![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
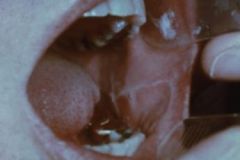
What is this hyperplastic response within the epithelium? It creates acanthosis and hyperkeratosis that produces a line of leukoplakia.
|
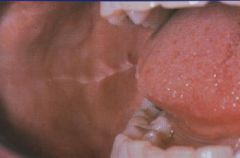
Linea Alba
White line, usually bilateral on buccal mucosa. Trauma from the facial surfaces of teeth. Benign. No treatment needed. |
|
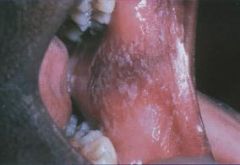
What is this Factitious Injury called?
|
Morsicatio Buccarum (Chronic Cheek Chewing)
Factitious Injuries are self-inflicted injuries, whether intentional or accidental |
|
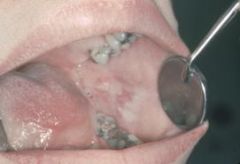
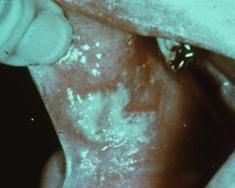
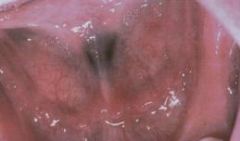
What are these white, shredded lesions that are produced by chronic nibbling?
|

Morsicatio Buccarum (Chronic Cheek Chewing)
Reasons for chewing: 1. Nervous habit 2. Psychiatric illness (people trying to punish themselves) 3. Can be intentional or accidental |
|
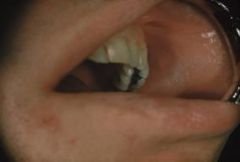
What are some variations of Morsicatio Buccarum (Chronic Cheek Chewing)?
|
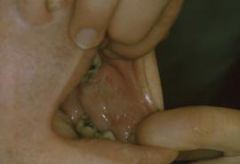
Morsicatio labiorum - affects labial mucosa
Morsicatio lunguarum - affects lateral border of tongue |
|
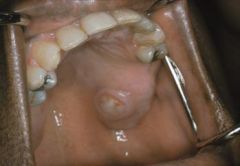
Explain the formation process of a traumatic ulcer
|
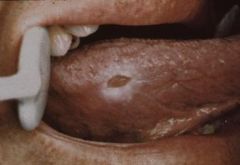
1. An ulcer is a complete loss of the epithelial surface covering
2. Exposed connective tissue allows microorganisms to invade into the tissue causing inflammation 3. Vascular changes of inflammation create an Exudate 4. exudate will cover over the surface with a Fibrin Clot 5. fibrin clot tends to be white or yellow due to moist environment 6. Most oral ulcers will be red at first because there is not enough time to create the fibrinous exudate (this is the pseudomembrane) 7. Areas of erythema (red halo) that surrounds central yellow pPeudomembrane (ulcer) or Focal Red Ulcerated Area Without Fibrin Covering |
|

How long does it take for a small traumatic ulcer to heal?
|
heals within days
|
|
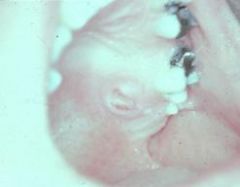
What conditions are related to slowly healing ulcers?
|
1. People who have poorly controlled diabetes tend to have persistent ulcers
2. Systemic steroids 3. Immunosuppression for various reasons |
|
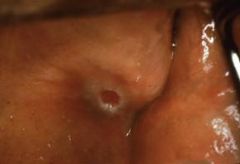
Surface ulcerations occur as a result of acute or chronic irritation or trauma. Where does it occur most often?
|
Tongue, lips, buccal mucosa
|
|
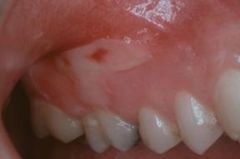
What is the and what are the two factors that can deprive the tissue of oxygen, causing it to undergo necrosis?
|
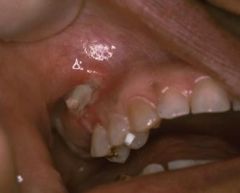
1. Physical Blockage of Flow - you're filling a confined space that normally would have blood flowing in it. You're displacing that blood flow by putting fluid into it and pushing back on the blood flow
2. Chemically Induced Stricture of the Vasculature - often, local anesthetics used in dentistry contain a vasoconstrictor |
|
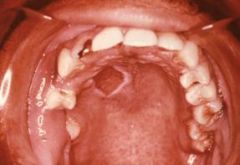
Where does this well-circumscribed area of ulceration at site of injection manifest most frequently?
