![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
199 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the formula for the gear ratio? |
Driven / Driving
|
|
|
What's the difference between a driven gear and a driving gear? |
Drive Gear (Input). A drive gear or driving gear is one that drives another gear or causes another gear to turn.
Driven Gear (Output). A driven gear is one that is driven by a drive gear or a shaft. |
|
|
What is an idler gear? |
An idler gear is a gear wheel that is inserted between two or more other gear wheels. The purpose of an idler gear can be two-fold. Firstly, the idler gear will change the direction of rotation of the output shaft. Secondly, an idler gear can assist to reduce the size of the input/output gears whilst maintaining the spacing of the shafts. (Wikipedia) |
|
|
What are two advantages of helical gears over spur gears? |
They are stronger and quieter. |
|
|
What does transmission starting gear depend on? |
The load. |
|
|
In order for gears to be meshed what must they both have? |
They must both have the same gear pitch. |
|
|
What are the major components in a typical transmission? |
Input and output shafts, main shaft and counter shaft gears, and shift mechanisms. |
|
|
What is overdrive? |
any drivetrain arrangement in which an output speed exceeds input speed. For instance, most transmissions have over drive ratio options, meaning that transmission tailshaft speed exceeds engine crankshaft speed. |
|
|
What is tailshaft? |
The output shaft of a transmission. |
|
|
What is the backbox? |
Another name for the auxiliary section of the transmission. |
|
|
Regardless of how many possible speeds available, how many speeds will the front box be, almost all of the time? |
You'll have a 5 speed front box, almost all of the time, regardless of how speeds the whole thing is. |
|
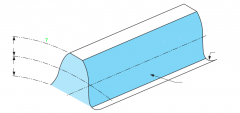
|
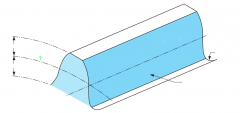
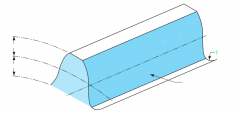
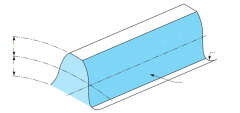
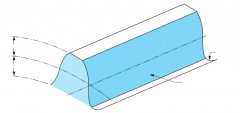
Outside diameter |
|
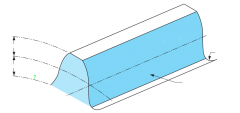
|
Root diameter |
|
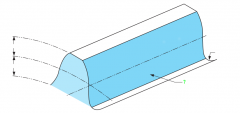
|
Tooth surface or flank |
|
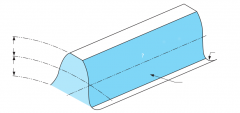
|
Pitch line |
|
|
Pitch diameter |
|
|
Fillet radii |
|
|
Addendum |
|
|
Dedendum |
|
|
What do you take off on a transmission first? |
The air system. |
|
|
What is gear pitch? |
the number of teeth per given unit of pitch diameter in a gear.
