![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
255 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is gravidity? Define parity and abortuses. What is the TPAL system and what terms does it consist?
|
Gravidity is the number of pregancies including current, pregnancy. This includes miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies, and stillbirths). Parity is the number of pregnancies that have ended at gestational age greater than 20 weeks. Abortuses are number of pregnancies that have ended at gestational age less than 20 weeks (includes ectopic pregnancies, induced abortions and spontaneous abortions). The TPAL system consists of term deliveries, preterm deliveries, number of abortuses, and number of live births.
|
|
|
Describe the order and main components of a obstetrics and gynecological history?
|
Basic information: a. age-important b/c some conditions are most important at certain ages (e.g. if under 17 increased risk of miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies and still births) B. gravidity C. parity D. Abortuses. Last Menstrual Period (LMP) a.helps calculate the gestational age and the EDD Chief complaint Past gynecological history a. menstrual history (nml menarche=9-16) b. character of menstrual cycles:interval history 21-35 days c. STDs hx-also STD partner hx -also STD partner hx d. obstetric history -date and gestational age of each pregnancy at termination and outcome -if induced abortion then gestational age andmethod -all complications e. PMH f. PSH g. allergies h. medications i. ROS -focused on common diseases e.g. sx of preclampsia-headache or visual disturbances or epigastric pain or facial swelling or in an elderly person sx of cardiac dz
|
|
|
Describe the order and main components of a obstetrics and gynecological history?
|
Basic information: a. age-important b/c some conditions are most important at certain ages (e.g. if under 17 increased risk of miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies and still births) B. gravidity C. parity D. Abortuses. Last Menstrual Period (LMP) a.helps calculate the gestational age and the EDD Chief complaint Past gynecological history a. menstrual history (nml menarche=9-16) b. character of menstrual cycles:interval history 21-35 days c. STDs hx-also STD partner hx -also STD partner hx d. obstetric history -date and gestational age of each pregnancy at termination and outcome -if induced abortion then gestational age andmethod -all complications e. PMH f. PSH g. allergies h. medications i. ROS -focused on common diseases e.g. sx of preclampsia-headache or visual disturbances or epigastric pain or facial swelling or in an elderly person sx of cardiac dz
|
|
|
How is EGA (estimated gestational age) calculated? EDD (expected due date)?
|
Estimated Gestational Age-is calcuated from the LMP or by U/S. EDD-is calculated by Naegele's rule. Add 7 days to the first day of the last normal menstrual flow and substract 3 months.
|
|
|
What does typical laboratory assessment for ob entail? 9 things
|
cbc+ blood type rh+ antibody screen+ hepatitis b surface antigen+ rubella titer+ syphillis nontreponemal test+ hiv test+ urine culture or u/a+pap smear+endocerivical assays for gonnorea/chlamydia-also 1st trimester screening for trisomies papp-a+bhcg+nt+-screening for gestational diabetes 26-28 weeks
|
|
|
What does typical lab test for gyn entail 3 things? and common imaging methods as well?
|
a. treatened abortion: quantative hcg and/or progesterone levelsb. menorrhagia due to uterine fibroids: cbc/endometrial biopsy/ap smearc. a woman 55 or older with adnexal mass: ca-125 and cea tumor markers for epithelial ovarian tumor. What are the common imaging modalities used in ob/gyn? specificially what is a sonohysterography and a hysterosalpingogram (hsg),a. ultrasoundb. ct-b/c radaiation not used on pregnant woman unless absolutely necessaryc. mrid. ivp-assess concentrating bility of the kidneys, useful in detecting hydronephrosis, ureteral stonre or uteteral obstructione. sonohysterography-is a special u/s in whicha small amount saline is injected into the endometrial cavity to better define the intrauterine cavity. Can be helpful in identifying endometrial polys or submucousa myomata.f. hysterosalpinogram (hsg)- small amount of radiopaque dye is introduced through a transcervical cannula and radiographs are taken.
|
|
|
What is Genuine stress incontenince? What is the treatment for Genuine stress incontinence?
|
Incontinence through the urethra due to suddent increases in intra-abdominal pressure, in the absence of bladder muscle spasm. Initially, Kengal exercises and timed voiding, If this is unsucessful options include urethropexy which places urethra back in intraabdominal position (surgical fixation of the proximal urethra above the pelvic diaghragm, suburethral sling, or transobturator) or transvaginal fixation.
|
|
|
What is urge incontinence?What is the mechanism/history/diagnostic test/treatment?
|
Loss of urine due to an uninhibited and sudden bladder detrusor muscle contraction. The history will be i ahve to go to the bathroom and can't make it there in time. The diagnostic test is cystometric exam will show uninhibited contractions. The treatment is anticholinergic medication to relax the detrusor muscle
|
|
|
What is overflow incontinence?What is the mechanism/history/diagnostic test/treatment?
|
Overflow incontinence is loss of urine associated with an overdistended, hypotonic bladder in the absence of detrusor contractions. Often associated with diabetes, mellitus, spinal cord injuries or low motor neuropathies. history can show loss of urine with valsalva, dribbling. diagnostic test-postvoid residual shows large amounts of urine. treatment=self catheretization.
|
|
|
What is fistula caused incontinence?What is the mechanism/history/diagnostic test/treatment?
|
Fistula between bladder and ureter and vagina can cause incontence. history-will show a constant leakage. diagnostic test includes dye into bladder will show vaginal discolaration. treatment is surgical repair of fistual tract.
|
|
|
What are the common imaging modalities used in ob/gyn? specificially what is a sonohysterography and a hysterosalpingogram (hsg)?
|
a. ultrasoundb. ct-b/c radaiation not used on pregnant woman unless absolutely necessary c. mrid. ivp-assess concentrating bility of the kidneys, useful in detecting hydronephrosis, ureteral stonre or uteteral obstructione. sonohysterography-is a special u/s in whicha small amount saline is injected into the endometrial cavity to better define the intrauterine cavity. Can be helpful in identifying endometrial polys or submucousa myomata.f. hysterosalpinogram (hsg)- small amount of radiopaque dye is introduced through a transcervical cannula and radiographs are taken.
|
|
|
Explain the pathophysiology of menopause and how it brings about its characteristic sx?
|
1. Natural atresia of almost all oocytes in the ovaries lead to increase in
FSH and LH and decrease in estrogen. 2. hypoestrogenemia, responsible for hot flushes 3. low estrogen also has affect on vagina by decreasing the epithelial thickness, leading to atrophy and dryness. 4. eventually low estrogen can precipitate bone loss leading to osteoperosis. 5. insomnia 6. mood changes 7. People who have both ovaries removed begin to experience perimenopause symptoms |
|
|
What is the treatment for menopause?
|
1. hot flushes-irregular impredictable episodes of increased skin temperature and sweating lasting about 3 to 4 minutes caused by vasomotor changes.
-selective estrogen receptor modulator -the addition of estrogen and progesterone is important in preventing endometrial cancer -clonidine may help if patient can't take estrogen. 2. bone loss -weight bearing exercises -calcium -vitamin d supplementation -estrogen replacement |
|
|
With estrogen levels what would the level of FSH and LH be?
|
Still increased because the pituitary only responds to inhibin.
|
|
|
Patients who use estrogen therapy are at an increased risk for?
|
cardiovascular disease and breast cancer
|
|
|
How is perimenopausal/menopause confirmed?
|
elevated fsh and lh levels used to confirm perimenopause
|
|
|
What is the treatment for necrotizing fasciitis?
|
1. IV saline, monitoring u/o and bp
2. broad spectum antibiotics 3. If bp still not appropriate try pressors such as dopamine or dobutamine 4. surgical debridement of infected area 5. when stabilized treat underling cause. |
|
|
Define the three stages of labor?
|
First stage: onset of labor to complete dilation of cerix. Second stage: complete cervical dilation to delivery. Third stage delivery of baby to placental delivery.
|
|
|
What is active phase and latent phase?
|
Active phase is the portion of labor where dilation occurs more rapidly usually when the cervix is greater than 4-cm dilated. The latent phase is the initial part where the cervix mainly effaces (thins) rather than dilates (usually cervical dilation is les than 4 cm).
|
|
|
Define accerations and decelerations?
|
15 bpm above baseline lasting for 15 seconds or 15 bpm below baseline for at least 15 seconds.
|
|
|
What are the three types of decelerations and what do they mean?
|
1. early decelerations are mirror images of uterine contractions, caused by fetal head compressions.
