![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If you see a traumatic ulcer, what should you ask the Pt?
|
If they recently injured themselves or if they've had this condition before.
**if there is an obvious irritant, remove it.** |
|
|
What is the apperance of a traumatic ulcer?
|
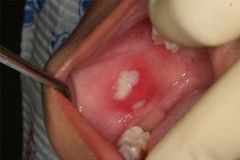
Can be "craterlike" or "ditched out".
Exudate or bleeding may be present |
|
|
What are some DD's of traumatic ulcers?
|
syphilis, gonorrhea, apthous ulcer.
|
|
|
How could someone Tx an traumatic ulcer?
|

Saline rinse, oragel.
It will usually resolve in 7-14 days…if not, then need to re-evaluate. |
|
|
What is necrotizing sialometaplasia?
|
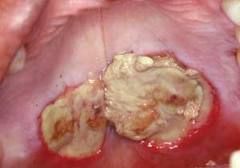
minor salivary gland necrosis related to (R/T) trauma
|
|
|
Where in the mouth is necrotizing sialometaplasia usually found?
|
Around tooth 2 & 14 (the 2nd Mx molars)
|
|
|
What are some DD's of necrotizing sialometaplasia?
|
syphilitic gummas,
deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
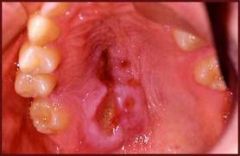
What are the 3 stages of syphilis?
|
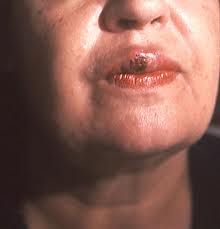
Primary-Chancre
Secondary-Mucous patches Third-gumma-->can show up 10-20 years later. |
|
|
During what stages is syphilis most contageous?
|
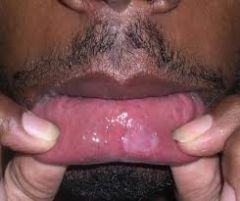
Primary-Chancre &
Secondary-Mucous patches |
|
|
Recognize image
|
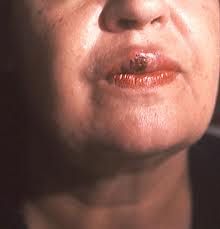
Primary Chancre
|
|
|
Recognize image
|
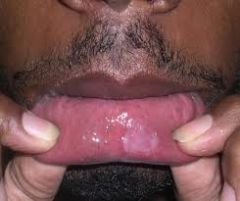
Secondary -mucous patches
|
|
|
Recognize image
|
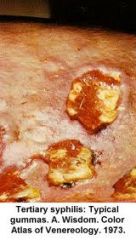
Gumma
|
|
|
Which populations is syphilis more promenent?
|
African-American Men & AIDS Pt's
|
|
|
How is syphilis transmitted?
|
Usually via sexual contact.
Can be passed mother to child or in blood transfusions |
|
|
If a Pt presents with stage 1 or 2 syphilis, how should I Tx them?
|
They are highly infectious-->Don't Tx Pt.
|
|
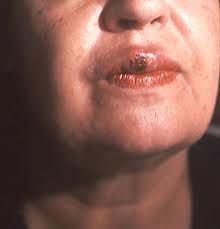
How long does the Primary-chancre stage last?
|
Usually 1-3 months and then resolves
|
|
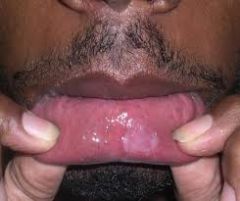
How long does the Secondary-mucous patch stage last?
|
Typically 4-12 weeks but can go latent for many years.
|
|
|
In congential syphilis what makes up the Hutchinson's Triad?
|
1) Inflammation of cornea
2) Deafness 3) dental abnormalities (notched incisors/mulberry molars) |
|
|
What age group is gonorrha usually found in?
|
15-29 year olds.
|
|
|
What symptoms of gonorrhea are usually found in men?
