![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diabetes
Effects on Pregnancy: |
Congenital malformation (2-4 fold)
Spontaneous abortion Fetal growth disturbance (β-cell hyperplasia) Sacral agenesis Increased erythropoesis Organomegaly Macrosomia Decreased surfactant production Effects of Pregnancy (con.) Unexplained fetal death (Uterine blood flow ↓ placenta function ↓) Polyhydramnios Intrapartum Risks Asphyxia Trauma; Shoulder dystocia Neonatal hypoglycemia |
|
|
Effects of pregnancy on epilepsy
|
Effects of Epilepsy
More difficulty in Disease control Effect of Liver enzyme, Renal Perfusion Increasing in circulating blood volume The Reproductive Hormones may affect the Reproductive health of woman with Epilepsy Oestrogen Enhances Neuronal Excitability, Lower Seizure Threshold Progesterone Enhances Inhibition , Increases the Seizure Threshold |
|
|
Effects of epilepsy on pregnancy
|
Congenital Anomalies / Malformations (1.5-2.5 times)
Higher Risk in Women taking Combination Therapy Teratogenic Anticonvulsants Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Valproic Acid… Neural Tube Defects Cardiac Defects Interfere with maternal Vit.K producion |
|
|
Early sign of congenital syphilis?
|
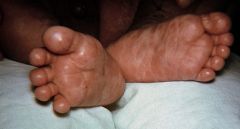
“barber’s pole” - umbilical cord
Hepatomegaly Rhinitis – Syphilitic rhinitis (“snuffles”) Cutaneous lesions – The rash of congenital syphilis usually appears one to two weeks after the rhinitis. It is maculopapular and consists of small, initially red or pink spots Generalized lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Late sign of congenital syphilis?
|
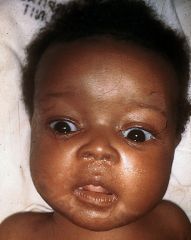
Facial features: Frontal bossing, saddle nose, short maxilla, protuberant mandible
Ophthalmologic: Interstitial keratitis, chorioretinitis, secondary glaucoma, corneal scarring, optic atrophy Ears: Sensorineural hearing loss Oropharynx: Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, perforation of hard palate Cutaneous: Rhagades, gummas Central nervous system: Intellectual disability, arrested hydrocephalus, seizures, optic atrophy, juvenile general paresis Skeletal: Saber shins (anterior bowing of the tibia), Higoumenakis sign (enlargement of the sternoclavicular portion of the clavicle), Clutton joints (painless arthritis), scaphoid scapula |
|
|
Effects of HIV on pregnancy?
|
The Incidence of Preterm Delivery, Intrauterine
Growth Retardation, Low Birth Weight -- Higher (3-4 times) (In one study, 1988) In Conclusion, A trend toward Small Babies in Seropositive Women Effect of HIV infection may be minimal when the woman is Well |
|
|
criteria for pre-eclampsia?
|
hypertension arises after 20 weeks gestation and is accompanied by one or more of the following:
Renal involvement: Significant proteinuria – dipstick proteinuria subsequently confirmed by spot urine protein/creatinine ratio ≥ 30mg/mmol. In view of the close correlation between spot urine protein/creatinine ratio and 24 hour urine excretion, the latter is rarely required 21 Serum or plasma creatinine > 90 μmol/L Oliguria Haematological involvement Thrombocytopenia Haemolysis Disseminated intravascular coagulation Liver involvement Raised serum transaminases Severe epigastric or right upper quadrant pain. Neurological involvement Convulsions (eclampsia) Hypereflexia with sustained clonus Severe headache Persistent visual disturbances (photopsia, scotomata, cortical blindness, retinal vasospasm) Stroke Pulmonary oedema Fetal growth restriction Placental abruption |
|
|
what are the maternal and fetal outcomes of pre-eclampsia?