|
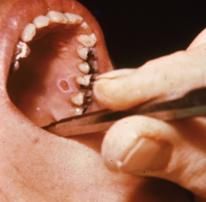
Anesthetic Necrosis occurs most commonly on the hard palate
|
|
|
What causes this and by what means does it occur?
|
Amalgam Tattoo
Dental amalgam can become impregnated into a patient's soft tissue or even the bone. This will discolor the COLLAGEN because the amalgam will corrode in the patient's tissue |
|
|
What causes this and by what means does it occur?
|
Amalgam Tattoo
Dental amalgam can become impregnated into a patient's soft tissue or even the bone. This will discolor the COLLAGEN because the amalgam will corrode in the patient's tissue |
|
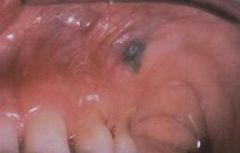
What is this and what is the underlying cause?
|
Amalgam Tattoo
Dental amalgam can become impregnated into a patient's soft tissue or even the bone. This will discolor COLLAGEN because the amalgam will corrode in the patient's tissue. |
|
|
What are the different colors that an amalgam tattoo may manifest?
|
Blue, Black, or Gray macules
(fragments are densely radiopaque) |
|
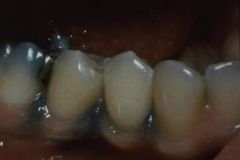
What colors do amalgam tattoos manifest as?
|
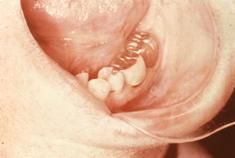
Blue, Black, or Gray Macules
(Fragments are densely radiopaque) |
|
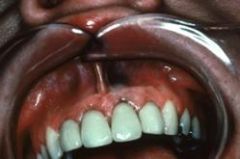
In what ways can amalgam particles get implanted into the tissue?
|
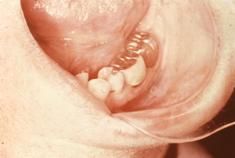
1. Amalgam dust in oral fluids
2. Broken amalgam pieces in extraction sites 3. Dental floss contaminated with amalgam particles 4. Amalgam from endodontic procedures left in soft tissue 5. Fine metallic particles driven by drill pressure |
|
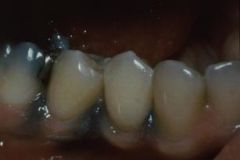
Where are the most common locations to get an amalgam tattoo and how is diagnosis confirmed?
|
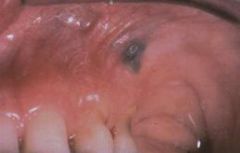
Gingiva, alveolar and buccal mucosa
Radiographs confirm diagnosis. No treatment necessary |
|
|
What are some types of Systemic Metallic Intoxications?
|
Lead
Mercury Silver Bismuth Arsenic Gold (rare) |
|
|
What systemic metallic intoxication leads to Ulcerative stomatitis, Gingival line (bluish along marginal gingival), and gray areas on buccal mucosa and tongue?
|
Lead
|
|
|
What type of systemic Metallic intoxication results in metallic taste, ulcerative stomatitis, inflammation and enlargement of salivary glands, gingiva, and tongue. Gingiva may become blue-gray to black, destruction of alveolar bone and exfoliation of teeth, Acrodynia (pink disease, Swift disease) from chronic mercury exposure in infants and children. Oral symptoms include excessive salivation, ulcerative gingivitis, bruxism, premature loss of teeth.
|
Mercury
|
|
|
What is attributed to Acrodynia (pink disease, Swift disease) which has oral symptoms of excessive salivation, ulcerative gingivitis, bruxism, and premature loss of teeth?
|
Mercury
|
|
|
What causes Argyria, which manifests as a diffuse bluish-black discoloration?
|
Silver
|
|
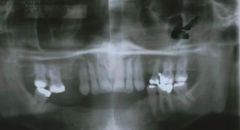
What is a Dome-shaped radiopaque lesion arising from the floor of the maxillary sinus that results in sessile elevation from inflamatory exudate and most of these disappear on their own in a 6-9 month period?
|
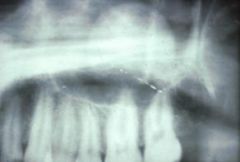
Antral pseudocysts<BR>(antral = maxillary sinus)
|
|
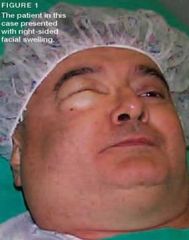
How does cervicofacial emphysema occur?
|
It arises from air forced into subcutaneous or fascial spaces of face and neck
|
|
|
What condition can manifest as CREPITUS (crackling) synchronous with heartbeat (Hamman's crunch)?
|
Cervicofacial Emphysema
|
|
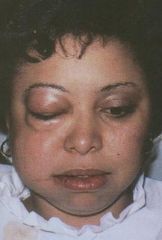
How might air get into fascial spaces of the face and neck, creating cervicofacial emphysema?
