![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
explain why most mechanisms of action given the neuropharmacologic drugs are approximations.
(o) |
Entire mechanism is generally unknown. Approximations of
CNS mechanism made from information regarding effects of drugs in isolated systems. CNS as a “Black Box” Extrapolation from biochemical events to behavior is difficult. |
|
|
define what is meant by specific mechanism of action.
(o) |
A specific drug action affects a recognized protein target, i.e., a receptor, an ion channel, an enzyme, or a transporter.
|
|
|
describe the various events in synaptic transmission which might be altered by drugs
(o) |
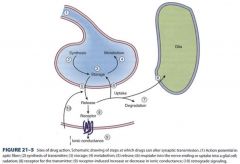
|
|
|
describe the various events in synaptic transmission which might be altered by drugs
(o) |
|
|
|
describe the various events in synaptic transmission which might be altered by drugs
(o) |
|
|
|
what is the difference between a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator?
(o) |
Neurotransmitter – a substance which is released locally and causes a change in post-synaptic potential.
Neuromodulator – a substance which acts to modify the response of the synapse to a neurotransmitter. (make a stimulus stronger or weaker) |
|
|
describe the various events in synaptic transmission which might be altered by drugs
(o) |
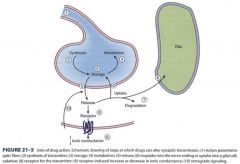
|
|
|
recognize the substances which have been proposed to act as CNS neurotransmitters
(o) |
Acetylcholine
Amino acids Biogenic amines Peptides Purines (ATP, adenosine) Nitric acid Endocannabinoids |
|
|
differentiate between ionotropic and metabotrophic receptors.
(o) |
Ionotropic receptors (also known as ligand-gated ion channels) are associated with ion channels, and change ionic conductance.
Mediate fast, short effects. Metabotropic receptors are coupled with enzymes via G-proteins and other intermediates. Mediate slow, long effects. |
|
|
describe the blood brain barrier and its implications in drug therapy (what are the characteristics that regulate diffusion of substance through capillaries)
(o) |
A term used to describe diffusional barriers retarding the passage of substances from the central circulation to nerve cells.
Characteristics which regulate diffusion of substances through capillaries are: Molecular weight Lipid solubility Ionization at physiological pH (ionized drugs are not lipid soluble) |