|
Maternal Outcome:
Cerebral Haemorrhage Pulmonary edema HELLP Syndrome (DIC) Eclampsia … Fetal Outcome: Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR) Iatrogenic prematurity |
|
|
Where are the majority of ectopic pregnancies?
|
Tubal – 98%
Ampulary – 80% Isthmic -- 12% Fimbrial -- 6% |
|
|
WHat is the triad of symptoms in ectopic pregnancy?
|
Amenorrhea
Vaginal bleeding Abdominal pain |
|
|
What are the symptoms of ectopic if it's ruptured?
|
If rupture (Hemoperitoneum)
Shoulder Pain (phrenic nerve irritation) Dyspnea, Vertigo, Syncope (Hemorrhage hypovoleima) |
|
|
What are the investigations for ectopic pregnancy?
|
Ultrasound
In ectopic pregnancy, serial β-hCG usually shows a failure to double in 48 hours or a static or slow increase or decrease Laparoscopy Culdocentesis pelvis through vagina (needle into p: non-clotting blood (hemoperitoneum) |
|
|
management of ectopic
|
There is no place for expectant management in ectopic pregnancy
§ Treatment options include: o Medical management with methotrexate o Surgical management (usually laparoscopy) Linear salpingectomy Segmental resection Salpingectomy |
|
|
What are some contra indications for medical management?
|
Contraindication
Absolute – Breast feeding, immunodeficiency, alcoholism, liver disease, sensitivity to MTX, active pul. Disease, peptic ulcer Relative – GS > 3.5cm, Embryonic cardiac motion |
|
|
causes of antepartum haemorrhage?
|
Causes
Placenta Previa* Placental abruption* Vasa Previa Preterm cervical change Preterm labor Uterine rupture Vulva / Vagina trauma, varicose vein Cervical polyp, ectropion, cervicitis, carcinoma |
|
|
Woman presents with antipartum haemorrhage:
painless what could it be? Painful what could it be? |
Painless - Placenta Previa
Painful - Placental abruption |
|
|
risk factor for placenta previa?
|
Risk factor
Prior Previa Prior Caesarean delivery Multiparity Advanced maternal age Cocaine, Smoking |
|
|
What is the management of placenta previa?
|
Management
IF Premature + Not severe Close observation, Fluid, Bed rest, Steroid IF Term or Severe Delivery (caesarean birth) |
|
|
What is a
Couvelaire Uterus? |
Couvelaire uterus (also known as uteroplacental apoplexy)[1] is a life threatening condition in which loosening of the placenta (abruptio placentae) causes bleeding that penetrates into the uterine myometrium forcing its way into the peritoneal cavity.
|
|
|
How do you manage a woman with antepartum haemorrhage of unknown cause?
|
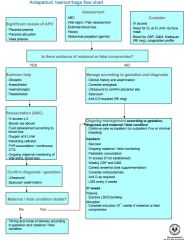
|
|
|
Risk factor for placental abruption
|
q
Risk Factors Chronic Hyperternsion Pre-eclampsia Prior Abruption Multiple gestation Advanced Maternal age Multiparity Cocaine, Smoking Chorioamnionitis Trauma |
|
|
mx for placental abruption
|
Management
Monitoring Vital signs (maternal & fetus),Fluid Delivery for severe condition Correct coagulopathy (DIC) |
|
|
You're delivering a baby and it does the:
Turtle Sign (The delivered fetal head may retract against the maternal perineum) What does this mean? |
Shoulder Dystocia
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for sholder dystocia?
|
Risk Factors
Multiparity Macrosimia Postterm gestation Prior shoulder dystocia |
|
|
Mx of shoulder dystocia:
|
Management
McRoberts Maneuver Suprapubic Pressure Rotational Maneuver Delivery of Post. Arm Zavanelli Maneuver Intentional Fracture of fetal clavicle |
|
|
causes of PPH
|
Uterine Atony Laceration of Lower Genital tract Retained Placenta Coagulation Defects Amniotic Fluid Embolism (DIC) Uterine inversion Uterine Rupture |