2. variable decelerations are abrupt in decline and abrupt in resolution and are caused by cord compression. 3. late decelerations are gradual in shape and are offset from the uterine contractions, caused by uteroplacental insufficiency (hypoxia) |
|
|
What are the 3 P's and how are they evaluated and treated?
|
1. The three P's stand for powers, passenger, and pelvis.
2. Powers refers to the uterine contraction strength and/or frequency. It can be evaluated by an internal uterine pressure catheter and is judged as greater than 200 montevideo above baseline. As a treatment oxytocin can be given to enhance uterine contractions. 2. cephalopelvic distortion can occur where the pelvis is too small or the baby is too large. 3. the passenger can be monitored via fetal monitoring for accelerations and decelerations. |
|
|
What are early declerations and what are there significantce?
|
Early declerations are commonly seen in active labor between 4 and 7 cms and are typically due to head compressions in which the vagal nerve is activated. They are not associated with hypoxia.
|
|
|
What are late decelerations and what are there significance?
|
Late decelerations occur as a result of several things most commonl hypotension from epidural or uterine hyperactivity from giving oxytocin. placental abruption can cause acute late decelerations.
|
|
|
What are variable decelerations and what are there significance?
|
Variable declerations can be caused by unmbilical cord compression.
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for endometrial cancer? 9 things
|
1. early menarche
2. late menopause 3. obesity 4. chronic anovulation 5. estrogen-secreting ovarian tumors 6. ingestion of unopposed estrogen 7. hypertension 8. diabetes mellitus 9. personal or family history of breast cancer. |
|
|
How is endometrial cancer staged? What does it entail?
|
1. Total abdominal hysteroctomy, bilateral salpingo-ophorectomy
2. Omenectomy 3. Lymph node sampling 4. Peritoneal washings |
|
|
How is endometrial thickness assessed? What is an abnormal thickness?
|
endometrial stripe (transvaginal sonographic assessment of thickness. greater than 5 mm is abnormal thickness.
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of postmenopausal bleeding?
|
atrophic endometrium
|
|
|
What is the treatment for endometrial cancer?
|
1.hysterectomy is the primary treatment of endometrial cancer.
2. postoperative therapy can be used for metastatic disease. |
|
|
What's the first thing you should do in a woman with postmenopausal bleeding?
|
endometrial biopsy (90-95% effective)
|
|
|
What types of cancer could an atypical glandular cells on a pap smear represent? How should it be worked up
|
It can represent endocervical or endometrial cancer. Therefore a colposcopic examination, curretage of the endocervix, and endometrial sampling is indicated.
|
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for antepartum bleeding (bleeding after 20 weeks gestation)?
|
1. placenta previa (painless bleeding with no contractions)
2 placenta abruption (assx w/ uternine contractions and excess uterine tone) |
|
|
What are risk factors for placenta previa? 5 things
|
1. grand multiparity-more than five previous pregnancies
2. prior cesarean delivery 3. prior uterine curettage 4. previous placenta previa 5. multiple gestation |
|
|
What is placenta previa? What are the subtypes?
|
1. placenta previa is defined as the placenta overlying the internal os of the cervix.
2. complete and partial placenta previa. 3. low-lying placenta-edge of the placenta is within 2 to 3 cm of the internal os. |
|
|
What imaging method should be used initially in the case of antepartum hemoorhage? Why not perform a speculum exam first?
|
1. ultrasound to locate placental location
2. it might cause more bleeding. |
|
|
What is placenta previa a risk factor for?
|
placenta accreta (invasion of the placenta into the uterus)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for placenta previa?
|
1. expectant management
2. treat patient with c/s |
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of abruptio placentae? what is one major complication
|
1. painful antepartum bleeding
2. uterine pain or hypertonus complication=coagulopathy |
|
|
What are the risk factors for abruptio placentae? 9 things.
|
1. HTN
2. cocaine use 3. short umbilical cord 4. trauma 5. uteroplacental insufficiency 6. submucous leiomyomata 7. sudden uterine decompression (hydramios) 8. cigarette smoking 9. preterm premature rupture of membranes. |
|
|
what is a concealed abruption? couvelaire uterus?
|
1. when bleeding occurs completely behind the placenta and no external bleeding is noted.
2. bleeding into th emyometrium of the uterus giving a discolored appearance to the uterine surface. |
|
|
How is placento abruptio diagnosed?
|
1. with great difficulty!
2. ultrasound-not particularly significant 3. serial hemoglobin and fundal heights-helfpful 4. Kleihaure-betke test-tests for fetal erythrocytes in maternal blood. |
|
|
Management of placento abruptio?
|
1. Delivery!-often by c/s
2. if premature expectant management if mom and baby are stable. 3. if abruption with fetal death-vaginal delivery. iv fluids/blood products should be given to keep hematocrit above 25%. |
|
|
What is the diagnostic procedure of choice when a cervical lesion is seen?
|
A cervical biopsy not a cervical pap smear.
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for cervical cancer?
|
1. early age of coitus
2. sexually transmitted diseases 3. early childbearing 4. low socioeconomic status 5. human papillomavirus 6. hiv infection 7. cigarette smoking 8. multiple sexual partners |
|
|
What is the management for ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance)
|
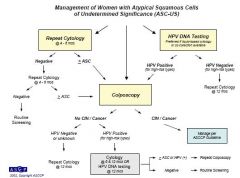
1. a patient with ASC-US should undergo HPV DNA testing or repeat cytology at 6 or 12 months.
2. Women who screen positive for HPV DNA are referred for a colposcopic examination. |
|
|
What is the management of LSIL (low grade intraepithelia l lesions)
|
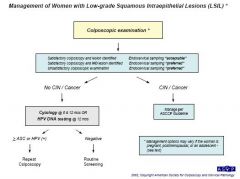
1.1. colposcopic examination
2. if CIN seen manage per ASCCP 3. if no CIN do HPV or cytology at 6 or 12 months |
|
|
Describe the management of Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia?
(preinvasive lesions of the cervix with abnormal cellular maturation, nuclear enlargement and atypica) |
1. Two methods are excisional and ablative.
2. ablative methods-destroy the affected cervical tissue. 2a. include cryotherapy, laser ablation, electrofulguration, and cold coagulation. 3. Excisional therapy-remove the affected tissue and provide aspecimen for pathologic evaluation 3a. cold-,knife conization, loop excision procedures, laser conization. 3b. if margins not clean repeat conization 3c. if high grade epithelila or cin found hysterectomy if person doesn't want children |
|
|
What is the treatment for cervical carcinoma.
|
1. Stage Ia-may be treated with conization of the cervix or simple extrafascial hysterectomy.
2. Stage Ia2-treat with radical hysterectomy with lymph node dissection or radiation therapy. 3. Stage Ib1-either radical hysterectomy with lymph node dissection or radiation therapy. 4. stage 2a-radical hysterectomy and lymph node disection or radiation therapy with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. 5. Stage 2b or greater should be treated with external beam and brachytherapy radiation and concurrent cisplatin chemotherapy. |
|
|
Define bracytherapy. radiation teletherapy.
|
brachytherapy-radioactive implants placed near the tumor bed.
radiation teltherapy-external beam radiation where the target is at some distance from the radiaiton source |
|
|
What are the current guidelines for cervical cytology?
|
1. Cervical cytology is begun 3 years after onset of sexual activity or by age 21 years
2. Annual pap until 30...then if negative it can be every 2 to 3 years. 3. if total hysterectomy for benign reasons no need for pap 4. if total hysterectomy for cin then vaginal cuff is still needed. |
|
|
What is amenorrhea?
|
No menses for 6 months
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of Sheehan syndrome and Asherman syndrome? What do these two syndromes have in common? How are they distinguished clinically?
|
1. Sheehan syndrome-anterior pituitary hemorrhagic necrosis caused by hypertrophy of the prolactin-secreting cells in conjunction with a hypotensive episode, usually in the setting of postpartum hemorrhage. The bleeding in the anterior pituitary induces pressure necrosis.
2. Asherman syndrome (intrauterine adhesions) -scar tissue that forms in the endometrium, leading to amenorrhea caused by unresponsive of the endometrial tissue. 3. Clinically this can be distinguished by the lack of anterior trophic hormones in sheehans and the lack of responsiveness to hormone therapy in intrauterine adhesions (asherman syndrome) |
|
|
What is a differential for amenorrhea in reporductive years?
|
1. Pregancy (most commone)
2. sheehans 3. ashermans 4. hypothyroidism 5. hyperprolactimena 6.pcos |
|
|
How is asherman (intrauterine adhesions) definitively diagnosed?
|
hysterosalpingogram
|
|
|
What are the respective treatments for sheehan and asherman syndromes?
|
1. Sheehan'sreplacement of hormones such as thyroxine, cotisol, and mineralcorticoid, and estrogen and progestin therapy.
