![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
164 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pulp exposure caused by caries occur more frequent in primary than permanent teeth?! |
because primary teeth have relatively 1.large pulp chambers , 2.more prominent pulp horns and 3.thinner enamel and dentin |
|
|
definition of pain type of pain |
unpleasant sensation 1.somatic pain 2.psychogenic pain 3.neurogenic pain |
|
|
pain in sound tooth |
odontolgya D.M Hypertension sickle cell anemia leukemia |
|
|
favorable condition for pulp therapy |
1.Small controllable amount of bleeding 2.Small pin - point exposure surrounded by sound dentine |
|
|
unfavorable condition for pulp therapy |
1.Excessive uncontrollable bleeding 2.Large exposure with watery exudate or pus |
|
|
Radiographic interpretation in children is more difficult than adult .... why ??? |
a ) Periapical changes as widening PDL b ) Rarefaction in supporting bone c ) Calcified masses within pulp chamber and root cannal 4 ) Periapical and interradicular radiolucenies of bone |
|
|
pedia restoration occlusion redaction |
stainless steel crown 1to 1.5 |
|
|
★pulpotomy definition ★pulpoctomy campers |
remove coronal pulp tissue vital teeth reversible pulpitis
remove narcotic pulp tissue non vital teeth irreversible pulpitis
|
|
|
pulpotomy indication 5 contraindications 5 |
1. Deep caries , with vital pulp exposure of primary teeth 2. No history of spontaneous pain 3. Where extraction is contraindication 4. Slight amount of bleeding at exposure site 5. Normal clinical and radiographic signs 1.Radicular pulp involvement 2.Abnormal mobility 3.History of unprovoked pain 4.Presence of fistula or swelling 5.necrotic / irreversible damage pulp 6.Uncontrolled pulp hemorrhage 7.Pathological resorption of pulp |
|
|
Pulpotomy Objectives |
1.Preserve vitality of radicular pulp 2.Amputate infected coronal pulp 3.Treatment remaining pulp with medicament 4.Avoid dystrophic pulpal change Avoid breakdown of periradicular area . |
|
|
Formocresol pulpotomy : It is recommended for |
primary teeth with carious exposure |
|
|
chemical composition Formocresol pulpotomy : |
19 % formalin , 35 % cresol in a vehicle of 15 % glycerin and distilled water . |
|
|
Formocresol & gluteraldehyde |
1.reversible due to week tissue fixative antimicrobial action low toxicity
2.irreversible due to strong tissue fixative bactericidal effect high toxicity root resorption |
|
|
There are two methods for formocresol pulpotomy : |
The one step technique ( one visit technique ) The tow steps technique ( 2 visit technique , Devitalization ) |
|
|
Pulp capping agents have developed along three main lines |
1- Devitalization Formocresol 19,35,15 Electro surgery Laser :
2- Preservation Glutaraldhyde 2-5% Ferric sulphate15.5%
3- Regeneration ca hydroxide 12 MTA 12.5 |
|
|
Formocresol another type |
Glutaraldhyde Ferric sulphate |
|
|
Failures following vital pulp therapy : |
1- Internal resorption : 2 - Alveolar abscess : |
|
|
General contraindications for pulp treatment of primary teeth : |
1 - A patient from family having un favorable attitude towards dental health and conservation of the teeth 2- Tooth , with gross breakdown that restoration would be impossible following pulp treatment 3 - A tooth with caries penetrating the floor of pulp chamber 4 - A tooth close to natural exfoliation 5 - A patient with poor general heath |
|
|
histological change of place ca hydroxide |
★first day -» necrotic zone. ★after week -» fibroblasts. ★after 14 -» odontoblast. ★28 day -» reprative dentine or secondary dentine |
|
|
why we don't Place calcium hydroxide primary teeth?? |
high vascularity |
|
|
used for cutting cavity preparation |
rounded end high speed carbide burs no 329,330,256 245 |
|
|
Treatment is judged successful if there is: |
1- No sensitivity to percussion 2- No history of pain following treatment 3- No radiographic evidence of periapical pathosis or root resorption 4- No clinical evidence of pulp exposure if the tooth was re-entered |
|
|
Direct pulp capping is not encourage in primary teeth because |
pulp tissue ages early and less active undifferentiated mesenchyme cells less active umscs |
|
|
partial pulpotomy It is indicated in primary molars as it is impractical to perform complete pulpectomy in such teeth |
1.difficulty to obtain adequate access to the root canals in the small mouth of children and due to the 2.complexity in morphology of root canals having lateral branching and apical ramifications where removal of all radicular pulp content is impossible. |
|
|
Local anesthesia |
loss of sensation in a circumscribed area not perment damage to nerve endings. |
|
|
properties for a local anesthetic |
1.It should not be irritating to the tissue
2.low systemic toxicity.
