![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Little Leaguer's Shoulder |
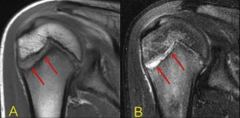
|
|
|
Proximal Humeral Fx |
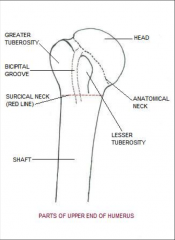
*1 part = nondisplaced *2 part = surgical or anatomical neck and/or greater or lesser tubercle
|
|
|
Surgical Neck Fx |
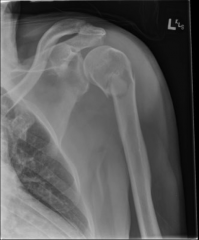
*Will need to be set and pinned |
|
|
Surgical Repair of Promixal Humeral Fx |
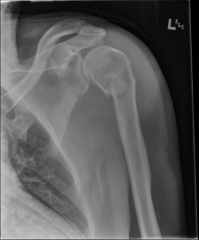
*Hardware not typically taken out. |
|
|
Rotator Cuff Pathologies |
*Rotator Cuff Tendonitis: Long term, loss of motion, weakness, overuse, wear and tear, *Rotator Cuff Tears: -Partial or full thickness, acute, chronic, traumatic, degenerative (aging) -Presentation: pain, weakness, decreased function, crepitus (pops) *More often see Partial Tears *Common in age 50 or up
|
|
|
Rotator Cuff Tears |
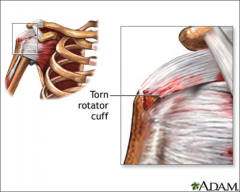
|
|
|
Shoulder Impingement |
*subacromial space/coracoacromial arch *Bursa, supraspinatus tendon, biceps tendon, joint capsule, nerves, arteries and veins *Activities above 90 degrees elevation (Flexion, Extension, Abd/Adduction) *Primary impingement- space is narrowed *Secondary impingement- mechanical/functional ex/ The way the scapula and tendon move together |
|
|
Shoulder Impingement Presentation and Types |
Clinical Presentation - Decrease mobility of posterior capsules, Blood supply restricted due to being pinched (supraspinatus)
Type 1 - Flat Type 2 - Round Type 3 - Hook
Other types of impingement- Wearing of tendons, bursa inflammation and specific pain
Posterior impingement
|
|
|
Secondarily involved structures during shoulder impingement? |
*Other muscles are trying to help, but will not always work *Subacromial bursa *Long head of biceps - Takes over for dysfunction muscles during impingement *Treatment: Therapy first, 90 degree limitations, then surgery (subacromial decomposition) which is the shaving of the clavicle |
|
|
Shoulder Osteoarthritis |
*Advanced degeneration of humeral head, underside of acromion, and clavicle
*Pain, loss of motion, rubbing of joints surfaces, altered mechanisms |
|
|
Total Shoulder Replacements |
*Traditional Total Shoulder/ Reverse Total Shoulder *Replace gleniod & head of humorous *Total Shoulder gets you back about 60% of function |
|
|
Adhesive Capsulitis |
*AKA Frozen Shoulder *Traumatic or insidious onset *Often occurs along RTC involvement (decreased mobility) *Thickening of synovium of shoulder joint capsule *Adhesion of joint capsule and surfaces leading to loss of motion, pain, and stiffness *Incidence - *More often in Women *50-70 years old *diabetics - insulin increases damage to capsule
|
|
|
Adhesive Capsulitis Clinical Presentation and Stages |
Clinical Presentation - Loss of both PROM and AROM, Firm end feel, capsular pattern (loses in all directions, some more than others) Stages- 1. Freezing Stage 2. Freeze 3. Thaw *Therapy involved, a lot of PROM and stretching. *Patient put to sleep and then manipulated, a lot of popping occurs, but ROM is a lot better. |
|
|
Shoulder Instability (Multidirectional) |
*Subluxation- voluntary/involuntary that will go out on their own *Dislocation- joint surfaces come uncontacted, can not go in by itself *Instability - Increased laxity/weakness in joint, sloppy joint (no limits) *Laxity - passively move humeral head off glenoid |
|
|
Shoulder Instability Incidence & Presentation |
*Incidence -Anterior and inferior (most common) -Men > Women - Multiple dislocations (must have 3 for surgery) *Clinical Presentation -Hypermobility -Feelings of sliding of joint surfaces with passive mobility -Typically painless |
|
|
Secondarily Injured Structures |
*Ligaments 0 Bankart Lesion *Capsule *Greater Tubercle -Hill Sach's Lesion *Labrum *RTC *Vascular Damage *Brachial Plexus Damage |
|
|
Surgical Intervention for Dislocations |
*Reduce ASAP (and put back in place) *Bankart Repair - AGHL and labrum repaired *Capsular pattern - tighten capsule to make stronger *Thermal Capsular Shrinkage - Heat and cool capsule to make it shrink
|
|
|
Labral Pathologies and Tears |
*Traumatic or atraumatic *Labrum is like the meniscus in the knee - Dinner plate? *SLAP Lesion - superior labrum anterior - posterior *Types 1-4 -Type 2 (Long head of biceps tears off and 3 (Bucket handle) are most common |
|
|
Labral Pathologies |
|
|
|
Labral Tears |
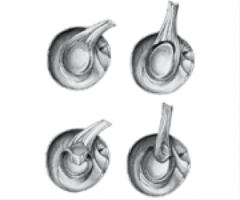
|
|
|
Clavicular Fx |
*Trauma *Midsection of clavicle Falls *Football injuries *Common in teens and older adults |
|
|
AC Joint Seperations |
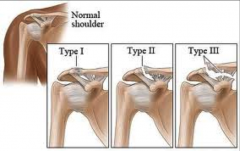
Type 1 - Small Fray Type 2 - Clean Cut Type 3- Tear of Coracoid clavicular
Mumford Procedure - although a lot are not repaired
|
|
|
Long Thoracic Nerve Injuary |
Scapular Winging - Comes from pulling |
|
|
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome |
*Vascular and neutral compression anteriorly causing referral into UP *Structural contributors- cervical ribs (space issue) tight chest muscles, large breasted women *Mechanical contributors - heavy backpack, repetitive overhead use Clinical Presentation?