36 teeth / 6" diameter = gear pitch teeth count / diameter = gear pitch |
|
|
When gears of equal size are meshed, what happens? |
Output speed equals input speed. |
|
|
When a small gear drives a large gear, what happens? |
It reduces output speed. |
|
|
When a large gear driving a small gear, what happens? |
It increases output speed (overdrive). |
|
|
What are the general methods of shifting standard transmissions? |
sliding gear, collar shift, and synchronized shift |
|
|
What is a sliding gear shift? |
A single countershaft transmission that uses a sliding gearshift mechanism has a main shaft and a countershaft supported parallel to each other. To change from one speed/torque range to another, gears on the main shaft are moved longitudinally until they engage the desired gear on the countershaft. To effect this movement, spur-cut sliding gears are used. These have a shift collar integral with the gear. When the driver makes a shift, a shift fork or yoke engages with a collar on the gear and slides it on the main shaft until it is brought into mesh with a mating gear on the countershaft. |
|
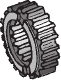
|
Shift Gear (Splined to Shaft) |
|
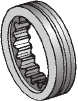
|
Shift Collar |
|
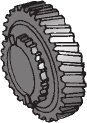
|
Driven Gear (Rides Free on Shaft) |
|
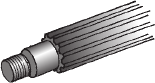
|
Shaft |
|
|
How do you check main shaft straightness? |
Put the sliding clutch on top of it and see if it can slide all the way down. If not, it's not straight enough. |
|
|
What is bottoming? |
A bottoming condition occurs when the teeth of one gear contact the root of the mating gear. Bottoming seldom occurs in a two-gear drive combination but is more common in multiple-gear drive combinations. The mating action of a two-gear drive combination tends to thrust the gears apart, so bottoming is unlikely in this arrangement. |
|
|
What two important functions does the synchronizer perform? What is the result? |
Its main function is to bring components that are rotating at different speeds to a common or synchronized speed. In a transmission, a synchronizer ensures that the main shaft and the main shaft gear about to be locked to it are both rotating at the same speed. The second function of the synchronizer is to actually lock these components together. If the driver and the synchronizer are both doing their jobs, the result is a clash-free shift. |
|
|
What is backlash? How is it measured? Why is it important? |
The term backlash describes rotational free play between mating gears, usually measured with thickness gauges or a dial indicator. All intermeshing gears should have some backlash to permit heat expansion of metal and proper lubrication. Out-of-specification backlash results in noise and rapid wear. Backlash increases as mating gears and shaft bearings wear. |
|
|
What is the drive side and coast side? |
The drive side of gear teeth is in contact with teeth of another gear while torque is being applied. Usually the drive side of gear teeth is subject to the most wear. The coast side of gear teeth is opposite to the drive side. |
|
|
What is the shift bar housing? |
The shift bar housing, also known as the shift rail assembly, houses the components required to convert gear stick movement into range gearshifts within the transmission. |
|
|
How do you determine the direction of rotation of gears in a transmission? |
To determine the direction of rotation of gears in a transmission, you should face the front of the transmission—that is, the end that couples to the engine. |
|
|
What does CW and CCW stand for? |
Clockwise and counterclockwise. |
|
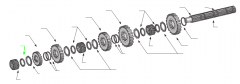
|
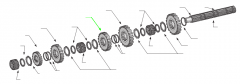
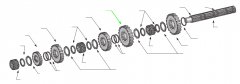
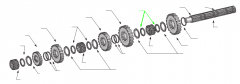
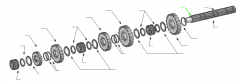
Washer |
|
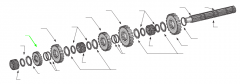
|
4th |
|
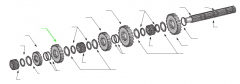
|
3rd |
|
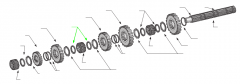
|
Washers |
|
|
2nd |
|
|
1st |
|
|
Washers |
|
|
Roll pin |
|
|
Key |
|
|
Splined main shaft |
|
|
Snap ring |
|
|
Reverse |
|
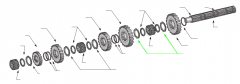
|
Spacers |
|
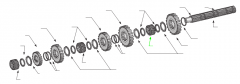
|
Sliding clutch |
|
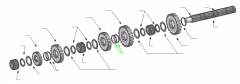
|
Snaprings |
|
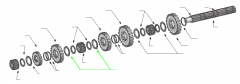
|
Spacers |
|
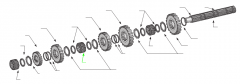
|
Sliding clutch |
|
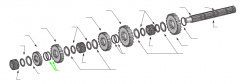
|
Snaprings |
|
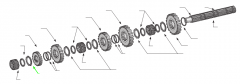
|
Spacer |
|
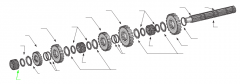
|
Sliding clutch |
|
|
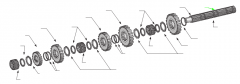
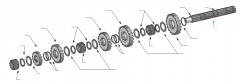
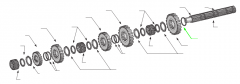
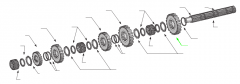
On a five-speed main shaft, what is the relative position of the sliding clutches and gears? |
One sliding clutch controls first and reverse shifts, another controls second and third shifts, and a third controls fourth and main gear engagement. Note: The main drive gear is not shown (in the diagram), but remember that this is part of the input shaft/drive gear assembly.
