![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
when does osteogenesis occur? |

|
|
|
|
when does embryos skeleton start to form? |
6/40 |
|
|
|
what gives rise to bone cells in embryos and name the processes |
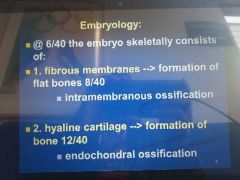
|
|
|
|
in utero what bone is formed? |
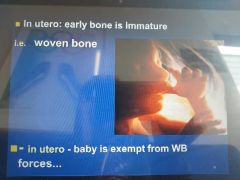
|
|
|
|
why is collagen structured haphazardly in bone in utero baby? |
force in lines of stress but no stress in womb so arranged haphazardly as baby is free floating |
|
|
|
extra info |
epiphysis remain cartilaginous last |
|
|
|
what is ossification absent from? |

|
|
|
|
what happens to bone following birth and why? |
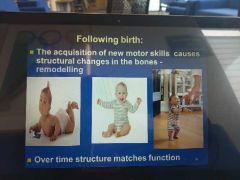
due to increased innervation and motor development so new functions so new forces and in new lines of stress increase bone mineralisation, density of collagen and reorientate osteons to best match function |
|
|
|
2 types of bone growth? |

|
|
|
|
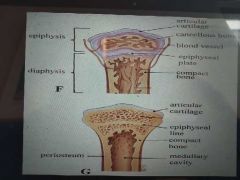
when/where/how does longitudinal bone growth occur? |
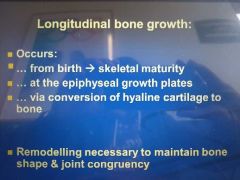
in epiphyseal plate theres chondroblasts which secretes extra cellular matrix of cartilage which is collagen type 2 and non collagenous proteins |
|
|
|
detailed description of longitudinal bone growth? |
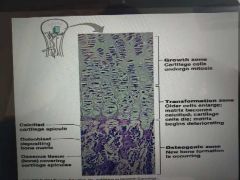
within epiphyseal plate lots of chondroblasts proliferate(mitosis) to produce more chondroblasts which produce cartilage the cartilage is mineralised (calcified) - harden blasts surrounded by mineralised hard extracellular matrix so no blood supply therefore chondroblasts die and cartilage deteriorates cartilage is broken down further and ossified so turn cartilage into bone resulting in elongation of diaphysis resulting in elongation of shaft osteoclasts remove/break down bone inside increasing size of medullary cavity |
|
|
|
what does linear growth depend on? |
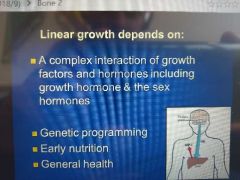
calcium, protein, vitamin D |
|
|
|
what does growth hormone do to growth plate? |
growth hormone causes epiphyseal plate to ossify water hygiene |
|
|
|
epiphyseal plate fractures and complications |
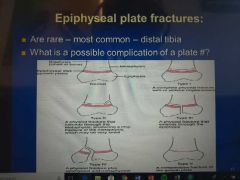
|
|
|
|
what/when and why does appositional bone growth occur? |

|
|
|
|
how does appositional bone growth occur? |
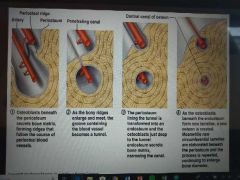
|
|
|
|
reasons for bone remodelling through life? |

|
|
|
|
what is bone remodeling? |

|
|
|
|
balance of cellular activity in bone remodelling - in children? |

|
|
|
|
balance of cellular activity in bone remodelling - in adults? |

|
|
|
|
balance of cellular activity in bone remodelling - in ageing adults? |
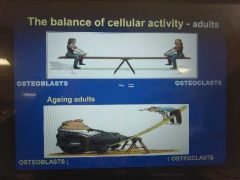
|
|
|
|
what is the remodelling unit? |

|
|
|
|
what controls the remodelling unit? |

|
|
|
|
what is control loop 1? |

|
|
|
|
how does the hormonal loop (Ca2+ homeostasis) control bone remodelling? |
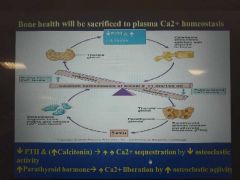
sequestration means deposition |
|
|
|
what is control loop 2? |

|
|
|
|
how does mechanical forces control bone remodelling? |

|
|
|
|
what can the activity of osteocytes and their interaction with the remodelling unit lead to? |

|
|
|
|
are the 2 control loops interdependent or independent mechanisms? |

|
|
|
|
extra info |

|
|
|
|
extra info |

|
|
|
|
wolfs law in action |

|
|
|
|
bone abnormalities (achondroplasia) |
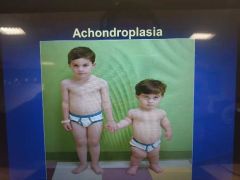
due to gene mutation faulty genetic programming of hyaline cartilage receptors hyaline cartilage doesn't function properly so lack of bone development especially in epiphyseal growth plate
|
|
|
|
bone abnormalities (stunting/dwarfism) |

|

|
|
|
bone abnormalities (stunting/dwarfism) |

|

|
|
|
bone abnormalities (gigantism) |

|
|
|
|
bone abnormalities (acromegaly) |

|

|