|
Men don't usually show symptoms
|
|
|
How is gonorrhea usually transmitted?
|
Sexually transmitted of via Mother to fetus
*Babies who don't get Tx can die from this.* |
|
|
What type of lesions will someone with gonorrhea usually present with and where?
|
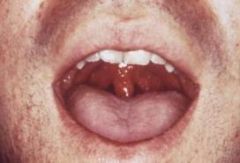
Pustular lesions on the tonsils & oropharynx
|
|
|
What does the affected area look like?
|
Red an inflamed?
|
|
|
What are some DD's Gonorrhea?
|
Aphthous ulcers, cancer of the tonsil, Pemphigus
|
|
|
What type of infection is actinomycosis?
|
Bacterial
|
|
|
Since a fistula is the primary characteristic of actinomycosis, what often accompanies the presence of a fistula?
|
Smelly Stink!
The sulfur granules stink! |
|
|
How is actinomycosis treated?
|
Antibiotics
|
|
|
What is another name for aphthous ulcers?
|
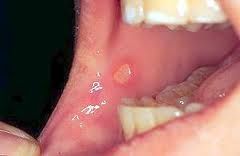
Cancer sore
|
|
|
What casuses apthous ulcers?
|
Stress, food trauma
|
|
|
Hos long do apthous ulcers usually take to heal?
|
They are self limiting and usually heal with in 7-10+ days (14 days)
|
|
|
Where in the mouth are apthous ulcers usually found?
|
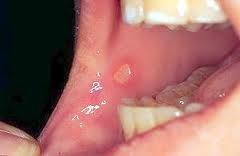
Nonkeratinized mucosa
|
|
|
What is the most common ulcer seen in the oral cavity?
|
Apthous Ulcers
|
|
|
How would you treat cancer sores?
|
With a saline rinse
|
|
|
The apthous ulcers that appear on keratinized tissue are cause by _______ ________.
|
primary herpes
|
|
|
What is a herpetiform?
|
A type of apthous ulcer.
|
|
|
What is the size of a herpetiform?
|
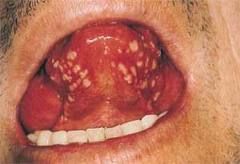
small would be 1-3mm but they can coalese into clusters of 10-100 ulcerations
(They are smaller and more numerous than minor Apthous Ulcers AU's) |
|
|
What is the size of a large AU?
|
1-3 cm (30mm)
|
|
|
What is erythema multiforme?
|
An acute inflammatory disease of the skin and mucous membranes/
|
|
|
Target lesions on the skin are…..
|
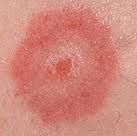
erythema multiforme….these lesions go" hand in hand" with this condition.
**Really know that target lesions are Erythema multiforme. Know these go together!** |
|
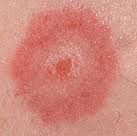
Where are the target lesions found?
|
On the hands, body and oral tissue may be involved.
|
|
|
What does erythema multiforme look like?
|
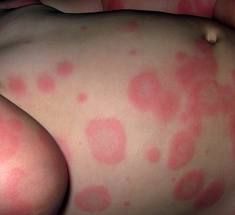
Blister, surrounded by red inflammed tissue with a lighter ring of edema surrounding it. (Give it a target look)
|
|
|
Are you going to have dental Tx in a Pt presenting with this condition?
|
No!
|
|
|
What is the more sever form of erythema multiforme called?
|
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Its self limiting but can be fatal. |
|
|
What causes oral lesions associated with hypersensitivity?
|
A product or medication that gives a tissue response.