|
|
|
Compare spur gears and helical gears, what are the advantages of each? |
- Helical gears have more teeth in contact than a spur gear. - Spur’s straight teeth minimize the possibility of popping out of gear. - Helical gears are quieter than spur gears. - Helical gears permit the tooth load to be evenly distributed. - The main disadvantage of helical gears is the axial thrust they create in operation. |
|
|
On Eaton's, how many teeth do the gears have on both the top/passenger's side and the bottom/driver's side? |
47 teeth on bottom/driver's side and 45 teeth on top/driver's side. |
|
|
What kind of gears inhabit backboxes generally? |
Helical gears are generally what’s in backboxes. |
|
|
What kind of gears inhabit frontboxes generally? |
Spur gears are generally what’s in frontboxes. |
|
|
What is timing? |
Timing is the procedure used to time interacting mechanical components. See timing marks. |
|
|
What are timing marks? |
Timing marks are a means of marking gear set teeth before installation so that they can be placed in proper mesh in the geartrain. |
|
|
Engine torque is transferred through the clutch to what, which drives what? |
Engine torque is transferred through the clutch to the input shaft of the transmission, which drives the gears in the transmission. |
|
|
What does the transmission do? |
It let's you move at different speeds and in different directions. It is the driver’s means of managing drivetrain torque and speed ratios to suit chassis load and road conditions, such as a fully loaded standing start to cruising at highway speeds. |
|
|
How do the transmissions differ between light and heavy duty trucks? |
Light-duty truck transmissions have a limited number of gear ratios and a single set of gears called main gearing, contained in a single housing. Most heavy-duty truck transmissions consist of two distinct sets of gearing: the main or front gearing and the auxiliary gearing located directly on the rear of the main gearing. |
|
|
What does auxiliary gearing do? How many compounds do heavy-duty trucks use? |
Auxiliary gearing compounds the available ratios in a transmission. Most heavy-duty trucks use at least one compound, whereas some use two compounds. |
|
|
What are the three stages of contact through which the teeth of two gears pass while in operation? |
The three stages of contact through which the teeth of two gears pass while in operation are coming-into-mesh, full-mesh, and coming-out-of-mesh. |
|
|
How is the relationship of input to output speeds expressed? |
The relationship of input to output speeds is expressed as gear ratio. |
|
|
Torque increase from a driving gear to a driven gear is directly proportional what? What is a consequence of this? |
Torque increase from a driving gear to a driven gear is directly proportional to speed decrease. Therefore, to increase output torque there is a resultant decrease in output speed and vice versa. |
|
|
What are the major types of gear tooth design used in modern transmissions and differentials? |
The major types of gear tooth design used in modern transmissions and differentials are spur gears and helical gears. |
|
|
What does a heavy-duty standard transmission consist of? |
A heavy-duty standard transmission consists of a main shaft and one, two, or three countershafts. |
|
|
How can standard transmissions generally be classified? What are three shift mechanisms that are used to effect shifts in standard transmissions? |
Standard transmissions can be generally classified by how they are shifted. Sliding gear, collar shift, and synchronized shift mechanisms are used to effect shifts in standard transmissions. |
|
|
What are synchronizers' primary functions? |
Synchronizers have two primary functions. First, they bring two components rotating at different speeds to a single, synchronized speed; and second, they lock these components together. |
|
|
What are the most common synchronizers in heavy-duty transmissions? |
Block or cone and pin synchronizers are the most common in heavy-duty transmissions. |
|
|
How are most standard truck transmission main sections shifted? What are types of them? |
Mechanically. Either a direct-actuated, shift tower assembly, or, in the case of COE trucks, a remote-actuated shift tower. |
|
|
What do most current compounded transmissions use to effect shifts in the auxiliary section? |
Most current compounded transmissions use air controls to effect shifts in the auxiliary section, though some older trucks used gear levers for both main and auxiliary section shifts. |
|
|
What do air-actuated gearshift systems consist of? |
