![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
COPD
|
limits airflow to and from the lungs, causing shortness of breath (dyspnea), caused by noxious particles or gas, which triggers an abnormal inflammatory response in the lung, no more then 2L of O2
|
|
|
pneumonia
|
an inflammatory condition of the lung—affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli.It is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria and less commonly other microorganisms
|
|
|
O2
|
Room Air (R.A.) is
21% oxygen*. “Supplemental” O 2 used w/ ↓ blood & tissue oxygen levels. Goal: Use lowest „fraction of inspired oxygen‟ (FIO 2 ) to obtain desired oxygen concentration, [O2] w/o harmful side effects. Turn down O 2 ASAP to prevent toxicity. Hint: O 2 improves [concentration](if circulated), but does NOT cure condition or disease |
|
|
Insulin
|
a peptide hormone, produced by beta cells of the pancreas, and is central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, skeletal muscles, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood. In the liver and skeletal muscles, glucose is stored as glycogen, and in fat cells (adipocytes) it is stored as triglycerides.
|
|
|
Asthma
|
a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Common symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath
|
|
|
anesthetic
|
is a drug that causes anesthesia—reversible loss of sensation. They contrast with analgesics (painkillers), which relieve pain without eliminating sensation. These drugs are generally administered to facilitate surgery.
|
|
|
Pre-Op Legalities
|
Nurse is a witness that the patent is in a sound state of mind and sign surgical release it is DR job to explain the procedure
|
|
|
Sedatives
|
a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement.
|
|
|
Hemophilia
|
is a group of hereditary genetic disorders that impair the body's ability to control blood clotting or coagulation, which is used to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is broken
|
|
|
steroid/ Prednisone side effects
|
have to wean, causes decreased wound healing, weight gain, immunity goes down, potassium level drops, insomnia , blood sugar and sodium levels go up, emotions go wild, altered metabolism, ulcers, increase in bp
|
|
|
Recovery Position
|
a lateral recumbent( on side) or three-quarters prone position of the body, in to which an unconscious but breathing casualty can be placed as part of first aid treatment.
|
|
|
O2 delivery systems
|
O2
per nasal cannula= 24-40% O2@1 -6 L/min (or ¼ or ½ L/min for babies) Simple face mask = 40-60% at 5-8L/min. Partial Rebreather = 60-75% at 6-11 L/min Non-Rebreather-80-95% O2@ 15 L/min. Intubation and using ventilator = 100%, but that‟s a very grim event |
|
|
Venturi mask
|
deliver a known oxygen concentration to patients on controlled oxygen therapy
|
|
|
non-rebreathers
|
device used in medical emergencies that require oxygen therapy. An NRB requires that the patient can breathe unassisted, but unlike low flow nasal cannula, the NRB allows for the delivery of higher concentrations of oxygen. mask covers both the nose and mouth of the patient and attaches with the use of an elastic cord around the patient's head
|
|
|
malignant hyperthermia
|
rare life-threatening condition that is usually triggered by exposure to certain drugs used for general anesthesia, specifically the volatile anesthetic agents and the neuromuscular blocking agent, succinylcholine. In susceptible individuals, these drugs can induce a drastic and uncontrolled increase in skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism, which overwhelms the body's capacity to supply oxygen, remove carbon dioxide, and regulate body temperature, eventually leading to circulatory collapse and death if not treated quickly
|
|
|
clopidogrel/Plavix
|
Used alone or together with aspirin to help prevent stroke, heart attack, and other heart problems. This medicine is a blood thinner.
|
|
|
Heparin
|
Prevents clots in the blood vessels before or after surgery or during certain medical procedures. Also treats certain blood, heart, and lung disorders and helps diagnose and treat certain bleeding disorders. This medicine is a blood thinner, antidote :protamine sulfate
|
|
|
depression
|
a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can have a negative effect on a person's thoughts, behavior, feelings, world view, and physical well-being.Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, worried, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, hurt, or restless. They may lose interest in activities that once were pleasurable, experience loss of appetite or overeating, have problems concentrating, remembering details, or making decisions, and may contemplate or attempt suicide. Insomnia, excessive sleeping, fatigue, loss of energy, or aches, pains, or digestive problems that are resistant to treatment may also be present.