2. Asherman's syndrome-intrauterine adhesions are treated by hysteroscopic resecxtion of the scar tissue. |
|
|
What are the steps to take with fetal bradycardia?
|
1. Confirm fetal heart rate (vs maternal heart rate) by internal fetal scalp electrode or U/S
2. Vaginal examination to assess for cord prolapse 3. Initial steps should be direcxted at improving maternal oxygenation and delivery of cardiac output to the uterus a. placement of the patient on her side to move the uterus from the great vessels thus increasing blood return to the heart b. i.v. fluid bolus if patient is volume depleted. c. administration of O2 d. stop oxytocin (sometimes giving a beta-agonist such as terbutaline helps in relaxing uterine musculature) |
|
|
What is the treatment for fetal bradycardia in the case of umbilical cord prolapse?
|
1.digital elevation of prolapse part
2. immediate c/s |
|
|
Artificial rupture of membranes?
|
Maneuver used to cause a tear in the fetal chorioamniotic membranes.
|
|
|
The use of misoprostol can cause prolonged fetal bradycardia through what mechanism?
|
uterine hyperstimulation (greater than five uterine contractions in a 10-minute window.
|
|
|
How does uterine hyperstimulation lead to fetal bradycardia? Epidural?
|
1. Oxytocin or misoprostol may hyperstimulate the uterus and cause frequent contractions. This then results in frequent vasoconstriction of the uterine vessels which decreases the amount of blood arriving to the placenta and fetus over time.
2. epidural can cause hypotension in the mother which may then lead to fetal bradycardia by also decreasing the amount of blood profusing the fetus per given time. |
|
|
What are the major causes of hyperprolactemia? 8 things
|
1. Drugs (tranqilizers, TCA's, antihypertensives, OCP, narcotics.
2. Hypothyroidism 3. hypothalamic causes 4. hyperplasia of the lactotrophs 5. Acromegaly 6. empty sella syndrome 7. Renal disease 8. Chest surgery |
|
|
What is the mechanism by which hypothyroidism causes hyperprolactinemia?
|
1. With primary hypothyroidism, both TRH and TSH are elevated. TRH acts as a prolactin-releasing hormone leading to elevated prolactin levels.
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach for someone who has galactorrhea?
|
1. Care H/P focusing on medications taken...discontinue meds that can cause galactorrhea
2. TRH and prolactin levels should be tested. 3.MRI- those with high prolacgtin levels or with neurological sx should receive an MRI. 4.MRI should also be given for anyone with galactorrhea and oligomenorrhea even if prolactin levels are normal. 5. monitoring of serial prolactin levels can be done if woman has normal menses and galactorrhea. |
|
|
What is the common treatment for galactorrhea?
|
1. if galactorrhea is secondary to hypothyroidism...give thyroxine.
2. if patient has hyperprolactinmena and low estrogen...give exogenous estrogen 3. bromocriptine and other dopamine agonists are useful if patient desires fertility. 4. if galactorrhea 2/2 prolactinoma...transphenoidal microsurgery 5. patients with hyperprolactinemia, with or without mi roadenoma with adequate estrogen levels should be treated with periodic progestin withdrawal. |
|
|
How does hyperprolactinemia cause menstrual irregularities?
|
prolactin inhibits GNRH by increasing release of dopamine from the arcuate nucleus
|
|
|
What should the first test for any woman with galactorrhea and amenorrhea be?
|
pregnancy test
|
|
|
What is the differential for pruritis in pregnancy?
|
1. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
2. Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPP) 3. Herpes gestationis |
|
|
Define cholestatis in pregnancy? What are some common complications? Treatment? How can they be distinguished from PUPPP and Herpes gestationis
|
1. intrahepatic cholestasis of unknown etiology in pregnancy, usually occurs in 3rd trimester, whereby the patient complains of pruiritis w/ or w/o jaundice and NO SKIN RASH.
2. associated with an increased risk of prematurity, fetal distress, and fetal loss esp when associated with jaundice. 3. 1st line tx is antihistamines and corstarch baths. other tx include bile salt binders (e.g. choletyramine) 4. both PUPP and herpes gestationins are assx with rashes. |
|
|
What's PUPP? How is Tx? Are there any fetal complications assx w/ PUPP?
|
1. common skin condition of unknown etiology characterized by intense pruritis and erythematious papules on abdomen and extremities.
2. treatment =topical corticosteroids and antihistamines 3. no adverse effect on fetal or maternal outcome. |
|
|
What's Herpes gestationis? How is Tx? Are there any fetal complications assx w/ it?
|
1. Rare skin condition assx with pregnancy. Charaterized by intense pruritis itching and vesicles on the abdomen and extremities.
2. Tx=oral corticosteroids 3. Yes. increased fetal growth retardation adn stillbirth |
|
|
How would you dx cholestatis in pregnancy, PUPP, and herpes gestationis?
|
1. cholestasis in pregnancy=you would see increased bile salts and pruritis with no rash.
2. PUPP- you would see erythemetous papules on the abdomen and extremeitis, intesne pruritis and no IgG and complement in immunoflourescence. 3. In herpes gestinationis-you would see intense itching and vesicles on the abdomen and extremities. IgG autoantibodies against the basement membrane could be seen with immunofloresence. Bullous lesions would thus be present. |
|
|
How is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease dx? How can it be differentiated from other diseases with similar presentations?
|
1. PID is generally dx clinically based on the common presentation symptoms: abdominal tenderness, cervical motion tenderness, adnexal tenderness, vaginal discharge, fever.
2. confirmatory tests include a test for gonorrhea or chlamydia culture, or an U/S suggesting a tubo-ovarian abscess. 3. if diagnosis is in doubt laparoscopy would show purulent discharge exuding from the fimbria of the tubes. |
|
|
What are somethings on the differential for PID?
|
1.salpingitis
2. pyelonephritis, 3. appendicitis 4. cholecystitis, 5. diverticulitis 6. pancreatisi, 7. ovarian torsion 8. gastroenteritis |
|
|
What are the common complications for PID?1
|
1. tubo-ovarian abscess-collection of purulent material around the distal tube and ovary. often treatable with abx instead of drainage.
2. infertility and ecopic pregnancy-this is directly related to the times of PID |
|
|
How is PID treated?
|
1. If pt has low-grade fever, tolerance of oral meds, and non peritoneal signs then they can be treated outpatient with IM ceftriaxone and oral doxycycline bid for 10 to 14 days.
2. If pt is pregnant, at the extremes of age, or can't tolerate p.o. meds then patient is candidate for inpatient therapy. This inlcludes, i.v. cefotan and oral IV doxycycline. 3. IT IS VERY IMPORTANT TO REEVALUATE PATIENT IN 48 HOURS FOR IMPROVEMENT. if pt does not improve consider laparoscopy to assess disease. |
|
|
What are Fitz-Hugh and Curtis syndrome?
|
salpingitis with perihepatic adhesions that can manifest itself as RUQ pain.
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiologic mechanism by whch pregnancy leads to an increase risk for DVTs?
|
1. Pregnancy causes venous stasis due to the mechanical effect of the uterus on the vena cava.
2. high estrogen level induces a hypercoaguable state due to the increase in clotting factors, particularly fibrinogen. |
|
|
What is the clinical approach for dyspnea in pregnancy?
|
1. Evaluation of pt's respiratory condition; including respiratory effort and rate; use of acessory muscles, cyanosis.
2. Pulse ox and ABGs should be ordered while information is gathered during the H and P. 2a. if PO2 greater than 85 and O2sat greater than 95% then careful examination and observation 2b. if PO2 and O2 sat not acceptable. PROVIDE O2. consider CXR. 3. CXR is clear but on exam extensive wheezing then likely asthma 4. CXR show infiltrate/cardiomegaly and on physical exam rales consider pneuoniae, CHF. 5. CXR clear consider PE with spiral CT or MR angiogram. NOT VQ. |
|
|
How is pulmonary embolism diagnosed in pregnancy?
|
Spiral CT or MR angiogram, but physical presentation can be sufficient.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for pulmonary embolism in pregnancy?
|
1. Full IV heparin anticoagulation therapy for 5-7 days.
2. Later on switched to SQ heparin therapy. 3. after 3 months full heparinization or prophylactic heparinization can be used. 4. This should be used until 6 weeks after pregnancy |
|
|
What are the typical ABG's during pregnancy?
|
1. Pregnancy induces a respiratory alkylosis (incrased PH) with parital metabolic compensation (decreased bicarbonate)
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach for herpes simplex virus during pregnancy?
|
1. Physician uses best clinical judgement ot assess for the presence of HSV in the genital tract during the timer of labor.