An air-actuated gearshift system consists of an air filter and regulator, slave valve, master control valve, range cylinder, and connecting air lines. |
|
|
Auxiliary section gearing can be optioned to include what? How is it used? |
Auxiliary section gearing can be optioned to include a third gear in addition to the high- and low-range gears. This third gear is engaged or disengaged by a splitter shift system air activated by a button on the shift lever. |
|
|
What is a transfer case and where is it located? What does it do? |
A transfer case is an additional gear box located between the main transmission and the rear axle. Its function is to divide torque from the transmission to front and rear drive axles and, in addition, to option driving force to the front axle. |
|
|
How are the accessory drive requirements on trucks met? What would be two examples? |
The accessory drive requirements on trucks are met by using power take-off (PTO) units. Hydraulic pumps for pumping loads off trailers and compressors for blowing loads off sealed bulk hoppers would be two examples of PTO-driven equipment. |
|
|
What are the six types of PTOs, classified by their installation? |
The six types of PTOs, classified by their installation, are side mount, split shaft, top mount, countershaft, crankshaft driven, and flywheel. |
|
|
air filter/regulator |
an integral filter regulator used on many standard shift truck transmissions. |
|
|
axis of rotation |
see axis. |
|
|
axis |
point about which a shaft, rotor, or component rotates. |
|
|
backlash |
the gapping or play between mating gear teeth usually measured with thickness gauges or a dial indicator. |
|
|
cab-over-engine (COE) |
a truck or tractor that locates the driver cabin in a forward position directly over the engine. There is no hood. |
|
|
climbing |
a gear problem caused by excessive wear in intermeshing gears or bearings. Climbing occurs when intermeshing gears move apart sufficiently for one gear to climb over the apex of its mate. |
|
|
constant mesh |
gears positioned to remain in permanent mesh, not engaged and disengaged by shifting action. |
|
|
direct drive |
a transmission ratio option in which the input and output shafts rotate at identical speeds, that is, engine speed. |
|
|
drive gear |
any gear that drives another. |
|
|
driven gear |
a gear that is driven by another. |
|
|
drivetrain |
term used to describe the components that move a vehicle down the highway from the engine, transmission, propeller shaft(s), drive axle carrier, drive axle shafts, and drive wheel assemblies. The engine is the prime mover of the drivetrain and the role of the transmission is to manage the output ratios. |
|
|
main shaft |
term used to describe the transmission shaft through which output torque is primarily routed. Term is used in both standard and automatic transmissions but the role played by the main shaft in each differs. |
|
|
overdrive |
any drivetrain arrangement in which an output speed exceeds input speed. For instance, most transmissions have overdrive ratio options, meaning that transmission tailshaft speed exceeds engine crankshaft speed. |
|
|
powerflow |
the mechanical flow path that conducts motive power through a system or component. For instance, the powerflow through a transmission in a specific gear ratio would be the sequential routing of the torque flow path through those gears that are actually engaged. |
|
|
rotation |
the act of rotating. Gears, shafts, wheels, and rotors are all subject to rotation. |
|
|
shift bar housing |
the manifold on top of a standard transmission that houses the shift rails, usually three, to which shift yokes are connected; the shift tower assembly mounts on top of the shift bar housing. Also known as shift rail housing. |
|
|
shift forks or yoke |
the fork-shaped components that connect shift rails with the sliding clutches in a standard transmission. Also known as shift yokes. |
|
|
slave valve |
any of a number of types of air or hydraulic actuators. |
|
|
transfer case |
an auxiliary transmission used to split drive torque from the main transmission between rear and forward drive axles; also known as a dropbox. |
|
|
brinelling |
minor indentations on the shoulder or in the valley of a bearing race, usually caused by improper installation. |
|
|
fretting |
a bearing or journal failure characteristic in which the contact surface picks up and then wears on the original manufacturing machining pattern. Also used to describe the rubbing wear that results when two clamped components expand and contract during heating and cooling at different rates. |
|
|
jumpout |
a condition caused when a sliding clutch is forced out of engagement. |
|
|
slipout |