|
|
|
metoprolol / Lopressor
|
Treats high blood pressure and angina (chest pain), and lowers the risk of repeated heart attacks. It is also used to treat heart failure. This medicine is a beta-blocker.
|
|
|
Peak Flow Meter
|
a small, hand-held device used to monitor a person's ability to breathe out air. It measures the airflow through the bronchi and thus the degree of obstruction in the airways
|
|
|
Anemia
|
is a decrease in number of red blood cells (RBCs) or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood.[1][2] However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin deficiency. Because hemoglobin (found inside RBCs) normally carries oxygen from the lungs to the capillaries, anemia leads to hypoxia (lack of oxygen) in organs. Since all human cells depend on oxygen for survival, varying degrees of anemia can have a wide range of clinical consequences
|
|
|
expectorant
|
Promoting or facilitating the secretion or expulsion of phlegm, mucus, or other matter from the respiratory tract
|
|
|
antitussive
|
drug used in an attempt to treat coughing and related conditions. For dry coughs, treatment with cough suppressants (antitussives) may be attempted to suppress the body's urge to cough.
|
|
|
Nitroglycerin
|
a vasodilator to treat heart conditions, such as angina and chronic heart failure.nitroglycerin is one of the oldest and most useful drugs for treating and preventing attacks of angina pectoris
|
|
|
Effective coughing
|
coughing and mucus comes out
|
|
|
Diabetes
|
is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced.[2] This high blood sugar produces the classical symptoms of polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia (increased thirst) and polyphagia (increased hunger).
types of diabetes mellitus (DM). Type 1 DM results from the body's failure to produce insulin, and currently requires the person to inject insulin or wear an insulin pump. This form was previously referred to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes". Type 2 DM results from insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to use insulin properly, sometimes combined with an absolute insulin deficiency. This form was previously referred to as non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes". |
|
|
finasteride /Proscar
|
Treats an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH) in men and causes hair growth in male pattern baldness. It may be used alone or in combination with other medicines such as an alpha-blocker (doxazosin, Cardura®) to treat BPH. This medicine is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor.
|
|
|
Diabetic Diet
|
'diet' most often recommended is high in dietary fiber, especially soluble fiber, but low in fat (especially saturated fat). Recommendations of the fraction of total calories to be obtained from carbohydrate intake range from 1/6 to 75% – a 2006 review found recommendations varying from 40 to 65%.
|
|
|
DASH Diet
|
The DASH diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy foods; includes meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans; and is limited in sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat, and added fats. In addition to its effect on blood pressure, it is designed to be a well-balanced approach to eating for the general public.
|
|
|
alpha-glucosidase inhibitors /Acarbose
|
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are oral anti-diabetic drugs used for diabetes mellitus type 2 that work by preventing the digestion of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are normally converted into simple sugars, which can be absorbed through the intestine
|
|
|
Biguanides / metformin/Glucophage
|
Biguanide can refer to a molecule, or to a class of drugs based upon this molecule. Biguanides can function as oral antihyperglycemic drugs used for diabetes mellitus or prediabetes treatment. They are also used as antimalarial drugs
|
|
|
Combo of glyburide/DiaBeta + metformin/Glucophage
|
more expensive, convenent,
|
|
|
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4) sitagliptin/Januvia
|
inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4, also DPP-4 inhibitors or gliptins, are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block DPP-4. They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2.