2. meticulous inspectionof the external genitalia, vagina, crevix 3. ask about prodromal signs of infetion. 4. If no lesions or prodromal signs then recommend vaginal delivery 5. if there are prodromal signs then you need c/s. 6. some practitioners recommend the use of acyclovir after first outbreak in pregnancy to reduce risk of out breaks. |
|
|
T or F acyclovir decreases the frequency of recurrences of HSV?
|
False. acyclovir decrhttp://www.flashcardexchange.com/mycards/add/947259#tab2eases the duration of shedding and the duration of the lesions but NOT the frequency of recurrences.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for symptomatic uterine fibroids (leiomyomata)
|
1. The initial treatment is medical, such as NSAIDS or progesterone therapy (e.g depoprovera).
2. Gondotropin-releasing hormone agonists lead to a decrease in uterine fibroid size...but uterine returns to original size once tx is stopped. Hence this is used primarily for before sx. 3. Hysterectomy-proven treatment when future pregnancy is undesired. 4. Myomectomy-is considered the choice for woman who desire pregnancy 5. Uterine artery embolization involves infuzing embolization particles into uterine artery that predominately effect fibroids. This seems to be succesful on the short term but long-term effects are not known. |
|
|
What is the most common reason for hysterectomy in the United States?
|
symptomatic uterine fibroids.
|
|
|
How does a uterine fibroid typically manifest itself? What is a common complication of fibroids?
|
1. menorrhagia
2 physical exam will show a firm nontender mass that moves contiguosly with the cervix. 3. Leiomyosarcoma-malignant with rapid growth. Also a submucosa leiomyomata can prolapse through the cervix, leading to labor like uterine contraction pains |
|
|
Where are 1. submucosa fibroids 2. subserosal fibroids and 3. intramural fibroids located?
|
1. primarily on the endometrial side of the uterus and impinge on the uterine cavity.
2. primarily on the outside of the serosal surfaces. PE may reveal a knobby sensation 3. Primarily in the uterine muscle. |
|
|
What is the spectrum of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy. Define each one?
|
1. Chronic hypertension-blood pressure of 140/90 Hg before pregnancy or at less than 20 weeks gestations.
2. Gestational hypertension: hypertension without proteinuria at greater than 20 weeks gestation. 3. Preeclampsia: hypertension with proteinuria, can be mild or severe. 4. Severe preeclampsia-systolic BP at or higher than 160 mmHg, diastolic BP of 110 mm Hg or higher or 24-hour urine protein level of more than 5 mg. |
|
|
How does severe preeclampsia generally manifest itself? Neurologic, Renal, Pulmonary, Fetal, Hepatic?
|
1. Neurologic-headache, vision changes, seizures, hyperreflexia, blindness
2. Rena- decreased GFR, proteinuria, oliguria 3. Pulmnonary-pulmonary edema 4. Fetal-Intrauterine growth restriction, oligohydraminos 5. hepatic -increased liver enzymes, subscapular hematoma, hepatic rupture. |
|
|
What is the common treatment for preclampsia?
|
1. If it is severe preclampsia then magnesium sulfate should be given and the baby should be delivered.
2. If it is mild preeclampsia and the baby is not term expectant management. 3. Eclampsia is one of the most feared complications of preclampsia so during labor magnesium sulfate should be given. MgSo4 should be given until 24 hours afer deliver. 5. for severe htn - hydralazine or another htn should be given during pregnancy |
|
|
What is the first sign of magnesium toxicity?
|
Loss of deep tendon reflexes.
|
|
|
What are the six basic etiologies of infertility? What are the history and laboratory tests for the six factors?
|
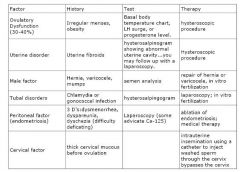
|
|
|
What are the three D's in endometriosis?
|
Dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and dyschezia.
|
|
|
What is infertility?
|
Inability to conceive after 1 year of unprotected intecourse.
|
|
|
What is the typical history/PE of someone with fibrocystic cystic disease? What is the common treatment?
|
1. classic clinical picture includes cyclic, painful engorged breast, more pronounced just before menstruation.
2. Treatment=decreasing caffeine intake, a tight fitting bra, oral contraceptives, or oral progestin therapy. As a last result danazol (a weak antiestrogen and androgenic compound) or a mastectomy is considered. |
|
|
What are the clinical presentation of some of the common causes of abdominal pain in pregnancy (acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, ovarian torsion, placental abruption, and ectopic pregnancy)
|

|
|
|
What is the common treatment for ovarian torsion?
|
1. Treatment is surgical with ovarian conservation if possible.
2. If untwisting the adnexa result in reperfusion an ovarian cystectomy may be perfomred. 3. However if perfusion cannot be restored oopherectomy is indicated. |
|
|
What are the differential diagnosis/clinical presentation for the common ovulatory causes of infertility?
|
1. PCOS
-most common -clinical dx w/ h/o obesity, anovulation, hirsutism, and possibly glucose intolerance 2. hypothalmic disturbances -hypothyroidism and hyperprolactinemia can cause disturbances in GnRH leading to prolactinemia -check TSH and prolactin levels 3. Premature ovarian failure -checking FSH for elevation would suggest POF |
|
|
What is the clinical approach to ectopic pregnancy?
|
One of the key strategies for ruling out ectopic pregnancy is to prove that an intrauterine pregnancy exists. Transvaginal sonography is more sensitive than transabdominal sonography.
1. A woman with an ectopic pregnancy typically complains of abdominal pain, amenorrhea of 4 to 6 weeks' duration, and irregular spotting. 2. The patient may or may not adnexal mass. 3. The ultrasound is primarily used to assess of an extrauterine for the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP). 4. hcG levels if greater than the threshhold of 1500 mIU/ml. 5. Laparoscopy is usually performed if hCG is elevated. 6. If the hCG is less than threshold and patient does not have severe abdominal pain, hypotension. measure hcg level in 48 hours to look for an appropriate rise in hcG Also try progesterone if greater than 25ng/ml than likely normal. If less than 5 ng/ml...than it is likely an abnormal pregnancy. |
|
|
Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy?
|
1. Salpingitis, particularly with Chlamydia trachomatis.
2. Tubal adhesive disease 3. Infertility 4. Progesterone-secreting IUD 5. Tubal surgery 6. Prior ectopic pregnancy 7. Ovulation induction 8. Congenital abnormalities of ectopic pregnancy. |
|
|
What are the main treatment for ectopic pregnancy?
|
1. Medical treatment with methotrexate can be performed if less than 4 cms.
2. Salpingectomy (removal of tube)-If patient does not desire to have another pregnancy. 3. Salpingostomy- surgical treatment for woman who wants to preserve her fertility. |
|
|
Diffuse diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy?
|
1. acute salpingitis
2. abortion 3. ruptured corpus luteum 4. acute appendicitis 5. dysfunctional uterine bleeding 6. adnexal torsion 7. degenerating liomyomata 8. endometriosis |
|
|
What is the classic presentation for ectopic pregnancy?
|
abdominal pain, amenorrhea of 4 to 6 weeks duration, and iregular vaginal spotting.
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic approach for to anemia in pregnancy?
|
1.If patient has no history/risk factors for beta thalassemia. It is appropriate to do a therapeutic trial of Fe.
2. If Hg does not improve. Fe studeis should be performed. 3. If Fe is normal than Hb analysis should be performed to rule out an hemoglobinopathy. 4. If a hemoglobinopathy is found parent should be adviced on the risk of having a baby with trait or disease. |
|
|
What is the physiology of pregnancy that contributes to the risk of anemia?
|
In prengancy, woman have decreased iron stores, and increased demands for Fe (due to fetus' need and expanded maternal blood volume)
|
|
|
What is the cut-off for anemia in pregnancy?
|
Hg less than 10.5 g/dl
|
|
|
What is on the differential for anemia during pregnancy?
|
1. Microcytic anemia's-iron deficiency versus thallasemias (these can be differentiated by electrophoresis)
2. macrocytic anemias-vitamin b12 or folate deficienct (folate deficiency more common because vitamin b12 stores take a long time to deplete) 3. normocytic anemias-acquired (e.g HELP) versus congenital (e.g. G6pd deficiency) |
|
|
Define preterm labor? How is it diagnosed in a nulliparous woman?
|
1. Preterm labor is a cervical change associated with uterine contractions prior to 37 completed weeks and after 20 weeks gestation.
2. In a nulliparous patient uterine contractions and a single cervical examination revealing 2-cm dilation and 80% effacement is sufficient to diagnose preterm labor. |
|
|
How is preterm diagnosed?
|
1. clinical presentation-uterine contractions and abdominal tightening.
2. PE-shows cervical change over time preferably by the same examiner. 3. Fetal-fribronecting assay-prior to cervical exam if positive may indicate risk of preterm birth. 4. transvaginal cervical length ultrasound measurement-a shortened cervix with lower uterine changes seen in preterm labor. |
|
|
What is fetal fibronectin assay?
|
A basement membran protein that helps bind placental membranes to the decidua of the uterus. A vaginal swab is used to detect its presence. If negative 99% chance of NOT delivering within 1 week.
|
|
|
What is the work-up for preterm labor
|
1. History to assess for risk factors.
2. PE with speculum exam to assess for ruptured membranes 3. Serial digital cervical examinations 4. CBC 5. Urine drug screen (especially for cocaine metabolites) 6. Urinalysis, urine culture, and sensitivity 7. Cervical tests for gonorrhea (possible chlamydia) 8. vaginal culture for group B streptococcus. 9. Ultrasound exam for fetal weight and presentation. |
|
|
What is the typical treatment/management of preterm labor?
|
1.Once preterm labor is dx one should consider tocolysis if gestation is less than 34 to 35 weeks.