**Talk with your Pt to see what "new" things have been added to their oral cavity lately. Toothpaste, mouthwash, gum.** |
|
|
What type of disease is Lupus erythematosus?
|
Autoimmune (The body attacks itself)
|
|
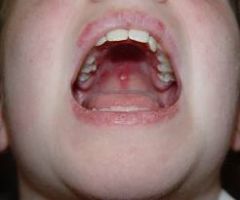
Who is more likely to experience lupus erythematosus?
|
Women in the 30 year old range.
|
|
|
What is the classic distribution of lupus erythematosus?
|
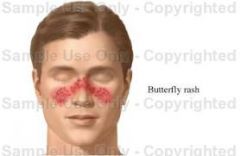
Butterfly distribution
**Know this term is synomous with Lupus Erythematosus** |
|
|
Skin involvement of Lupus Erythematosus is most common in areas with _____ ________.
|

Sun Exposure.
|
|
|
How do oral lesions appear with Lupus Erythematosus?
|
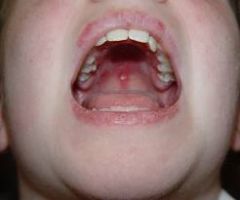
Eroded lesions, gingiva may be sluffing and erosive. Erythematous (red)
|
|
|
What type of disease is Crohn's disease?
|
GI disease
|
|
|
What do the oral lesions of Crohn's disease look like?
|
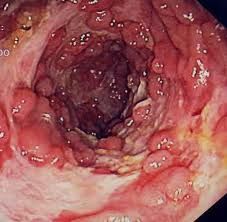
Ulcer looking, have the "cobble stone effect"
They are Extremely painful and slow to heal! |
|
|
Keratin Pearls is synomous with what condition?
|
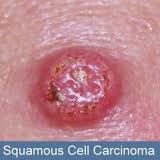
Squamous cell carcinoma--Cancer of the stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
Which population is squamous cell carcinoma most common?
|
Males 45+
|
|
|
Which cancer accounts for 90% of all oral cancers?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What are risk factors in squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Tobacco, betel nut, alcohol and sunlight
(diet and stress also contribute) |
|
|
What are the primary areas for developing oral cancer?
|
Later border of Tongue, Floor of mouth, gingiva. (salivary glands and areas of drainage are frequent sites)
|
|
|
Outside of the oral cavity where is a popular site for squamous cell carcinoma?
|
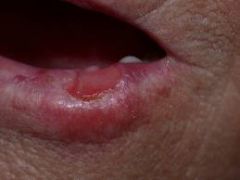
The LIPS!
|
|
|
What is another name for Oral squamous papilloma?
|
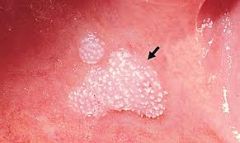
Oral WART!
Its very common |
|
|
What virus causes oral squamous papilloma?
|
HPV…which means its sexually transmitted.
Be aware when discussing with juvenilles under 18 |
|
|
What is the look of oral squamous papilloma?
|
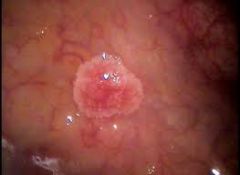
Cauliflower look and texture…usually white to pink in color.
|
|
|
What is the TX for oral warts?
|
Excise them
|
|
|
Verruca Vulgaris is a common ______ _______.
|
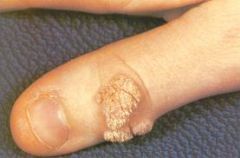
skin wart.
Caused by HPV |
|
|
What is the Tx for verruca vulgaris?
|
Excise the wart.
|
|
|
Condyloma Acuminatum is a ________ wart cause the the ________ virus.
|
venereal wart
HPV |
|
|
What does Codondyloma acuminatum look like?
|
Cauliflower-like growth similar to papilloma.