|
|
|
Elbow |
*Ulnohumeral Joint *Radiohumeral Joint *Promixal radioulnar joint *Middle radioulnar articulation *UCL - ulnar collateral ligament |
|
|
Elbow Anatomy |
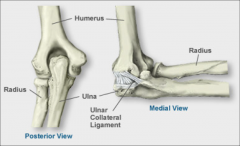
|
|
|
Elbow Fractures |
*Olecranon *Radial Head *Supercondylar humeral fx *General rule for elbow fx: -Non displaced are not surgically repaired - Displaced are surgically repaired |
|
|
Olecranon Fx |
*Body of olecranon fractures off the ulna *Fall onto outstretched arm, direct blow *Post fracture instability changes joint mechanics *ORIF - instability in elbow later on |
|
|
Coronoid Fx |
*Coronoid process of the olecranon *Provides stability *High impact injuries or with dislocation |
|
|
Radial Head Fx |
*Radial head fractures off shaft of radius *MOI- fall onto outstretch shoulder or dislocation *Necessary for stability against value stress *Surgical intervention - mindful of promixal radial migration |
|
|
Elbow Dislocations |
*2nd most commonly dislocated joint *High incidence in children *Fall onto outstretched arm *Fractures commonalty occur with dislocations *Medical intervention- -reduce ASAP -rule out fx |
|
|
Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture |
*Dominant arm, middle aged men *Sudden, forceful overload in midrange flexion *Presentation -Popeye deformity -Forearm weakness -unable to supinate/pronate *Surgical repair- -Has to be repaired, bones can fuse distally |
|
|
Nerve Entrapments |
*Cubital tunnel syndrome - ulnar nerve (causes tingling and numbness) *Common in throwers -2nd most common compression neuropathy to carpal tunnel syndrome, 1st is carpal tunnel -Ulnar nerve trapped under ulnar ligament and flexor carpi ulnaris tendon -causes: trauma, traction of area, compression, sublux of elbow, degenerative changes in age *Presentation- pain along ulnar nerve distribution |
|
|
Cubital Tunnel Sydrome |
Conservative Treatment: Activity Modification Rest Immobilization/elbow stabilized anti-inflammatory meds then surgery: translocation of ulnar nerve |
|
|
Nerve Entrapment |
*Pronator Syndrome - median nerve -Median nerve is entrapped in pronator teres and flexor digitorum profundus -causes: repeated forceful pronation and finger flexion, trauma, compression, gripping and turning -Presentation: pain along median nerve, anterior elbow and forearm, vascular signs (coldness/numbness) no symptoms at night, pain will radiate distally toward the wrist over area near cmc Conservative treatment: Same as Cubital tunnel Surgery: Nerve decompression (create space for nerve to function) |
|
|
Lateral Epicondylitis |
*Tennis Elbow *Most common overuse injury in the elbow *Extensor wad - extensor carpi radialis brevis *Treatment: steroids, PT streching, surgically removing abnormal tissue *Surgery: Releasing structures and introduce healing |
|
|
Radial Tunnel Syndrome |
Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve trapped in extensor carpi radiallis brevis and supinator muscle |
|
|
Medial Epicondylitis |
*Golfers elbow *May also involve ulnar nerve *Causes: Repititive vagistress, tennis (forearm stroke), golf, over head-throwing *Presentation: Tender, pain with resistive testing and passive stretching of involved structures *Treatment: more steroidal injections, not as successful as lateral epicondylitis |
|
|
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Rupture |
*Repitive valgus stress *Overhand throwers (youth especially), tennis, golfers *Presentation: tender over medial epicondyl, pain over medial elbow, pain during throwing, can lead to a rupture of UCL Surgery: Replace the ligament with palmarus longus or extender hallicus ligament |
|
|
Heterotrophic Ossification/Myositis Ossificans |
*Bone formation in nonosseous tissues -Bone where it does not need to be -Surgically: ulnar nerve transposition and removal of bone growth Presentation: pain, swelling, stiffness, loss of ROM
|
|
|
Humeral Fx |
*Typically occur in promixal humerus *Very young or elderly (due to osteoporosis or fracture from fall with an outstretched arm) *Little Leaguer's Shoulder: caused by forceful release *Promixal Humeral Fx |