2. seroids are administered if the gestational age is less than 34 weeks. 3. antenatal steroids can be given between24 and 34 weeks if no sign of infection 4. weekly injection of 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate from 20 -36 week gestation has been shown to prevent preterm labor in those with high risk. |
|
|
Describe the main drugs used for tocolysis there moa/se/ci's?
|
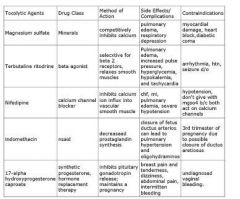
|
|
|
What is tocolysis?
|
pharmacological agents used to delay delivery once preterm labor is diagnosed. Commonly used agents are indomethacin, nifedipine, terbutaline, and ritrodine.
|
|
|
1. Risk factors for preterm labor?
|
1. Preterm premature rupture of membranes
2. multiple gestations 3. previous preterm labor or birth 4. hydraminos 5. cocaine abuse 6 AA race 7. abdominal trauma 8. abdominal trauma 9.abdominal sx in pregnancy |
|
|
What are the common presentation for urinary tract infection?
|
1. for a simple cystitis-dysuria, urgency, and frequency
2. pyelonephritis-presents as flank pain and fever. 3. urethritis can have a similar presentation as simple cystitis |
|
|
What is the typical work-up/treatment for a UTI?
|
1. Generally based on history of urgency, dysuria and frequency a UA and/or urine culture is performed.
2. If positive then treat for UTI 3. then negative to a urethral swab for chlamydia for urethritis 4. If negative also consider a candidial yeast infection. 5. if all is negative could be urethral syndrome. |
|
|
What is urethral syndrome?
|
urgency and dysuria caused by urethral inflammation of unknown cause. cultures are negative.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose cystitis?
|
1. based on bacteria in the urine (greater than 100,000 cfu/ml)
2. if symptomatic as few as 1000 cfu may be significant. |
|
|
Name some common tx for UTI?
|
1. trimethorpim/sulfa, nitrufurantoin, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and cephalasporins.
|
|
|
Should asymptomatic bacturia be treated in pregnant women?
|
yes! because there is a 25% chance of developing symptoms anyway.
|
|
|
What does the diagnosis of urethritis hinge on?
|
Having bacteria in the culture
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of pylonephritis? u/a will show.
|
1. dysuria, urgency, frequency costovertebral tenderness, fevers chills and nausea
2.pyuria and bacturia with greater than 100,000 cfu. |
|
|
What is the treatment for pylonephritis in pregnancy?
|
1. hospitlization
2. i.v. abx such as cephalosporins (e.g. cefotan or ceftriaxone) or combination of ampicillin and gentamicin. 3. treat until fever/flank pain has improved and then switch to oral abx and suppressive therapy for the remainder of pregnancy. 4. if not clinical improvement after 48 to 72 hours then suspect a urinary tract obstruction or a perinephric abscess. |
|
|
What are the epidemiological data for pylenephritis? What are some its complications?
|
1. 2-5% of pregnant women with pyelonephritis will develop ARDS (caused by endotoxins)
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of septic shock in pregnancy?
|
pylonephritis
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which pregnancy predisposes to DVTs?
|
1. increased levels of clotting factors
2. increased venous stasis from uterus pushing down on vena cava |
|
|
How is DVTs dx in pregnancy?
|
1. Doppler U/S at 5 to 7.5 MHZ should be used in anyone suspected of DVTs.
|
|
|
What is the common treatment for DVTs in pregnancy?
|
1. heparin NOT COUMADIN
2. heparin via i.v. for 5 to 7 days. 3. then switch to heparing subqtaneous to maintain PTT at 1.5 to 2.5 times. 4. after 3 months of full heparinization you may switch to prophylactic heparinization. 5. this can be utilized for the remainder of the pregnancy and 6 weeks postpartum |
|
|
what are complications of long-term heparin use?
|
osteoporosis and thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach for palpable breast masses? when should a cystic, fluid-filled, lesion be biopsied?
|
1. Women should receive annual mammograms beginning at age 50.
2. Any palpable mass, regardless of mammographic findings require histological diagnosis. 3. The type of biopsy will vary depending on the risk of cancer. For example a likely fibroadenoma in 25 year old might only require a fine needle biopsy. While any mass in a 74 year old might require an excisional biopsy. 5. If a fine needle aspiration of a cystic lesion reveals a clear or serosanguineous nipple discharge then you can monitor if the fluid is bloody then you should do a histological analysis of fluid. |
|
|
What is skin dimpling?
|
retraction of the skin, which is suspicious for an underlying malignancy due to the cancer being fixed to the skin
|
|
|
What should the health maintenance screening of someone between the ages of 40-64 entail?
|
1. cancer screening=pap smear, age 50 stool for occult blood, barium enema with flexible sigmoidospy q 5 years, or colonoscopy q 10 y, annual mammograpy
2. IMmunizations-tetanus q 10y, age 50: annual influenza vaccine, age 60 varizella zoster vaccine 3. other diseases:cholesterol screening q 5 years beginnning at age 45. -fasting blood sugar level q 3 year at age 45 -TSH q 5yr at age 50 4. Most common causes of mortality=cancer, cardiovascular disease |
|
|
What are the common types of tumors? What are their characteristics? What is stroma tumor ovarii?
|

|
|
|
What is the clinical approach of adnexal masses (i.e. when do you operate when do you observe?)
|

1. during reproduction years functional cysts such as corpus luteal cysts make evaluation difficult (while in extremes of age very few functional cysts)
2. generally if greater than 8 cm operate, if smaller than 5 observe (b/c likely a cyst) and between 5-9 sonographic features help determine if it is a neoplasm |
|
|
What is pseduomyoma peritoni?
|
a common complication of rupture of mucinous tumors. it can lead to repeated bouts of bowel obstruction
|
|
|
Ascites is a common sign of ....?
|
ovarian malignancy
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach for a dermoid cyst (benign cystic teratoma)?
|
1. perform an ovarian cystectomy
2. if benign then do nothing else 3. if maliganant perform salpingo-oophorectomy or oophorectomy |
|
|
Define surgical site infection. evisceration
|
Infection related to the operative procedure that occurs at or near the surgical incision within 30 days of an operation.
2. evisceration is disruption of ALL layers of the incision with omentum or bowel protruding through the incision |
|
|
Define the 3 types of surgical infections (i.e. superficial separations, dehicience, and evisceration)? What are their clinical presentations/treatments?
|
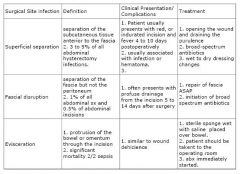
|
|
|
What are risk factors for surgical site infections?
|
diabetes,obesity, cancer, vertical incision,corticosteroid use, exposure to radiaiton, infection, coughing
|
|
|
1. What diseases are associated with hemoperitoneum? How do you differentiate them?
|
1. Ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of hemoperitoneum. Corpus luteum pregnancy is also assx w/ hemoperitoneum.
2. Both ectopic pregnancy have abdominal pain and perhaps bleeding/spotting. Only corpus luteum would hav passage of tissue with "frond like" consistency |
|
|
What is hemoperitoneum?
|
a collection of blood in the peritoneal cavity. The blood initially clots and then lyses, so that there may be a combinatin of clots and hemorrhagic fluid that will not clot.
|
|
|
1. Define corpus luteum rupture.
2. What is its clinical presentation 3. How is it diagnosed? 4. How is it treated? |
1. bleeding occurring in a corpus luteum, which may cause hemoperitoneum or cyst enlargement.
2. Patients with hemoperitoneum usually present with the sudden onset of severe lower abdominal pain. some complain of unilateral cramping. rebound tenderness. 3. clinical presentation, u/s will show free intraperitoneal fluid and perhaps fluid around ovary. LAPAROSCOPY IS THE GOLD STANDARD 4. first step in the treatment is to secure hemostasis via laparotomy -once bleeding stops no tx required -if bleeding continues cystectomy -if before 10 weeks must supplement with progesterone -if after 10 weeks placenta is sufficient |
|
|
What is the first sign of hypovolemia?
|
decreased urine output.
|
|
|
What are the common causes of secondary amenorrhea?
|
1. hypothalmic etiologies (hypothyroidism or hyperprolactinemia)
2. pituitary conditions (sheehan syndrome) 3. ovarian causes-premature ovarian failure 4. intauterine adhesions (asherman syndrome) 5. cervical stenosis after conization (this is associated with cramping every month) |
|
|
what is secondary amenorrhea?
|
absence of menses for a period of 6 months or more in a woman who has had spontaneous menses.
|
|
|
How do you diangose intrauterine adhesive disease?
|
1. hysterosalpinogram-radiologic study where radiopaque dye is injected into the endometrial cavity via a transcervical catheter.
