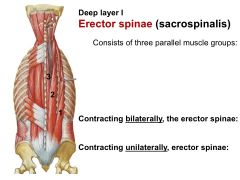
What is the ACTION of the 3 areas of the iliocostalis
|
Bilaterally: Extends the spine
Unilaterally: Bends spine ipsilaterally |
|
|
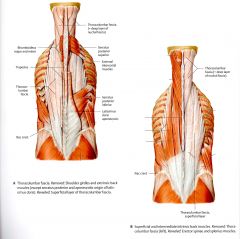
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the 3 areas of iliocostalis?
|
ILIOCOSTALIS LUMBORUM
ORIGIN: Sacrum; illiac crest, thoracolumbar fascia (Thieme) INSERTION: 6-12th ribs, thoracolumbar fascia, transverse process of upper lumbar vertebrae ILIOCOSTALIS THORACIS ORIGIN: 7th - 12th ribs, INSERTION: 1st - 6th ribs ILIOCOSTALIS CERVICIS ORIGIN: 3rd - 7th ribs INSERTION: Transverse Processes of C4-C6 |
|
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the 3 areas of the iliocostalis?
|
Spinal Dorsal Rami lateral branches C8-L1
|
|
|
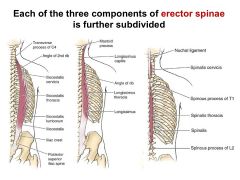
What are the 3 subdivisions of the Longissimus?
|
1) Longissimus Thoracis
2) Longissimus Cervicis 3) Longissimus Capitis |
|
|
|
What are the ACTIONS of the Longissimus Thoracis, Cervicis, and Capitis?
|
LONGISSIMUS THORACIS AND CERVICIS
BILATERAL: Extends the spine UNILATERAL: Ipsilateral bending of the spine LONGISSIMUS CAPITIS BILATERAL: Extends Head UNILATERAL: Flexes and rotates the head ipsilaterally |
|
|
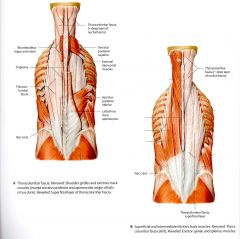
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Longissimus Thoracis, Cervicis, Capitis?
|
LONGISSIMUS THORACIS
ORIGIN: Sacrum , iliac crest, Spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae and the Transverse processes of the lower thoracic vertebrae INSERTION: 2nd-12th ribs, Costal processes of the lumbar vertebrae, Transverse Processes of the thoracic vertebrae. LONGISSIMUS CERVICIS ORIGIN: Transverse Processes of the T1-T6 INSERTION: Transverse Processes of C2-C5 LONGISSIMUS CAPITIS ORIGIN: Transverse Process of T1-T3 and Transverse and Articular Processes of C4-C7 INSERTION: Mastoid Process of the Temporal Bone |
|
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Longissimus?
|
Dorsal Spinal Nerves Lateral branches (C1-L5)
|
|
|
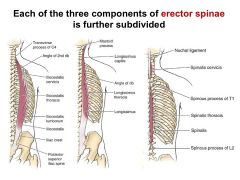
What are the 2 subdivisions of the Spinalis?
|
1) Spinalis Thoracis
2) Spinalis Cervicis |
|
|
|
What is the ACTION of the Spinalis Thoracis and Spinalis Cervicis ?
|
SPINALIS THORACIS AND CERVICIS
BILATERAL: Extends thoracic and cervical spine UNILATERAL: Bending of the thoracic and cervical spine ipsilaterally |
|
|
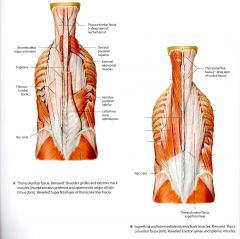
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Spinalis Thoracis and Cervicis?
|
SPINALIS THORACIS
ORIGIN: Lateral surface of the Spinous Process T10-L3 INSERTION: Lateral Surfaces of the Spinous Process T2-T8 SPINALIS CERVICIS ORIGIN:Spinous Processes of C5 - T2 INSERTION: Spinous Processes of C2 - C5 |
|
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Spinalis Thoracis and Spinalis Cervicis?
|
Dorsal Spinal Rami
|
|
|
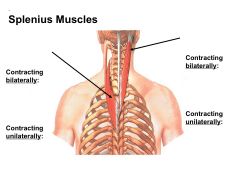
What are the two Splenius Muscles?
|
1) Splenius Cervicis
2) Splenius Capitis |
|
|
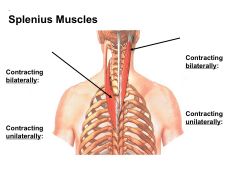
What is the ACTION of the Splenius Cervicis?