It is white-pink in color |
|
|
Where is condyloma acuminatum usually found?
|
Lips, tongue, palate, labial & lingual frenum
There can be multiple and coalesce. |
|
|
What is the Tx for Condyloma Acuminatum?
|
Excise the wart.
|
|
|
Which conditions are related to HPV?
|
Oral Squamous Papilloma,
Verruca Vulgaris, Condyloma Acuminatum |
|
|
What are some possible DD's for "wart lesions"?
|
Oral Squamous Papilloma,
Verruca Vulgaris, Condyloma Acuminatum |
|
|
Focal epithelial hyperplasia is more common in which population?
|
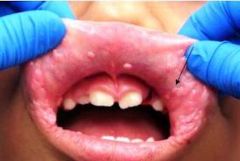
Native Americans (first noted in Navajo Indians)
|
|
|
What is another hame for focal epithelial hyperplasia?
|
Hecks Disease
|
|
|
What does Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia look like?
|
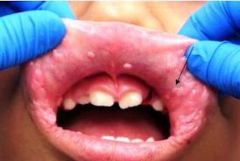
Multiple nodules on lower lip, buccal mucosa and tongue, cauliflower like and pink-white.
|
|
|
What is the DD for Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia?
|
Crohn's disease?
|
|
|
How is Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia transmitted?
|
Genetics and HPV
|
|
|
What is papillary hyperplasia associated with?
|
Wearing dentures 24 hours a day or ill fitting dentures
|
|
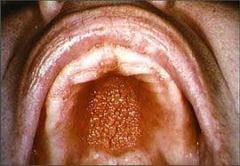
What should you advise the Pt to do if presenting with papillary hyperplasia?
|
Remove the dentures and let the tissue rest.
Dentures may need to be "re-lined" |
|
|
Verrucous Carcinoma is related to what habit?
|

Chewing tobaco (comes from the carcinogens)
|
|
|
Who is more likely to encounter verrucous carcinoma?
|
Men 55+
|
|
|
How does Verrucous Carcinoma present?
|
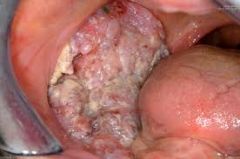
White patches early and then cauliflower like larger areas as the cancer grows. Ulcerations may be present.
|
|
|
What are the 3 major forms of skin cancer?
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Sell Carcinoma & Melanoma |
|
|
Who might be the first to detect skin cancer lesions?
|

Dental Hygienists!
|
|
|
What is the most common cancer among women ages 20-29?
|
Melanoma!
Its also the #1 cancer in men over 50! |
|
|
What is the most common form of skin cancer?
|
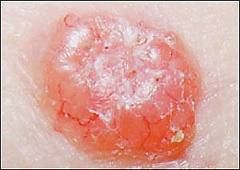
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are risks for Basal Cell Carcinoma?
|
Ultaviolet light, genetics & arsenic ingestion
|
|
|
What is it about basal cell carcinoma that makes it look different from other skin cancers?
|
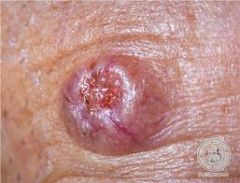
The Pearly Border!
**Don't forget basal cell carcinoma is very slow growing.** |
|
|
What is the TX for basal cell carcinoma?
|
Excise the lesion.
*If you catch the lesion before it metastasizes there is a 99% 5 yr survival rate. If the lesion has matastasized there is only a 10% survival rate.* |
|
|
What are some risks for Squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Sun exposure, tobacco use, burned skin & genetics
|
|
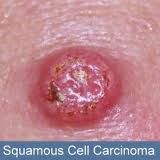
What is a key factor for squamous cell carcinoma?
|
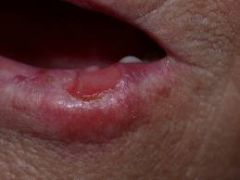
It develops in pre-existing actinic keratosis.
**Any lesion that is non-healing NEEDS to be evaluated.** |
|
|
Melanoma makes up ____% of skin cancers?
|
4%
Looks like a nevi **But if it metastasizes…it can be deadly!** |
|
|
What is the Tx for Melanoma?
|
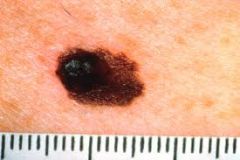
Excise the lesion Possibly chemo or radiation.