|
|
|
Sulfonylureas glipizide/Glucotrol /glyburide
|
oral antidiabetic drug in the biguanide class. It is the first-line drug of choice for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, in particular, in overweight and obese people and those with normal kidney function.[1][2][3] Its use in gestational diabetes has been limited by safety concerns. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, and has been investigated for other diseases where insulin resistance may be an important factor. Metformin works by suppressing glucose production by the liver. Used with diet and exercise to help control blood sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes
|
|
|
glargine/Lantus
|
a long-acting basal insulin analogue, given once daily to help control the blood sugar level of those with diabetes. It consists of microcrystals that slowly release insulin, giving a long duration of action of 18 to 26 hours, with a "peakless" profile
|
|
|
DVT prevention
|
walking, ted hose, Intermittent pneumatic compression, drugs such as warfine
|
|
|
promoting venous return
|
larger lumens of veins with valves, Skeleton muscle activity and Respiratory pump
Three factors that are important in promoting venous return are: 1. Intact system 2. Good pump - valves - size of vessels - PR 3. Breathing - respiratory pump |
|
|
laryngeal trauma
|
can occur following direct trauma to the neck region and may lead to life-threatening airway obstruction. For this reason, a patient suspected of having a fractured larynx should be treated in an emergent manner. NPO
|
|
|
thyroidectomy
|
operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. Surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland (such as hyperthyroidism) or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic (very enlarged thyroid), or symptomatic obstruction (causing difficulties in swallowing or breathing
|
|
|
parathyroidectomy
|
surgical removal of one or more parathyroid glands. This procedure is used to remove primary tumors or hyperplasia of the glands, especially when they produce excessive parathyroid hormone. As drugs such as Fosamax do not treat the underlying cause of parathyroid-related osteoporosis, surgery is the only cure. Bone loss is reversible.
The location of the glands is generally behind the thyroid, but there is a lot of variation. Usually, the location of an enlarged gland has been confirmed via a sestamibi scan or on ultrasound. |
|
|
Dehiscence
|
a surgical complication in which a wound ruptures along surgical suture. Risk factors are age, diabetes, obesity, poor knotting or grabbing of stitches, and trauma to the wound after surgery.[
|
|
|
evisceration
|
removal of the abdominal viscera. usually through a horizontal incision made across the abdominal area
|
|
|
glycosolated hemoglobin A1c
|
is a form of hemoglobin that is measured primarily to identify the average plasma glucose concentration over prolonged periods of time. It is formed in a non-enzymatic glycation pathway by hemoglobin's exposure to plasma glucose. Normal levels of glucose produce a normal amount of glycated hemoglobin. As the average amount of plasma glucose increases, the fraction of glycated hemoglobin increases in a predictable way. This serves as a marker for average blood glucose levels over the previous months prior to the measurement. n general, the reference range (that found in healthy persons), is about 20–40 mmol/mol 4%–5.9%
|
|
|
E. coli
|
a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls due to food contamination. The harmless strains are part of the normal flora of the gut
|
|
|
Heliobactor pylori
|
Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach, linked to the development of duodenal ulcers and stomach cancer
|
|
|
Streptococcus
|
streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat), certain Streptococcus species are responsible for many cases of pink eye[4], meningitis, bacterial pneumonia, endocarditis, erysipelas and necrotizing fasciitis (the 'flesh-eating' bacterial infections). However, many streptococcal species are nonpathogenic, and form part of the commensal human microbiome of the mouth, skin, intestine, and upper respiratory tract.
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
frequently found in the human respiratory tract and on the skin. Although S. aureus is not always pathogenic, it is a common cause of skin infections (e.g. boils), respiratory disease (e.g. sinusitis), and food poisoning. Disease-associated strains often promote infections by producing potent protein toxins, and expressing cell-surface proteins that bind and inactivate antibodies. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant forms of pathogenic S. aureus (e.g. MRSA) is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine.
|
|
|
intestinal obstruction
|
mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines, preventing the normal transit of the products of digestion. It can occur at any level distal to the duodenum of the small intestine and is a medical emergency. The condition is often treated conservatively over a period of 2–5 days with the patient's progress regularly monitored by an assigned physician. Surgical procedures are performed on occasion however in life-threatening cases, such as when the root cause is a fully lodged foreign object or malignant tumor.
|
|
|
diverticulitis
|
digestive disease particularly found in the large intestine. Diverticulitis develops from diverticulosis, which involves the formation of pouches (diverticula) on the outside of the colon. Diverticulitis results if one of these diverticula becomes inflamed. often present with the classic triad of left lower quadrant pain, fever, and leukocytosis (an elevation of the white cell count in blood tests). Patients may also complain of nausea or diarrhea; others may be constipated.
|
|
|
hiatal hernia
|
is the protrusion (or herniation) of the upper part of the stomach into the thorax through a tear or weakness in the diaphragm.
|
|
|
GERD
|
a chronic symptom of mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus.