occurs in transmission gearing, usually when pulling under full power or decelerating with load momentum driving forward movement. Worn sliding clutch teeth walk out of engagement with the gear. |
|
|
timing |
the procedure used to time interacting mechanical components. See timing marks. |
|
|
yoke sleeve kit |
a driveline yoke repair kit consisting of an interference fit sleeve that is installed over the seal race. |
|
|
adjusting ring |
used on Allison automatic transmissions to alter shift speeds. Changing the position of the adjusting rings determines the retaining force of the valve springs in the valve body. |
|
|
auxiliary filter |
any of a number of different types of add-on filters used in hydraulic circuits. Often installed on an Allison transmission after a catastrophic failure to remove particulate debris. |
|
|
breather |
a device that allows a circuit to be vented to atmosphere; used on reservoirs, axles, etc. |
|
|
engine stall point |
the rpm at which an engine is overloaded to the extent that it begins to either lug or stall; a factor in performance testing of automatic transmissions. |
|
|
shift bar |
sliding shaft to which shift yokes are clamped: When the bar is moved by the gearshift lever spade, the bar slides in bushing supports, moving the shift yoke to effect a gear change. Also known as a shift rail. |
|
|
stall test |
a test performed on vehicles with automatic transmissions to verify the performance of the engine and transmission, usually to determine if one is at fault. |
|
|
TranSynd |
a synthetic heavy-duty automatic transmission oil recommended by Allison, which states that it extends oil change intervals by 300 percent. |
|
|
valve ring adjusting tool |
a special tool required to adjust the valve rings in Allison automatic transmissions. |
|
|
What is key to a good transmission maintenance program? |
Scheduled lubrication services are key to a good transmission maintenance program. |
|
|
What kind of lubrication system do most standard transmissions depend on? What does it mean? How do you make sure it's effective? |
Most standard transmissions depend on splash lubrication, meaning that some of the rotating components contact, pick up, and circulate oil from the oil in the sump. Maintaining the correct oil level is critical for splash lubrication to be effective. |
|
|
What kind of lubricants can be used in a transmission? |
Only lubricants recommended by the transmission OEM should be used in a transmission. These could be gear, engine, or synthetic oils. |
|
|
When mineral oils are used, when should the first oil change be performed? |
When mineral oils are used, the first oil change should be performed shortly after the transmission enters service, often between 3,000 and 5,000 miles of operation in a linehaul application, or less in vocational service. This is not required with synthetics. |
|
|
In general linehaul application, how often should you schedule a transmission oil change? |
In general linehaul application, it is good practice to schedule a transmission oil change from 50,000 to 100,000 miles of service. Oil change intervals can be extended up to 500,000 miles when synthetics are used. |
|
|
What does a good preventive maintenance (PM) do? |
Good preventive maintenance (PM) lowers the incidence of breakdowns, minimizes downtime, and reduces the cost of repairs. |
|
|
What is leakage in transmission rear seals? |
Leakage in transmission rear seals is a relatively common problem in truck transmissions but one that is easily repaired. |
|
|
When diagnosing transmission complaints, it is important that you do what? |
When diagnosing transmission complaints, it is important that you confirm that the transmission is the actual cause of the problem before removing it for repair. |
|
|
What should you do when disassembling a transmission? |
When disassembling a transmission, each component should be carefully inspected for abnormal wear and damage. Components that are not reusable should be ordered after disassembly, not discovered during reassembly. |
|
|
When should a cause of failure be determined and why? |
Ensure that a cause of failure is determined before reassembly, or the failure is likely to recur within a short period. |
|
|
What causes bearing failures? |
Bearing failures occur because of dirt contamination and poor lubrication. More than 90 percent of bearing failures are caused by dirt. Cleanliness is critical when repairing and servicing standard transmissions. |
|
|
Detent |
The detent mechanism locates the transmission shift lever in the correct location in each range select position. It provides an element of gearshift feel to the driver when shifting from one gear to another.