|
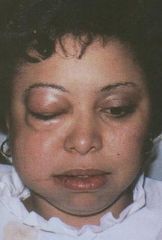
If you're using an air/water syringe and blowing in the patient's tissue, if there is no attached gingiva and you are blowing in the sulcus, where is the air going to go? Down into the patien's tissue somewhere. Along with that air, you are sending oral microbes. The organisms can start spreasing through tissue (even the mediastinum) and cause problems. Most cases resolve spontaneously or you may treat with antibiotics
|
|
|
This patient complained of pain in the maxillary first molar area after arriving at his orthodontist's office. He indicated he brushed his teeth very well so he would not get scolded for too much plaque by the assistant in charge of oral hygiene. Which of the following is the Most likely diagnosis of the lesion causing the pain?
a) Marginal gingivitis b) Traumatic ulcer c) Aphtous ulcer d) Herpetic ulcer e) Chancre |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the grayish black lesions observed mesial and distal to the left mandibular second premolar?
a) Amalgam tattoo b) Basal cell nevi c) Melanoma d) Melanotic macules e) Cafe au lait spots |
Amalgam tattoos
|
|
|
Which of the following is Least Likely to be included in the differential list for oral melanoma?
a) Nevus b) Amalgam tattoo c) Superficial mucocele d) Oral melanotic macule e) Focal hemosiderin deposit |
Superficial mucocele
|
|
|
This patient complained of pain in maxillary first molar area after arriving at his orthodontist's office. He indicated he brushed his teeth very well so he would not get scolded for too much plaque by the hygienist. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the lesion causing the pain?
a) Marginal gingivitis b) Traumatic ulcer c) Aphthous ulcer d) Herpetic ulcer e) Chancre |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely dagnosis of the solitary, reddish, ulcerated lesion observed in this projected photograph?
a) Traumatic fibroma b) Pyogenic granuloma c) Parulis d) Papilloma e) Pulp polyp |
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the projected solitary, firm, smooth mass of the buccal mucosa?
a) Traumatic (irritation) fibroma b) Peripheral ossifying fibroma c) Papilloma d) Hemangioma e) Lipoma |
Traumatic (irritation) fibroma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common oral ulcer?
a) Aphthous ulcer b) Herpes simplex ulcer c) Traumatic ulcer d) Ulcer associated with odontogenic infection e) Ulcer associated with cicatrial pemphigoid |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
Traumatic ulcers of the oral cavity may result from which of the following?
a) Biting b) Cotton roll injury c) Pizza burn d) all of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following usually heal with scar formation?
a) Minor aphthous ulcers b) Recurrent herpetic ulcers c) Traumatic ulcers d) All of the above e) None of the above |
None of the aboveq
|
|
|
All of the following lesions would be expected to be painful except?
a) An infected cyst b) An aphthous ulcer c) A pleomorphic adenoma d) An acutely inflamed tissue e) A traumatic ulcer |
A pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
The most common oral mucosal ulcer is which of the following?
a) Recurrent aphthous ulcers b) Recurrent herpes ulcers c) Mucous patch d) Chancre e) Traumatic ulcer |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
This red and white pattern was observed bilaterally on the buccal mucosa during routine examination of an apprehensive 23 yr male. Close examination of the white component showed ragged tags of tissue. This condition is most likely which of the following?
a) Erythroleukoplakia b) The result of chronic cheek chewing c) Candidiasis d) Ectopic geographic tongue e) Erosive lichen planus |
The result of chronic cheek chewing
|
|
|
This firm, slowly developing mass has been present for well over a year. It is most likely which of the following?
a) Papilloma b) Neurofibroma c) Fibroma/ traumatic fibroma/ irritation fibroma d) Mucocele e) Verrucous carcinoma |
Fibroma/ Traumatic fibroma/ irritation fibroma
|
|
|
This bluish lesion of the tongue, which has been present for several years, was described as being soft and fluctuant. It is most likely which of the following?
a) Amalgam tattoo b) Hemangioma/vascular malformation c) Mucocele d) Melanoma e) Oral melanotic macule |
Amalgam tattoo
|
|
|
This patient first noticed this solitary painfule lesion shortly after brushing his teeth to get ready for a dental appointment.
a) Aphthous ulcer b) Herpetic ulcer c) Herpangina d) Traumatic ulcer e) Erythema multiforme |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
Which of the following are clinical features associated with the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome?
a) Palmar and plantar pits b) Mild hypertension c) Rib anomalies d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of the oral irritation (traumatic) Fibroma?
a) Treatment of choice is conservative surgical excision b) Site predilection is the anterior portion of the tongue c) Most are considered to be reactive hyperplasias rather than true neoplasms d) All of the above e) A & C |
Most are considered to be reactive hyperplasias rather than true neoplasms
|