2. sonohysterography iand vaginal u/s are also useful |
|
|
What is the treatment for intrauterine adhesions?
|
1.operative hysteroscopy-procedure of direct visualization of the endometrial cavity with an endoscope, a light source and a distension media
2. postoperative management-may include insertion of IUD or a pediatric Foley to prevent reformation of foley. 3. administration of conjugated estrogens and progesterone should be considered 4. uterine cavity should be reevaluated before conception is attempted again |
|
|
What are some common causes of intrauterine adhesions?
|
1. D & C
2. radiation 3. infections 4. anything that causes endometrial trauma |
|
|
in any case of secondary amenorrhea what should you first rule out?
|
pregnancy
|
|
|
What are mammographic findings that are suggestive of breast cancer?
|
1. mass
2. speculated and invasive borders 3, architectural distortion 4. asymmetric increased tissue density when compared with other studeis or corresponding area in other breast |
|
|
T or F a palpable mass in the face of a normal mamogram requires a biopsy
|
T= there is up to a 10% false negative rate so a biopsy is still required.
|
|
|
Define primary amennorhea
|
No menarche until the age of 16 years.
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach to primary amenoorhea?
|
1. When a woman presents with primary amenorrhea, the differential dx can be narrowed based on whether or not normal breast tissue is present.
2. if no normal breasts are present think hypoestrogenic state such as gonadal dysgenesis (turner syndrome) 3. If pt has normal breasts tink mullerian agenesis or androgen insensitivity. |
|
|
What are the clinical features of mullerian agenesis and androgen insensitivity? What are the key differences?
|

|
|
|
What are the key differences between mullerian agenesis and androgen insensitivity?
|
1.androgen insensistivity has an elevated testosterone while mullerian agenesis has a normal level.
2. androgen insensitivity has scant public/axillary hair while mullerian agenesis has a normal amount. |
|
|
What is androgen insensitivity? Mullerian agenesis?
|
1. AI-an androgen receptor defect in which 46, XY individuals are phenotypically female with normal breast development
2. MA-congenital absence of development of the uterus cervix, and fallopian tubes in a 46, XX female leading to primary amenorhhea |
|
|
What is Kallman syndrome?
|
An example of hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism, or hypothalmic hypogonadism disorder caused by a deficiency in GNRH secreted by the hypothalmus.
2. Patiens with Kallman syndrome also have a deficiency to smell. Females present with delayed puberty and lack of breast development. |
|
|
What should be the first tes performed on any woman that has primary or secondary amenorrhea?
|
a pregnancy test
|
|
|
How do you differentiate mullerian agenesis from androgen insensitivity?
|
karyotype and testosterone level
1. mullerian agenesis often has renal problems is XX, and has normal testosterone. 2. androgen insensitivity, has no renal problems is XY and has eleveated testoterone |
|
|
What is septic abortion?
|
Any type of abortion associated with a uterine infection.
|
|
|
What is septic shock?
|
The septic portion refers to the presence of an infection (usually bacteria) and the shock describes a process whereby the patient's cells, organs, and/or tissues are not being sufficiently supplied with nutrients and/or oxygen.
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of septic abortion?
|
1. uterine and or bleeding in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
2. Fever and generally have a leukocyte count greater than 10,500 cells/ul 3.There is usually lower abdominal tenderness, cervical motion tenderness, and a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. |
|
|
What is the treatment for septic abortion?
|
1. maintain the blood pressure
-i.v. isotonic fluids, if not efective dopamine or vasopressor 2. monitor the blood pressure, oxygenation, and urine output 3. start antibiotic therapy-broad spectrum 4. perform uterine curettage. -wait 4 hours after abx |
|
|
What should the initial dx tests be for septic abortion?
|
1. cbc with differential
2. blood chemistries including electrolytes 3. cervical discharge should be sent for gram stain and culture for sensitivity. 4. bp O2 sat heart rate and urine output should be monitored |
|
|
what is the mechanism for septic abortion?
|
ascending infection...vagina to cervix to uterus (endometrium to myometrium) to peritoneum
|
|
|
Define postpartum hemorrhage (pph)
|
Classically defined as greater than 500 ml blood loss at a vaginal delivery and greater than 1000 ml during a cesarean delivery. Practically speaking, it means significant bleeding that may result in hemodynamic instability if unabated.
|
|
|
What is methylergonovine maleate? What is its main contradindication
|
An ergot alkyloid agent that induces myometrial contraction as a treatment of uterine atony, contraindicated in hypertension
|
|
|
What is prostaglandin F2 what is it main contraindications?
|
A prostaglandin compound that causes smooth muscle contraction, contraindicated in asthmatic patients.
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach to postpartum hemorrhage ?
|
1. The most common cause of PPH is uterine atony. Thus one should feel for the uterus. If it is boggy thing uterine atony.
2. If uterus if firm...look for genital lacerations] 3. women who have retained placenta will have uterine cramping and spotting and may have a fever. 4. Other causes =placenta acretta. |
|
|
What is a common cause of late PPH?
|
1. subinvolution of the placenta site commonly occurs between 10 and 14 days
2. In this disorder the eschar over the placental bed usually falls off and the lack of myometrial contraction at that site leads to bleeding. |
|
|
What is the treatment approach for postpartum hemorrhage if caused by uterine atony?
|
0. First assess ABCs! assess bp and hr. Put in two peripheral bore ivs.
Asess for uterine firmness if boggy then... 1. The initial management should be uterine massage with bimanual compression. 2. concurrently iv oxytocin should be given. 3. If this is ineffective other pharmacological agents such as rectal misoprostol methergine or prostaglanding F2-alpha should be given . 4.If medical therapy is not effective then two bore iv's should be placed, the blood bank should be notifid. 5. Surgical therapy may include exploratory laparotomy, with interruption of the blood vessels to the uterus such as uterine artery ligation or internal iliac artery ligation |
|
|
What is the treatment approach for genital lacerations?
|
1. should be suspected for a firm contracted uterus.
2. carefully inspect vaginal side walls and cervix. 3. try to ascertain the location of the bleeding if it is supracervical this could be a coagulopathy, retianed POC, or atypical uterine atony. 3. repair of the complete extent of laceration is important |
|
|
What is the treatment for subinvolution of the placenta site?
|
Classically oral ergot alkyloid and careful follow-up.
|
|
|
What are the two types of primary amenorrhea? How are they diagnosed and what are some examples?
|

|
|
|
Define delayed puberty
|
Lack of secondary characteristics by age 14 years
|
|
|
How can you distinguish a central cause of low estrogen from a ovarian cause in primary amenorrhea?
|
look at fsh
|
|
|
What is the most common bacteria cause of postpartum mastitis?
|
staph aureus
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of postpartum mastitis?
|
1. fever, induration and redness /tenderness of breast. Sometmies malaise, fever, and tachycardia
2. usually occurs 2-4 weeks after delivery |
|
|
What is the typical treatment for postpartum mastitis
|
generally doxycycline for staph aureus
|
|
|
When does one become suspicious of a breast abcess? what i the treatment?
|
1. persistent fever lasting more than 48 hours
2. fluctuant mass 3. drainage-sometime u/s can help distinguish 4. antibiotics |
|
|
What is a galactocele?
|
A noninfected collection of milk due to a blocked mammary duct leading to a palpable mass and symptoms of breast pressure and pain. Treatment=can resolve by itself or aspiration
|
|
|
What's the best treatment for cracked nipples?
|
air-drying and avoidance of a harsh soap
|
|
|
What is a thyroid storm?
|
Extreme thyrotoxicosis leading to central nervous system dysfunction (coma or delirium) and autonomic instability (hyperthermia, hypertension, or hypotension)
2. hallmark of thyroid storm is autonomic instability. symptoms suggestive of storm include altered mental status, hyperthermia, hypertension and diarrhea. |
|
|
Why is a thyroid storm dangerous?
|
1. The mortality is high
2. maternal hyperthyroidism may result in either fetal hyper or hypothyroidism. |
|
|
What is the clinical management of thyroid storm?
|
1. Patients best monitored in the ICU.
2. beta-bloackers are used to control the symptoms of tachycardia. 3. acetominophen or cooling blankets for hyperthermia. 4. corticosteroids may also be used to prevent the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. |
|
|
What is the clinical treatment of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy?
|
1. medical or surgical usually used.