GERD is usually caused by changes in the barrier between the stomach and the esophagus, including abnormal relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally holds the top of the stomach closed; impaired expulsion of gastric reflux from the esophagus, or a hiatal hernia. These changes may be permanent or temporary. Treatment is typically via lifestyle changes and medications such as proton pump inhibitors, H2receptor blockers or antacids with or without alginic acid |
|
|
Sartans
|
Angiotensin II receptor antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), AT1-receptor antagonists or sartans, are a group of pharmaceuticals which modulate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Their main uses are in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage due to diabetes) and congestive heart failure.
|
|
|
angiotensin receptor blockers
|
also known as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), AT1-receptor antagonists or sartans, are a group of pharmaceuticals which modulate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Their main uses are in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage due to diabetes) and congestive heart failure.
|
|
|
diuretics
|
substance that promotes the production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way
|
|
|
furosemide
|
a loop diuretic used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and edema. It is most commonly marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the brand name Lasix, and also under the brand name Frumex.[2] It has also been used to prevent Thoroughbred and Standardbred race horses from bleeding through the nose during races. depleats of K+
|
|
|
ACE-inhibitors
|
sed primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension) and weak heart muscle. (congestive heart failure).
This group of drugs causes dilation of blood vessels which results in lower blood pressure. In treating heart disease ACE inhibitors are usually used with other medications. A typical treatment plan will often include an ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, a long acting nitrate and a calcium channel blocker in combinations that are adjusted to the individual patient's needs. |
|
|
alpha1 blockers
|
( end of name is -osin ) onstitute a variety of drugs that block α1-adrenergic receptors in arteries, smooth muscles and central nervous system tissues The blockade or reduction of epinephrine and norepinephrine binding on alpha adrenoreceptors reduce arteriolar resistance and increase venous capacitance causes reflex tachycardia. Depending on plasma concentration they may cause postural hypotension. Alpha-1 blockers may decrease LDL and triglycerides and increase HDL,
These drugs may be used to treat: benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)[1] Lower urinary tract symptoms Post Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) and Transurethral needle ablation of the prostate (TUNA) procedures high blood pressure (hypertension). This is not typically the drug of choice unless the patient also has BPH. symptoms of non inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome, a type of prostatitis. |
|
|
beta blockers
|
9end in- olol) target the beta receptor. Beta receptors are found on cells of the heart muscles, smooth muscles, airways, arteries, kidneys, and other tissues that are part of the sympathetic nervous system and lead to stress responses, especially when they are stimulated by epinephrine (adrenaline). Beta blockers interfere with the binding to the receptor of epinephrine and other stress hormones, and weaken the effects of stress hormones.Glucagon, used in the treatment of overdose
|
|
|
calcium channel blockers
|
calcium channel blockers is to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly efficacious in treating elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate, to prevent cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris. Despite their effectiveness, CCB's often have a high mortality rate over extended periods of use, and have been known to have multiple side effects.Potential major risks however were mainly found to be associated with short-acting CCB's.[4]
|
|
|
antihypertensive effects & precautions
|
lass of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure,dizziness and orthostatic hypotension, Persistent cough is a common side effect.ACE inhibitors,potassium depletion, dangerous heart rate abnormalities
|
|
|
peripheral arterial insufficiency PAD
|
obstruction of large arteries not within the coronary, aortic arch articulature, or brain. PAD can result from atherosclerosis, inflammatory processes leading to stenosis, an embolism, or thrombus formation. It causes either acute or chronic ischemia (lack of blood supply). Often PAD is a term used to refer to atherosclerotic blockages found in the lower extremity.
PaD also includes a subset of diseases classified as microvascular diseases resulting from episodal narrowing of the arteries |
|
|
peripheral venous insufficiency
PVD |
obstruction of large arteries not within the coronary, aortic arch vasculature, or brain. PVD can result from atherosclerosis, inflammatory processes leading to stenosis, an embolism, or thrombus formation. It causes either acute or chronic ischemia (lack of blood supply). Often PVD is a term used to refer to atherosclerotic blockages found in the lower extremity.[1]
PVD also includes a subset of diseases classified as microvascular diseases resulting from episodal narrowing of the arteries |
|
|
cardiac dysrhythmias
|
is any of a large and heterogeneous group of conditions in which there is abnormal electrical activity in the heart. The heartbeat may be too fast or too slow, and may be regular or irregular. A heart beat that is too fast is called tachycardia and a heart beat that is too slow is called bradycardia
|
|
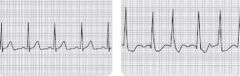
what is this rhythm
|
normal sinus rhythm
|
|
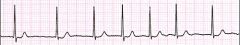
what is this rhythm
|
atrial fibrillation
|
|
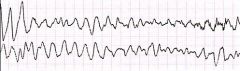
what is this rhythm
|
Ventricular fibrillation
|
|
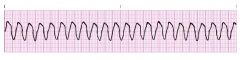
what is this rhythm
|
Ventricular tachycardia
|
|
|
creatinine
|
s a break-down product of creatine phosphate in muscle, and is usually produced at a fairly constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
reference ranges for serum creatinine are 0.5 to 1.0 mg/dl (about 45-90 μmol/l) for women and 0.7 to 1.2 mg/dl (60-110 μmol/L) for men. While a baseline serum creatinine of 2.0 mg/dl (150 μmol/l) may indicate normal kidney function in a male body builder, a serum creatinine of 1.2 mg/dl (110 μmol/l) can indicate significant renal disease in an elderly female |
|
|
alkaline phosphatase
|
a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation. normal range is 20 to 140 IU/L.[12] High ALP levels can show that the bile ducts are obstructed.[13] Levels are significantly higher in children and pregnant women. Also, elevated ALP indicates that there could be active bone formation occurring as ALP is a byproduct of osteoblast activity (such as the case in Paget's disease of bone). Levels are also elevated in people with untreated Celiac Disease.
|
|
|
BUN
|
he liver produces urea in the urea cycle as a waste product of the digestion of protein. Normal human adult blood should contain between 7 to 21 mg of urea nitrogen per 100 ml
|
|
|
potassium
|
3.5 - 5.0 mEq/L
|
|
|
asystole
|
olloquially known as flatline, is a state of no cardiac electrical activity, hence no contractions of the myocardium and no cardiac output or blood flow. Asystole is one of the conditions that may be used for a medical practitioner to certify clinical or legal death.
|
|
|
CPR
|
niversal compression to ventilation ratio of 30:2 is recommended.[5]:8 With children, if at least 2 rescuers are present a ratio of 15:2 is preferred.[5]:8 In newborns a rate of 3:1 is recommended unless a cardiac cause is known in which case a 15:2 ratio is reasonable.[:S647 If an advanced airway such as an endotracheal tube or laryngeal mask airway is in place delivery of respirations should occur without pauses in compressions at a rate of 8–10 per minute
|
|
|
defibrillation
|
ommon treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Defibrillation consists of delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the affected heart heart muscle, terminates the dysrhythmia
|
|
|
cardioversion
|
an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a normal rhythm, using electricity or drugs. Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart, at a specific moment in the cardiac cycle. Pharmacologic cardioversion, also called chemical cardioversion, uses antiarrhythmia medication instead of an electrical shock
|
|
|
Morphine/Narcotics Precautions
|
respiratory depression have narcan for over dose
|
|
|
Foley catheter use & precautions
|
use sterile techneque stay in no more then 30 days, dayily cleaning in area, drink water and canberry juice
|
|
|
3-way bladder irrigation (TURP)
|
have a third channel, which is used to infuse sterile saline or another irrigating solution. These are used primarily after surgery on the bladder or prostate, to wash away blood and blood clots.
|
|
|
pyelonephritis
|
s an ascending urinary tract infection that has reached the pyelum or pelvis of the kidney. It is a form of nephritis that is also referred to as pyelitis. Severe cases of pyelonephritis can lead to pyonephrosis (pus accumulation around the kidney), urosepsis (a systemic inflammatory response of the body to infection), kidney failure and even death.