The detent mechanism consists of a spring-loaded detent steel ball or poppet. The spring loads the steel ball into the recess in the shift bar. The detent ball holds the shift bar in position and prevents unwanted movement of the other bars. When drivers make a shift, they must overcome the spring pressure of the detent ball to move the shift bar. |
|
|
What is the formula for output torque? |
Input torque * Ratio |
|
|
What is the formula for output speed? |
Input speed / Ratio |
|
|
What do geartrains do? |
They transmit speed and torque unchanged; They decrease speed and increase torque; They increase speed and decrease torque. |
|
|
Which of the following gear ratios indicates the most amount of overdrive: high:low ratio or low:high ratio? |
low:high ratio |
|
|
Which type of gear is more likely to develop gear whine at higher speeds? |
a spur gear |
|
|
When an idler gear is placed between the driving and driven gear, the driven gear does what? |
rotates in the same direction as the driving gear |
|
|
When sliding gearshift mechanisms are used, which gears do they control? |
first and reverse gears in the main box |
|
|
Which type of transmission requires double-clutching between shifts? |
nonsynchronized |
|
|
What component is used to ensure that the main shaft and the main shaft gear about to be locked to it are rotating at the same speed? |
a synchronizer |
|
|
What is the most widely used standard transmission geartrain arrangement in heavy-duty trucks? |
twin countershaft |
|
|
What does a twin-countershaft standard transmission do? |
It divides input torque between two separate shafts; It allows the face width of each gear to be reduced; It allows the main shaft to float between the countershafts. |
|
|
In a range shift air control system, which component distributes inlet air pressure to both the low and high-range air hoses running to the range cylinder? |
a slave valve |
|
|
To provide for overdrive gearing in the high- and low-auxiliary transmission ranges, what components are added to the basic range-shift air control system? |
a splitter cylinder and a button-actuated shift lever valve |
|
|
What component retains a shift rail in position following a shift? |
a detent ball |
|
|
An auxiliary mechanical drive for truck accessories driven by the transmission is known as a(n): |
power take-off (PTO) unit |
|
|
Which is the function of a transfer case? |
It transfers torque from the transmission to a front drive axle; It transfers torque from the transmission to the rear drive axle(s); It may provide an additional gear reduction in the drivetrain. |
|
|
What component in a typical heavy-duty, twin-countershaft transmission could be described as floating? |
the main shaft |
|
|
What is step #1 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install lower reverse gear. |
|
|
What is step #2 in reassembling a transmission? |
Place lower countershaft in case and install bearings. |
|
|
What is step #3 in reassembling a transmission? |
Place upper countershaft in case - DO NOT install bearings. |
|
|
What is step #4 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install input shaft and main drivegear. Time main drive gear to lower countershaft. |
|
|
What is step #5 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install main shaft & countershaft. Leave reverse gear against 1st gear. |
|
|
What is step #6 in reassembling a transmission? |
Temporarily install rear mainshaft bearing or use timing tool. |
|
|
What is step #7 in reassembling a transmission? |
Time upper countershaft to drive gear. |
|
|
What is step #8 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install upper reverse idler. (Has to happen before you slide rear gear to gear.) |
|
|
What is step #9 in reassembling a transmission? |
Reverse mainshaft bearing/timing tool. |
|
|
What is step #10 in reassembling a transmission? |
Slide rear gear to gear. |
|
|
What is step #11 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install retainer washer and snap ring. (13 and 18 speed units. Star washer has internal taper. This must be torward rear or bearing will not fit correctly.) |
|
|
What is step #12 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install rear bearing and retainer. |
|
|
What is step #13 in reassembling a transmission? |
Install auxiliary driving gear and snap ring. |
|
|
What is step #14 in reassembling a transmission? |
Turn 10 times left and 10 times right. |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does R mean? |