|
Bilateral Contraction: Extends Cervical Spine and Head
Unilateral Contraction: Flexes and Rotates head ipsilaterally |
|
|
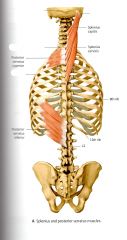
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Splenius Cervicis?
|
ORIGIN:
Spinous processes of T3* - T6 INSERTION Transverse processes of C1-C2 |
T3 landmark is the scapular spinal root
|
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Splenius Cervicis?
|
Dorsal Rami, Lateral Branches C1-C6 Spinal nerves*
|
Same innervation for Splenius Capitis
|
|
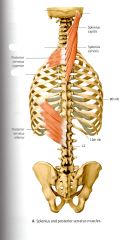
What is the ACTION of the Splenius Capitis?
|
Bilateral Contraction: Extends the Cervical Spine and Head
Unilateral Contraction: Flexes and Rotates the head ipsilaterally. |
|
|
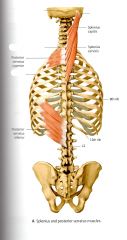
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Splenius Capitis?
|
ORIGIN:
Nuchal Ligament, Spinous Processes of C7* - T3* INSERTION Lateral 1/3 of the Superior Nuchal Line on the Occipital Bone and the Mastoid Process on the temporal bone |
C7 can be palpated and is called the vertebral prominence
T3 landmark is the Scapular Spine Root |
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Splenius Capitis?
|
Dorsal Rami, lateral branches of C1-C6 Spinal Nerves
|
|
|
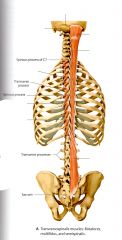
1) What are the Superficial Back Muscles?
2) Reflection of the Superficial Back Muscles show what intermediate Back Muscles? 3) Reflection of the Intermediate Back Muscles displays which Intrinsic Back Muscles? 4) Reflection of the previous Intrinsic (deep) Back muscles displays what muscles? 5) Deep to these muscles are which Deep Neck and Suboccipital muscles ? |
1) Trapezius and Latissimus Dorsi
2) Rhomboid Major and Minor, Levator Scapula, Serratus Posterior Inferior and Superior 3) Erector Spinae (Sacrospinalis) - Iliospinalis, - Longissimus, and - Spinalis 4) Splenius Cervicis and the Splenius Capitis 5) Transversospinalis - Semispinalis - Multifidus - Rotatores |
All Tansversospinalis muscles for Unilateral movement rotates the head contralaterally.
|
|
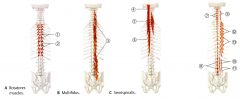
What is the ACTION of the Semispinalis?
|
Bilaterally: Extends head, cervical and thoracic vertebrae
Unilaterally: Bends head, cervical and thoracic spines ipsilaterally and rotates contralaterally |
1/2 of the superior side of the spine.
Most prominent at skull - semispinalis capitis |
|
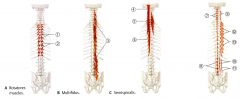
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Semispinalis?
|
ORIGIN
Vertebral transverse processesC4-T10 INSERTION Fibers run superomedially to the occipital bone and the spinous processes in upper thoracic and cervical regions spanning 4-6 segments (Clinical) |
|
|
What is the INNERVATION of the Semispinalis?
|
Dorsal Spinal Rami Nerve
|
|
|
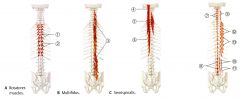
What is the ACTION of the Multifidus?
|
Bilateral: Extends the spine
Unilateral: Ipsilateral flexion of the spine and Contralateral rotation |
Largest and most powerful in lumbars.
Deep to erector Spinae |
|
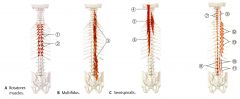
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Multifidus?
|
ORIGIN & INSERTION
C2-Sacrum (between transverse and spinous processes, skipping two to four vertebrae) thickest portion in the lumbar region |
|
|
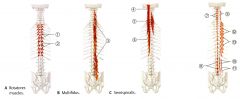
What is the INNERVATION of the Multifidus?
|
Dorsal Spinal Rami Nerve
|
|
|
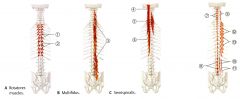
What is the ACTION of the Rotators?
|
BILATERAL: Extends spine
UNILATERAL: Contralateral spinal rotation Propiroception organ |
Shortest
1 or 2 segments Not much leverage for movement . |
|
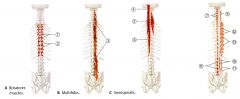
What is the ORIGIN and INSERTION of the Rotators?
|
Arises from the Transverse Processes of verterbrae and best developed in thoracic region
|
|
|
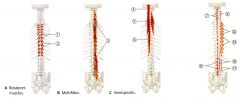
What is the INNERVATION of the Rotators?
|
Dorsal Spinal Rami Nerve
|
|