2. medically-PTU or methamaziole treatment is commonly used 3. radioactive iodine is contraindicacted in pregnancy 4. surgically thyroidectomy-if patient is noncompliante or can't tolerate medical therapy. 5. baby can receive thyroxine if it is found that it has hypothyroidism. studiens shows this leads to improved outcomes |
|
|
What is the effect of pregnancy on thyroid hormone?
|
Pregnancy due to the estrogen hormone causes INCREASES IN THE THYROID BINDING GLOBULIN AND TOTAL T4. It does not change the free T4 or TSH. Hence ingeneral pregnancy is a euthyroid state.
|
|
|
What is the most common of hyperthyroidism postpartum?
|
lymphocytic thyroiditis NOT graves disease.
|
|
|
What is the tetracycline effect?
|
tetracycline compounds, such as doxycycline, taken by pregnant women can lead to staining of the fetal teeth.
|
|
|
Discuss the 1. clinical presentation. 2. diagnosis. 3. treatment. 4complications of chlamydia infections during pregnancy.
|
1. clinical presentation-can cause mucopurulent cervicitis, urethritis, and late postpartum endmetritis. However usually chlamydial infections are asymptomatic.
2. diagnosis-DNA test for chlamydia is fast effective and sensitive. gonorrhea culture. 3. treatment-oral erythromycin or amoxicillin for 7 days. azithromycin as a one-time dose. 4. no increased risk of prom, or preterm labor. during delivery transmission can lead to chlamydial conjunctivitis and pneumonia. |
|
|
What is the 1.clinical presentation 2. diagnosis. 3. treatment 4.complication of gonorrheal infection during pregnancy?
|
1. cp-cervicitis,disseminated gonococcal disease is more common in pregnant women presenting as pustular skin lesions, arthralgias, and septic arthritis.
2. dx-gonococcal cultures 3. tx-ceftiaxone intramuscularly in addition for antibiotics for c. trachomotisis. baby can recieve erythomycin eye drops. 4. preterm labor, premature rupturer of membranes. neonatal sepsis, postpartum infection, chorioamnitis. |
|
|
What are some of the risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse (POP)?
|
1. multiple vaginal births
2. coughing 3. lifting. 4. connective tissue disorders. 5. obesity 6. lack of estrogen |
|
|
1. What are the four types of pelvic organ prolapses and what are their respective treatments/locations?
|
1. cystocele (anterior), enterocele (central), rectocele (posterior), paravaginal (lateral)
|
|
|
What are the treatments for the four types of pelvic organ prolapses (1. cystocele,2. enterocele,3. rectocele, 4. paravaginal defect)
|
1. cystocele-anterior repair-colporrhapy (surgical procedure that repairs a defect in the pelvic wall)
2. enterocele-resection of the enterocele hernia sac and fixation of the vagina to secure ligamentous tissue rectocele-posterior colporrhaphy paravaginal-paravaginal repair, reattachment of the levator ani muscle to its tendinous insertion site of the pelvic wall. ALSO MINOR PROLAPSE CAN BE TREATED WITH STRENGTHENING OF PELVIC MUSCLES WITH STRENGTH EXERCISES |
|
|
What is a positive Q-tip test?
|
sticking a q-tip in the urethra and have a patient do a valsalva. if q-tip moves more than 60 degrees than it is a hypermobile urethra and the patient has a positive q-tip test
|
|
|
What is the clinical approach to a pelvic organ prolapse?
|
1. On history patient may complain of various things depending on the location/type of pelvic organ prolapse, such as , heaviness or pressure in the pelvis, a bulging mass (central), difficulty voiding or incomplete bladder emptying, urinary incontinence (anterior), constipation or having to use one's fingers to push on the vagina to splint to achieve a bowel movement (posterior), sexual dysfunction or pain with intecourse.
2. Physical exam should be performed both supine and standing. Examine bladder, rectum, perform q-tip test. cervix and uterus should be felt while bearing down. palpate the lateral aspects of the vagina for paravaginal defects. 3. once grade/extend of pop is determined discuss medical and surgical options. 4. medical options include pelvic floor exercises, pessaries (hammock-like structures desgined to support pelvic floor) or surgical options such as resection, vaginal fixation |
|
|
How is POP graded?
|
1. Stage 0= no prolapse
2. S1=leading part of prolapse is more than 1 cm above the hymen 3. S2=the leading edge is less than or equal to 1 cm above or below hymen 4. S3=leading edge is more than 1 cm beyond the hymen but less than or equal to the total vaginal lenght 5. S4=complete eversion |
|
|
Define cystocele.
|
cystocele-defect of the pelvic muscular support of the bladder allowing the bladder to fall down into the vagina. Often the urethra is hypermobile. This is an anterior POP defect
|
|
|
Define enterocele.
|
enterocele-defect of the pelvic muscular support of the uterus and cervix (if still in situ) or the vaginal cuff (if hysterectomy). The small bowel and/or omentum pushes the organs into the vagina. This is a central POP defect.
|
|
|
Define rectocele.
|
Defect of the pelvic muscular support of the rectum to impinge into the vagina. The patient may have constipation or difficulyty evacuating stool. This is a posterior POP defect.
|
|
|
Define paravaginal defect.
|
paravaginal defect-defect in the levato ani attachment to the lateral pelvic side wall leading to lack of support of the vagina, known as a lateral pelvic defect.
|
|
|
1. What is vasa previa? 2. How is it diagnosed? 3. What are common risk factors for vasa previa?
|
1. vasa previa-umbilical vessels that are not protected by cord or membranes, which cross the internal cervical os in front of the fetal presenting part; this most commonly occurs with a velamentous cord insertion or a placenta with one or more accessory lobes.
2. prenatal diagnosis is difficulty-ultrasound may give some hint (be suspicius with individuals with common risk factors) 3. risk factors for vasa previa-bilobed, succenturiate-lobed, or low-lying placenta, multifetal pregnancy, pregnancy resulting from in-vitro fertilization. |
|
|
What is velamentous cord insertion?
|
Umbilical vessels separate before reaching the placenta, protected only by a thin fold of amnion, instead of by the cord or the placenta itself; these vessels are susceptible to tearing after rupture of membranes.
|
|
|
Define Chorionicity and Amnbiocity?
|
1. Chorionicity-the number of placenta in a twin or higher gestation; monozygotic twins can either be monochorionic or dichorionic. Dyzogotic always have one placenta.
2. Amnionicity-the number of amniotic sacs in a twin or higher order gestation; monozygotic twins mauy be monoamnionic or diamnionic whereas dizygotc twins are always diamnionic. |
|
|
dizygotic twins always have what chorionicity and amniocity?
|
dichorionic/diamniotic
|
|
|
What is the relationship between chorionicity and amniocity and length between division of the zygote?
|
the longer the division the lower the chorionicity and amniocity
2. for example if division occurs in the first 72 hours it is dichorionic/diamniotic if done at day 8 it is monochorionic/monoamniotic |
|
|
What are some of the risks of twin gestation?
|
1. congenital anomalies
2. ;preterm labor 3. preeclampsia 4. postpartum hemorrhage 5. maternal death |
|
|
What is the treatment of vasa previa?
|
1. planned cesearan delivery before rupture of membranes
|
|
|
What is the treatment for twin-to-twin syndrome?
|
1. laser ablation of the shared anastomic vessels
2. seria amniocentesis for decompression |
|
|
What are the physiological changes that occur in pregnancy? (hint: cardiovascular, respiratory, arterial blood gas, renal, hematologic, gastrointestinal)
|
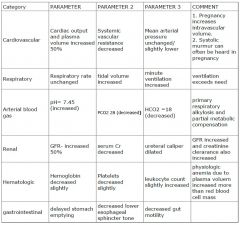
|
|
|
Define isoimmunizations.
|
1. the development of specific antibodies as a result of antigenic stimulation bny material from the red blood cells of another individual.
2. for example Rh isoimmunization means an Rh-nmegative woman who develops anti-D (RH factor) antibodies in response to exposure to Rh (D) antigen. |
|
|
Define antenatal testing. What is it used to test for?
|
1. A procedure that attempts to identify whether the fetus is at risk for uteroplacental insufficiency and perinatal death. Some of these tests include nonstress test and biophysical profile.
|
|
|
define advanced maternal age
|
pregnant woman who will be 35 years or beyond at the estimated date of delivery
|
|
|
What are the lab tests ramifications and appropriate "next steps" for infectious outcomes during pregnancy? (hint list 9)
|
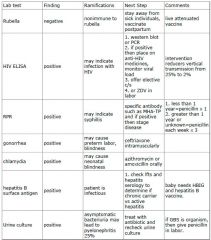
|
|
|
What are the ramfications/treatments for common hematological lab tests performed in pregnancy (e.g. rh test, antibody screen also pap smear)?
|

|
|
|
What are the outcomes/treatments of common lab tests performed for maintence (e.g. glucose screening also gbs culture)?
|
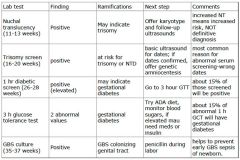
|
|
|
What are the typical screening exams performed during pregnancy and when are they performed?