Pyelonephritis presents with fever, accelerated heart rate, painful urination, abdominal pain radiating to the back, nausea, and tenderness at the costovertebral angle on the affected side. Pyelonephritis that has progressed to urosepsis may be accompanied by signs of septic shock, including rapid breathing, decreased blood pressure, violent shivering, and occasionally delirium. Pyelonephritis requires antibiotic therapy, |
|
|
nephrostomy
|
artificial opening created between the kidney and the skin which allows for the urinary diversion directly from the upper part of the urinary system (renal pelvis).
An urostomy is a related procedure performed more distally along the urinary system to provide urinary diversion |
|
|
multiple sclerosis
|
is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms.[1] Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women
|
|
|
spinal cord injury
|
any injury to the spinal cord that is caused by trauma instead of disease. Depending on where the spinal cord and nerve roots are damaged, the symptoms can vary widely, from pain to paralysis to incontinence.] Spinal cord injuries are described at various levels of "incomplete", which can vary from having no effect on the patient to a "complete" injury which means a total loss of function
|
|
|
orthopedic complications
|
Compartment syndrome, fat embolism syndrome, and venous thromboembolism
|
|
|
Compartment syndrome
|
a limb- and life-threatening condition which occurs after an injury, when there is not a sufficient amount of blood to supply the muscles and nerves with oxygen and nutrients because of the raised pressure within the compartment such as the arm, leg or any enclosed space within the body and leads to nerve damage because of the lack of blood supply. The severity of compartment syndrome can be divided into acute, subacute, and chronic compartment syndrome.
|
|
|
Cast care
|
Wet: only touch w/ palms, not any points!
Once dry, keep dry! Don‟t ever stick ANYTHING inside cast! (May be applied with gauze itching loop!) if compound, espitchy when healing & espnecessary to PREVENTwatch for infection. Petal cast‟s rough edges. |
|
|
compression fractures
|
usually occurs in the vertebrae, for example when the front portion of a vertebra in the spine collapses due to osteoporosis (a medical condition which causes bones to become brittle and susceptible to fracture, with or without trauma).
|
|
|
phantom limb sensation
|
pain after a amputation bc the nerve is still present
|
|
|
radioisotope injection
|
give 2 hrs prior to injection check for shellfish, iodine, or dye allergies
|
|
|
bone marrow aspirations
|
Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells
|
|
|
Parkinson’s disease
|
a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system. The motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease result from the death of dopamine-generating cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain; the cause of this cell death is unknown. Early in the course of the disease, the most obvious symptoms are movement-related; these include shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement and difficulty with walking and gait. Later, cognitive and behavioural problems may arise, with dementia commonly occurring in the advanced stages of the disease. Other symptoms include sensory, sleep and emotional problems. PD is more common in the elderly, with most cases occurring after the age of 50.
|
|
|
Alzheimer’s
|
most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death Early symptoms are often mistakenly thought to be 'age-related' concerns, or manifestations of stress.[5] In the early stages, the most common symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. When AD is suspected, the diagnosis is usually confirmed with tests that evaluate behaviour and thinking abilities, often followed by a brain scan if available.[6] As the disease advances, symptoms can include confusion, irritability and aggression, mood swings, trouble with language, and long-term memory loss. As the sufferer declines they often withdraw from family and society plaques on the brain and brain deterateds
|
|
|
CVA
|
is the rapid loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia (lack of blood flow) caused by blockage (thrombosis, arterial embolism), or a hemorrhage.[1] As a result, the affected area of the brain cannot function, which might result in an inability to move one or more limbs on one side of the body, inability to understand or formulate speech, or an inability to see one side of the visual field.[2]
A stroke is a medical emergency and can cause permanent neurological damage and death. Risk factors for stroke include old age, high blood pressure, previous stroke |
|
|
Brain tumors effects and care
|
Brain tumors include all tumors inside the cranium or in the central spinal canal. They are created by an abnormal and uncontrolled cell division, usually in the brain itself, but also in lymphatic tissue, in blood vessels, in the cranial nerves, in the brain envelopes (meninges), skull, pituitary gland, or pineal gland. Within the brain itself, the involved cells may be neurons or glial cells Treatment, :Surgery, Radiation therapy,Chemotherapy
|
|
|
osteomyelitis
|
infection of the bone or bone marrow. It can be usefully subclassified on the basis of the causative organism (pyogenic bacteria or mycobacteria), the route, duration and anatomic location of the infection
|
|
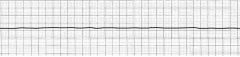
what is this rhythm
|
asystole
|
|
|
peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
|
most common ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm. As many as 70–90% of such ulcers are associated with Helicobacter pylori, a helical-shaped bacterium that lives in the acidic environment of the stomach; however, only 40% of those cases go to a doctor. Ulcers can also be caused or worsened by drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and other NSAIDs.