Roadranger |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does T mean? |
Twin Countershaft |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does L mean? |
Low-Inertia |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does an O with no number mean? |
Overdrive w/ Direct Shift Pattern |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does C mean? |
Convertible |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does F mean? |
Forward Opening Shift Housing |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what do the first 2 numbers mean? |
This (x) 100 = Nominal Torque Capacity |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does the 4th and 5th numbers mean? |
Forward Speeds |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does the first letter after the numbers mean? |
Ratio set |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does 6 mean if it's the 3rd number? |
Multi-Mesh Gearing |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does 7 mean if it's the 3rd number? |
Helical Auxiliary Gearing and Multi-Mesh Front Section Gearing |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does 9 mean if it's the 3rd number? |
Improved Seal System |
|
|
What is the serial number? |
The Serial Number is the sequential identification number of the Transmission. |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does MT stand for? |
Multi-Torque |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does T stand for? |
Top Speed |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does AS stand for? |
Autoshift |
|
|
In transmission nomenclature, what does FRO stand for? |
Fuller RoadRanger Overdrive |
|
|
When troubleshooting an air system, where should you check pressure at? |
At the regulator. |
|
|
What does RTO stand for? |
Roadranger Twin countershaft Overdrive |
|
|
What does RTAO stand for? |
Roadranger Twin countershaft Automated Overdrive |
|
|
What does RTLO stand for? |
Roadranger Twin countershaft Low inertia Overdrive |
|
|
What OEM-approved lubricant would produce the longest service life in a standard transmission? |
synthetic E-500 gear lube |
|
|
After breaking in a new transmission filled with E-500 synthetic lube on a truck used in a linehaul application, when should the first oil change take place? |
after 500,000 miles of linehaul service |
|
|
Which of the following would indicate that transmission oil in a truck standard transmission is at the correct level? |
Oil is level with the filler hole. |
|
|
What are two possible causes of a rear seal area oil leak of a standard transmission? |
A damaged speedometer sleeve O-ring or gasket and a cracked bearing cover. |
|
|
How can a damaged transmission output yoke can be repaired? |
By installing a yoke sleeve kit or replacing the yoke. |
|
|
In order for an auxiliary section to be removed and overhauled, what needs to be done? |
Removal of the transmission from the chassis. |
|
|
In order to remove and repair a shift rail assembly, what must be done first? |
A shift rail assembly cannot be removed and repaired without first removing the transmission from the vehicle. |
|
|
What is the cause of driveline vibrations? |
Driveline vibrations are caused by loose yokes, excessive drive shaft radial runout, slip spline joint radial play, bent drive shaft tubing, and failing U-joints. |
|
|
What are two possible causes of the vehicle jumping out of gear when driven over a bumpy road surface? |
Worn detent notches in the shift rail and worn gear clutch teeth. |
|
|
What would most likely result in hard shifting? |
Lack of lubricant in remote shift linkage. |
|
|
What is one disadvantage of synthetic transmission lubes? |
They are not compatible with all other gear lubes. |
|
|
What can high gear lube level in a standard transmission cause? |
Aeration and result in lubrication failures. |
|
|
What is a transmission component that is splined to the main shaft in a standard, twin countershaft transmission? |
sliding clutch |
|
|
When towing a truck from the front what should be done? |
When towing a truck from the front, the axle shafts should be pulled. |
|
|
What does the 13 speed shifter knob have that prevents shifting to overdrive while in low range? |
A safety interlock. |
|
|
What can destroy the synchronizer? |
A shock load to the output shaft of the transmission. |
|
|
Where is the pilot port on the slave valve? |
On the front of the valve. |
|
|
On a Rockwell 13 speed, the range cylinder and the splitter cylinder are both located where? |
At the upper right corner on the rear section. |