|
1. nuchal translucencuy (11-13 weeks)
2. trisomy screen (16-20 weeks) 3. 1 hr diabetic screening exam (26-28 weeks) |
|
|
What is screening for gestational hypertension adn preeclampsia? when is it performed?
|
it's performed at each prenatal visit
2. it includes semiquantatitve urine dipstick for proteinuria and hypertension |
|
|
What are the main objectrives of prenatal care?
|
1. educate the patient
2. prevent complications 3. screen for signifcant conditions that can affect maternal or fetal health 4. prevention 5. also initally dating baby's gestational age |
|
|
1. What is lichen schlerosis?
2. What is its typical presentation? 3. What type of people does it typically affect? |
1. Lichen sclerosis-chronic, inflammatory dermatologic disease characterized by pruritis and pain, which mainly affects the anogenital region
2. women w/ disease present complainin of itching which can be worse at night and pain 3. more common in women who are postmenopausal |
|
|
1. What is the differential for lichen planus
2. What are the potential complications |
1. lichen planus, psoriasis, vulvar intraepethelial neoplasia, and vitiligo
2. vulvar cancer can occur with constant scratching and itching of vulvar |
|
|
1. How is lichen sclerosis diagnosed?
2. How is it treated? |
1. LS is diagnosed by biopsy. This is to r/o cancer and lichen planus
2. primarily with corticosteroid creams -in addition pt must be educated in regards to vulvar hygeine; -frequent surveillance is necessary because of risk of vulvar cancer |
|
|
How are bartholin gland cysts treated?
|
1. incision and placement of a small balloon catheter in to the gland
2. marsupilization-which is surgical fixation of they cyst wall everted against the mucosa of the vulva 3. purspose of both is to drainthe infection for several weeks. 4. I&D doesn't work |
|
|
What are the diagnosis/treatment/ clinical characteristics of bacterial vaginosis, trichomonis, and candididasis infections?
|
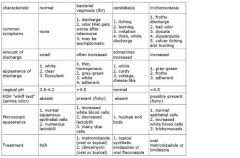
|
|
|
What is the most common type of vaginal cancer? What is its typical presentation?
|
1. Squamous cell cancer
2. most common symptoms are vaginal bleeding and malodorous discharge. |
|
|
What is the typical treatment for vaginal cancer for:
1. Stages 1 and 2 (no extension to the pelvic wall and no metasteses) 2. Stages 3 and 4 |
1. Stages 1 and 2 which are less than 2 cm may be removed surgically.
2. Stages 1 and 2 which are more than 2 cm are treated with radiation 3. Chemotherapy is used for Stage 3 and 4. 4. Radiation is a highly effective for squamous cell cacinoma S1 and S2. It is an excellent alternative for patients who are poor surgical candidiates. |
|
|
What is the clnical approach once intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD) has been diagnosed?
|
1. a coagulation profile should be drawn to look for DIC
2. If fibrinogen levels are low normal, if platelet count is decreased, if there is an increase in PT and PTT or the presence of FDB suspect DIC and deliver 3. if patient does not have indicators of DIC it is the patient's choice whether to induce labor or to expectantly wait for delivery 4. if patient labs are profoundly abnormal indicating DIC then fresh frozen plasma should be given. |
|
|
How is preterm premature rupture of membranes diagnosed?
|
1. history consistent iwth a gush of fluid per vagina
2. speculum examination whowing the pooling of amniotic fluid in the posterior vaginal vault, alkaline changes of the vaginal fluid and a ferning pattern on microscopy. 3. can be confirmed by ultrasound showing oligohydraminios |
|
|
How is premature rupture of membranes typically managed?
|
1. If less than 32 weeks gestation usually managed expectantly. Babies are given antenatal steroids
2. If after 35 weeks gestation usually delivered. |
|
|
When should Rh screening be performed? What is the clinical approach thereafter?
|
1. At the first prentatal visit
2. Unsensitized Rh-negative women should be retested between 24 and 28 weeks. 3. If patient at risk of alloimunization should be given anti-Rh immune globin at 28 weeks and again at delivery. |
|
|
How is syphillis diagnosed?
|
1. Nontreponemal serologic tests (VDRL, RPR) are used as a screening test for syphillis and treponemal tests (FTA-ABS) are used for confirmation
2. In syphillis there is a high rate of false-negative and therefore darkfiled is necessary |
|
|
Describe chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis. What are there pros and cons and when are they used?
|
1. CVS-is a technique that involves aspiration of a small amount of chorionic villi from the placenta. It can be done between 10 and 12 weeks and offers the advantage of early diagnosis. Fetus derived cells are karyotped by FISH and enzyme deficiencies can be screened. The risk of complications is higher than amniocentesis however.
2. Amniocentesis is done between 16th and 18th week. |
|
|
Define Labor
|
The progressive change in a woman's cervix in the setting of regular, rhythmic uterine contractions.
|
|
|
How can you differentiate between True Labor and False Braxton hicks labor.
|
1. Braxton hicks contractions are not associated with dilation of the cervix and are less intense than true labor contractions, with the discomfort being characterized as over the lower abdomen and groin areas.
2. True labor is associated with contractions that the patient feels over the uterine fundus, with radiation of discomfort to the low back and lower abdomen. |
|
|
What is cervical effacement?
|
1. An event that commonly occurs during the onset of labor in which the internal os is slowly drawn into the lower uterin segment
|
|
|
What is Lie?
|
1. Lie is the relation of the long axis of the fetus with the maternal long axis. It is longitudinal in 99% of cases, occasionally transverse, and rarely oblique (when the axes cross at a 45-degree angle, usually converting to transverse or longitudinal lie during labor).
|
|
|
Define presentation.
|
determined by the presenting part
|
|
|
Define Position.
|
relation of the fetal presenting part to the right or left side of the maternal pelvis.
|
|
|
What are the purpose of the Leopald's maneuvers? What are the 4 Leopald maneuvers?
|
1. LM is a series of four palpations of the fetus through the abdominal wall that helps accurately determine fetal lie, presentation, and position
2. a. determination of what it is in the fundus b. evaluation of the fetal back and extremities; c. palpationof the presenting part above the symphisis; d. determination of the direction and degree of flexion of the head. |
|
|
What is effacement?
|
is the shortening of the cervical canal from a length of about 2 cm to a mere circular orifice with almost paper-thin edges
|
|
|
How is fetal station determined?
|
1. by identifiying the level of the fetal presenting part in the birth canal in relation to the ischial spines which are located approximately halway between the pelvic inlet and outlet.
|
|
|
What is the clinical significance of being at 0 station?
|
1. 0 station is at the level of the ischial spine
2. it means that the fetal head at the biparietal diameter has negotiated the pelvic inlet |
|
|
What are the signs that the placenta is about to be delivered?
|
1. gush of blood
2. lengthening of the umbilical cord. 3. uterus rises in the abdomen |
|
|
How is labor induced?
|
1. oxytocin can be used to cause uterine contractions
2. cervical ripening -misoprosol (a prostaglandi E analog), mechanical dilation with a laminara. |
|
|
What is a prolonged latent phase in a nulliparous woman? multiparous?
What are the management options during this time? |
1. more than 20 hours and 14 hours respectively.
2. observation and sedation |
|
|
What is a prolonged active labor in a nulliparous and multiparous woman?
|
1. less than 1 cm/hr and less than 1.2-1.5 cm/hr respectively?
|
|
|
What is the management for prolonged active stage labor?
|
1. observation
2. augmentation (considered when frequency of contraction is less than 3 per 10 minutes or the intensity of contractions is less than 25 mmHg) -amniotomy and/or oxytocin administration 3. c/s delivery if patient/fetal show signs of distress |
|
|
What is a second stage protraction disorder? What's the typical management?
|
1. more than 3 hours if regional anethesia or 2 hours if no regional anesthesia
2. a. as long as fetus/mom ok then 2nd stage can continue b. oxytocin if contractions are too weak. c. bearing down/changing labor positions d. non-reassuring signs is an indication for a c/s or operative deliery |
|
|
What is shoulder dystocia? what is one of its main complications?
|
1. shoulder dystocia is an inabilit of the fetal shoulders to deliver spontaneously usually due to the impaction of the anterior shoulder behind the maternal symphysis pubis.
2. erb palsy or other brachial plexus inury |
|
|
What is the management of shoulder dystocia?
|
1. mcrobert's manuever (maternal thighs are sharply flexed against the maternal abdomen)
2. suprapubic pressure 3. if first two steps fail then you could try wood's corkscrew 4. zavanelli maneuver 5. also try delivery of posterior arm |
|
|
What are contraindications to expectant management in a person with severe preeclampsia?
|
1.thrombocytopenia less than 100,000
2. inability to control blood pressure with the use of two hypertensives 3. non-reassuring fetal signs 4. LFTs elevated above 2 times normal 5. eclampsia |
|
|
What is HELP syndrome?
|
1. a disesae process in the spectrum of severe preeclampsia
2. hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets |

