![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Goodpasture syndrome |
◆Anti-glomerul basement membrane anti-GBM antibody against type IV collagen ◆IgG deposit on renal biopsy ◆HLA27 ◆Rapid progressive glomerulonephritis ◆Normal complementlevel ◆Haemoptsis + renal failure ◆plasma exchange , steroidb, cyclosphisphamide |
|
|
Glomerulonephritis & low complement |
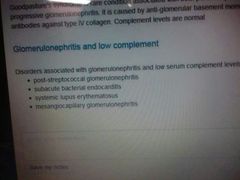
|
|
|
ANCA positive vasculitis - Wegener's granulomatosis |
Rapid progressive glomerulonephritis |
|
|
Mixed essential Cryoglobulinemia |
◆Palpable purpura , proteinuria , hematuria , arthralgia , hepatosplenomegaly & hypocomplementemia ◆HCV + |
|
|
Alport's syndrome |
◆X-linked dominant ◆Defect 4 collagen Recurrent hematuria Sensorineural deafness Family history renal disease |
|
|
Membranoproliferative - mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis |
Cryoglobulinaemia HCV Partial lipodystrophy ◆Positive for C3 not immunoglobulin persistent activation of the alternative complement pathway |
|
|
Minimal change glomerulonephritis |
◆Podocyte fusion ◆Nephrotic syndrome ◆HTN & hematuria is rare ◆Only cancer -lymphoma |
|
|
Diffuse prolifrative GN |
Post-streptoccal SLE |
|
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis Focal segmental GN |
◆Membranous glomerulonephritis Related to malignancy ◆Focal segmental GN related to HIV |
|
|
IgA nephropathy |
◆after URI wothin 5 days adult ◆Histological = mesangial hypercellularity + posarive IgA C3 ◆Macroscopic heamaturia , male ◆Coeliac disease ◆henoch-schonlein purpura ◆Alcoholic cirrhosis |
|
|
Renal tubular acidosis |
Hyperchloraemic metabolic acidosis - Normal anion gap ◆RTA type1 : hypokalaemia , nephrocalcinosis & renal stone , RA , SLE , sjogren's ◆RTA2 : hypokslemia , osteomalacia RTA: hyperkalaemia |
|
|
Renal & prerenal uraemia |

|
|
|
Stag-horn calculi |
Composed of struvite -magnesium ammonium phosphate |
|
|
Benign recurrent hematuria Thin basement membrane nephropayhy |
Familial , microscopic |
|
|
Acute interstitial nephritis |
Ren tubule & intetstitium following exposure to drug ◆Penicilin , cephalosporine , sulphonamide ◆Fever , rash , arthralgia ◆WBC cast present , RBC cast rare |
|
|
UTI |
Dipstick = Leukocyte esterase + nitrites |
|
|
Wilms tumor , nephroblastoma |
Primary renal neoplasm ◆Asymptomatic abdominal mass , hematuria ◆Ab U/S ◆surgery , Chemotherapy , radiation |
|
|
Henoch-Schonein purpura Mesangial deposition of IgA |

. |
|
|
Focal segmental GN |
◆Cause end stage renal disease ◆Oedema , hematuria , ◆Mesangial scleosis ◆Heroin , alport syndrome , SCD , HIV , idiopathic |
|
|
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia |
Autosomal dominant - mutation calcium-sensing receptor ◆⬇Urinary calcium excration ◆Complicated pancreatitis , chondrocalcinosis |
|
|
ًrenal tubular acidosis |
◆nonanion gap metabolic acidosis for all type of RTA ◆Type1 = Defect hydrogen excretion hypokalemia , related to RA,SLE,sjogren Comp: nephrocalcinosis , stone
◆Type2 ◆Defect bicorbonate resorption in the kidney , hypokalemia , Comp: osteomalacia , fanconi
◆Type4 ⬇bicorbonate resorption ,hyperkalamia , DM
◆Failure to thrive due to chronic normal anion gab metabolic acidosis ◆Treatment oral bicorbonate replacement |
|
|
Oliguria |
Urine < 250 ml in 24 hours |
|
|
Iatrogenic hyponatremia |

|
|
|
Renal cell carcinoma |

Ct scan |
|
|
Anion gap metabolic acisosis |

|
|
|
Postictal lactic acidosis |
Skeletal muscle hypoxia ◆Transiet self limiting resolve within 90 minutes |
|
|
Primary polydipdsia |
◆Serum osmalarity => 290 ◆urine osmalarity < 100 ◆psychiatric condition |
|
|
Primary adrenal insufficiency |
Addison disease ◆Aldosterone deficiency ◆Non-anion gap hyperkalemic , hyponatremic metabolic acidosis ◆⬇Cortisol ,⬆ACTH |
|
|
Systemic osmatic demylination syndrome |
Treated hyponatremia , by 3% hypertonic saline more than .5 /hrs |
|
|
Ethylene glycol poisining |
Metabolic acidosis with anion & osmolal gap ◆Renal failure ◆Urine = rectangular envelope shaped crystals |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome due to amyloidosis |
AA amyloidosis due to RA ◆MM , nonhodging lymphoma ◆Biopsy = stain with congo red ◆Apple-green birefringence under polarized light ◆ |
|
|
Rapid progressive GI |
◆Crescent formation autoimmune |
|
|
Aspirine toxicity |
◆Tinnitus & vertigo , fever tacypnea Cause = mixed respiratory alkolosis , metabolic acidosis due to ⬆production ,⬇eliminatiom of organic acid ◆Near normal pH |
|
|
Hepatorenal syndyome |
In pt with liver cirrhosis ◆Splanchnic arterial dilation ◆⬇ GFR , Reduced renal perfusion ◆No response to volume resucitation ◆ARF + ⬇urine Na level = acute renal tubular necrosis |
|
|
ARF with rhabdomyolysis |
Myoglobinuria = large amount blood & absence RBCs on urine microscopy ◆⬆⬆Creatine phosphokinase |
|
|
Hypovolumia due to A.pancreatitis |
⬆Renin angiotensin system Vasoconstriction , Na & water reabsorption |
|
|
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction |
◆Urinary retention , distended bladder ◆Overflow incontinance with post-void residual valume |
|
|
Uric acid estone |
Reduced recurrency by alkalazation of urine by K citrate |
|
|
Manegment of hyperkalamia |

|
|
|
Urine cast |

|
|
|
Drug faciliate stone passage |
Alpha-1 receptor blocker as tamsulosin |
|
|
Diabetes insipidus DI |
Euvolemic hypernatremia ◆Severe polyuria & mild hypernatrimia ◆⬆serum osmalarity ◆Complate u.o >300 ◆Partial u.o 300-600 ◆Central ID = ⬇ADH ◆Nephrogenic = drug lithium , hypercalcemia , |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome |
◆Proteniuria , ◆hypoalbumineria ◆edema ◆hyperlipidemia & lipiduria |
|
|
Hypercalcemia |

Cause weakness , GI distress , neurosychiatric symptoms |
|
|
Pt with Ca calculi |
◆⬆Fluid intake ◆⬇Na intake ◆Normal Ca intake |
|
|
Hematuria |

|
|
|
Papillary necrosis |

NSAID , SCD renal medullary carcinoma , analgesia , infection , DM |
|
|
Gordon dyndrome |
. |
|
|
Bartter syndrome |
. |
|
|
Thiazide diuretics ( chlortholidone , hydrocholothiazide ) |
Impair insulin release from pancrease & glucose utilization ◆Effect = dose dependent ◆⬆LDL cholesterol , plasma triglyceride , hyperuricemia ◆Hyponatremia , hypokalemia , hypomagnesimia , hypercalcemia |
|
|
Na nitropusside |
Cyanide toxicity ◆Headache , confusion , arrhythmias , flushing , respiratory depression |
|
|
SIADH |

|
|
|
Vesicoureteral reflux |
First UTI u/s Second = voiding cystourethrogram |
|
|
Nephrotic vrs nephritic syndrome |

|
|
|
Acute tubular necrosis |
◆ACI ◆Muddy brown granular cast |
|
|
Refractary hypokalemia |
Due to hypomagnesemia mainly in chronic alcoholic |
|
|
Renal stone |
◆75-95% kidney stone = Ca oxalate - SBD , malabdorption ◆ |
|
|
Acute interstitial nephritis |

|
|
|
Alport syndrome |
◆X-linked dominant , defect type4 collagen ◆Recurent hematuria ,protenuria ◆family history , deaffness ◆Biopsy = alterating thin &tick capillary loob with splitting GBM |
|
|
Metabolic alkolosis |
◆Saline responsive = ⬇urine coliride ◆Saline nonresponsive = normal urine choliride |
|
|
Cyanide poisning |
Venous &arterial blood contain same oxygen content |
|
|
Hyposthenuria |
Inability of the kidney to concentrate urine ◆SCD , SCT , ◆Pt with polyuria , ⬇urine specific gravity , normal serum sodium |
|
|
ADPKD |
Major extrarenal complication ◆IC Berry aneurysm 5-10% ◆hepatic cyst ◆Valvular heart disease ◆colonic diverticula ◆Abdominal wall &I. hernia |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome |

|
|
|
Posterior urethral valve |

Prenatal U/S bilateral hydronephrosis , hydroureter , ◆Oligohydrominous ◆Pulmonary hypoplasia , postnatal RD |
|
|
Nephrosclerosis due to htn |
Initimal thikening and Luminal narrowing of renal arteriole with evidence os sclerosis |
|
|
Urine incontinance |

|
|
|
Tubulointerstitial nephritis |

|
|
|
APDGN |

|
|
|
Diabetic nephropathy |
Nodular glomeruloscletosis kimmelstiel-wilson nodule is pathogonomic ◆Tteatment , glycemic control , treat htn , angiotensin axis blockade |
|
|
Membrabous nephropathy |
◆HBV |
|
|
Crystalluria with renal tubular obstruction |

◆⬆Dose IV acyclovir , fluid reduce risk |