|
|
|
pancreatitis
|
inflammation of the pancreas which requires immediate medical attention and hospitalization during an attack that has multiple causes and symptoms. It occurs when pancreatic enzymes (especially trypsin) that digest food are activated in the pancreas instead of the small intestine. It may be acute—beginning suddenly and lasting a few days, or chronic—occurring over many years
|
|
|
Alpha-2 blocker
|
and are antagonists to the α2 adrenergic receptor.uses in treating depression; the tetracyclic antidepressants mianserin and mirtazapine, significantly increase adrenergic, dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmitters, and induce insulin secretion and decreases blood sugar levels
|
|
|
Digoxin
|
used in the treatment of various heart conditions, namely atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and sometimes heart failure that cannot be controlled by other medication, narrow therapeutic index, adverse effects (include: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea as gastrointestinal motility increases. Other common effects are blurred vision, visual disturbances (yellow-green halos and problems with color perception), confusion, drowsiness, dizziness, insomnia, nightmares, agitation, and depression, as well as a higher acute sense of sensual activities, antidote is antidigoxin Toxicity can also be treated with higher than normal doses of potassium. Digoxin is not removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis with enough effectiveness to treat toxicity.
|
|
|
atrial fibrillation
|
Rapid and irregular heart rates may be perceived as palpitations, exercise intolerance, and occasionally produce angina (if the rate is faster and puts the heart under strain) and congestive symptoms of shortness of breath or edema. Sometimes the arrhythmia will be identified only with the onset of a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA).
|
|
|
Ventricular fibrillation
|
a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients.[1] While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arterie
|
|
|
Ventricular tachycardia
|
s a tachycardia, or fast heart rhythm, that originates in one of the ventricles of the heart. The ventricles are the main pumping chambers of the heart. This is a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia because it may lead to ventricular fibrillation, asystole, and sudden death.
|
|
|
septicemia
|
presence of pathogenic organisms in the bloodstream, leading to sepsis.The term has not been sharply defined. It has been inconsistently used in the past by medical professionals, for example as a synonym of bacteremia, causing some confusion.
Sepsis is caused by the immune system's response to a serious infection, most commonly bacteria, but also fungi, viruses, and parasites in the blood, urinary tract, lungs, skin, or other tissues. Sepsis can be thought of as falling within a continuum from infection to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.[5] Common symptoms of sepsis include those related to a specific infection, but usually accompanied by high fevers, hot, flushed skin, elevated heart rate, hyperventilation, altered mental status, swelling, and low blood pressure. In the very young and elderly, or in people with weakened immune systems, the pattern of symptoms may be atypical, with hypothermia and without an easily localizable infection |
|
|
Nursing Process
|
assess,
Dx - NURSING dx ( not medical dx ) P - goal: realistic (& pt specific), measurable & time limited (or it‟s wrong). Goal is the cure - state or opposite of the problem. I - ( measurements/assessments are NOT interventions!!!) Doing something physically or verbally that brings client closer to goal. Include the ordered medical care in your care plan. (not “if appropriate”, IS it appropriate? NOT contradictory?) E - Did the client meet the goal or not? If not, why not & what are you going to do about it now? |
|
|
Atelectasis
|
alveolar collapse
|