**5 Year survival rate is 90-97%** |
|
|
What are the ABCD's of skin cancer?
|
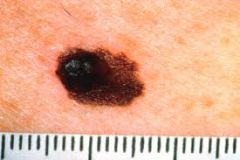
A-->Asymmetry is there a lack of uniformity to the lesion?
B--> Border Irregularity are the edges of thelesion blurred, notched or ragged C-->Color Variation Does the lesion vary in shades of tan, brown, black w/red white or blue pigments D--> Diameter Noted when lesions ismore than 6mm or larger (size of pencil eraser) |
|
|
What is the most common type of precancerous lesion? (Know This!)
|
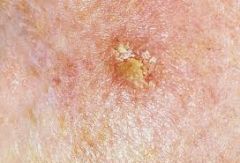
Actinic Keratosis!
(Often seen in the lips where someone is chronically burning them.) |
|
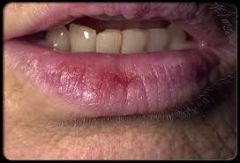
Actin Keratosis is an early marker for ________ _________ ___________.
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
(Check the back of hands, ears, forehead and lower lip!) |
|
|
What does actin Keratosis look like?
|
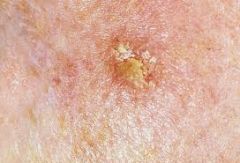
Scaly or crusty patches
|
|
|
_________ _________ is a form of actinic keratosis. (Apparently we will see this all the time in practice)
|
Actinic Cheilitis
|
|
|
Where is Actinic Cheilitis usually found?
|
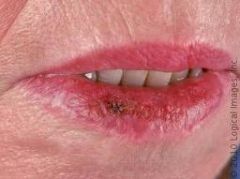
Lip mucosa (exposed to sunlight)
**Has a blothcy apperance and smokers are more at risk!** |
|
|
Neoplasms can be either __________ or ____________.
|
Benign or Malignant
|
|
|
Describe the traits of a benign neoplasm.
|
Encapsulated
Grow Slowly Don't Spread Can be Fatal (A benign tumor in the brain for example) |
|
|
Describe traits of a Malignant neoplasm
|
Not Encapsulated,
Grow Quickly Spreads Metastasizes to other sites Can't tell where normal tissue starts and malignant tissue ends, Fatal if undetected. (Terms used Carcinoma & Sarcoma) |
|
|
Dysplasia
|
Creation of abnormal cells from normal cells
|
|
|
Carcinoma in Situ
|
Early stage of cancer/carcinoma…when dysplastic cells are separated from the surrounding tissues by the basement membrane.
|
|
|
Invasive carcinoma
|
A malignant neoplasm composed of epithelial cells that infiltrate & destroy surrounding tissues and may metastasize!
|
|
|
Metastasis
|
The spread of cancer to distant parts of the body from where it orginated.
|
|
|
What is cancer staging? (In general)
|
In general, it describes the extent or severity of an individuals cancer based on:
Location of primary tumor Size & number Lymph node involvement Cancer type & grade (how closely the cancer cells resemble normal tissue) Presence or absence of metastases |
|
|
What does TNM refer to?
|
T= based on extent of Tumor
N=extent of spread to lymph Nodes M= presence of Metastasis **A number is added to each letter to indicate the size or extent of tumor and extend to the spread of the disease.** |
|
|
Localized
|
limited to the area it begain w/o spreading
|
|
|
Regional
|
spread beyond orginal primary site to nearby lymph tissues/nodes
|
|
|
Distant
|
Cancer has pread from primary site
|
|
|
What are the biggest causes of cancer?
|

Tobacco 30% & Diet/Obesity 30%
|
|
|
What are 3 BIG oral side effects of cancer Tx? (KNOW THIS!)
|
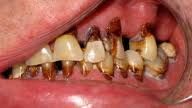
1) Xerostomia--loss of function of salivary glands
2) Mucositis--painful oral ulcers on any mucocal tissues 3) Radiation caries--happens VERY FAST Seen at cervial 1/3, destruction of salivary glands and inadequate OHI **4) Candidiasis may be present due to compromised immune system.** |