3.short time of onset.
4.long duration of action .
5.It should not cause any permanent alternation of nerve structure |
|
|
composition of a local anesthesia agent |
1 - Local anesthesia 2 - Vasoconstrictor 3 - Preservative 4 - Isotonic solution 5 - Preservative 6 - Sterile water |
|
|
commonly used local anesthesia- |
1 ) -2 % lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine , most commonly used 2 ) -4 % articaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine 3 ) -0.5 % bupivacaine with 1 : 200,000 epinephrine- long acting 4 ) -3 % mepivacaine with 1 : 20,000 levonordefrin . |
|
|
كيف تحسب L. A |
maximum dose 4.4 4.4×w.t ÷44 يطلعلك عدد الكربولات كل 10 كيلو كربوله |
|
|
تحويل من باوند الى kg |
÷2.205 |
|
|
upper L. A. buccal side upper L. A lingual side |
posterior superior alveolar n middle superior alveolar n anterior superior alveolar n grater palatine n block posterior teeth naso palatine nerve block |
|
|
1-...... -» short acting 2-...... -» intermediate acting 3-........ -» long acting |
1-Procaine -» short acting 2-Lidocaine -» intermediate acting 3-bupivacaine -» long acting |
|
|
*Ester group* .....،....،...، |
Cocaine Benzocaine Procaine tetracaine |
|
|
*Amide* .....،....،....،...، |
Lidocaine، Mepivacaine، Prilocaine، Etidocaine، bupivacaine |
|
|
بعد تعطي L. A قداش تستنى مش تبدا |
2m |
|
|
شن نديرو irrigation وما نستعملوش؟؟ |
N/S Na chl
hydrogen beroxide attack cardiac problem |
|
|
ART CAT PRR |
Alternative restoration treatment
caries activities test |
|
|
another name of art |
hand instrument technique |
|
|
لما تاخد tetracycline شن الاسنان يلي يصيرلهم discoloration |
. |
|
|
شن الفرق بين padio opaque and radiopsyti |
. |
|
|
lamina dura شن نشوفو فيها في x ray |
. |
|
|
The most common supernumerary teeth 1.is the ...... occur in.....، 2.More in ... than ..... 3.Supernumerary teeth more in .... |
1.misodens 2.palatal midline . maxilla male 2:1 |
|
|
ectopic eruption& gingival eruption |
ectopic eruption يعني سن طالعه ف مكان مش مكانها gingival eruption |
|
|
oral manifestation of down syndrome other name |
crossrmy 21 mangolzm
1.excessive saliva 2.large tongue 3. 4. |
|
|
talon cusp other name ومكانها |
cingulum accessory cusps |
|
|
Is fluoride more in enamel or dentin? وين بزبط E, D, P |
dentine |
|
|
anomalies def |
The primary and permanent dentitions are subject to variation in no . , size & shape of teeth and the structure of the dental tissues |
|
|
These developmental anomalies may be due to...,....,,.... |
1.Genetic factors . 2.Environmental ( systemic or local ) 3.Combination factors . |
|
|
Abnormalities of tooth number : والسبب |
➤ Hyperdontia ( Supernumerary teeth ) ➤ Hypodontia . Result from problems during the initiation of dental lamina stage of dental development producing extra or missing teeth |
|
|
Abnormalities of tooth size : |
Crown size macrodontia ( gemination & fusion Microdontia ( peg shape lateral incisors )
Root size . Large root size 3|3 Small root size 5-2-1|1-2-5 |
|
|
Abnormalities of tooth shape |
1.Crown shape . 2.Accessory cusps . 3.Invaginated teeth 4.Evaginated teeth |
|
|
Abnormalities of root shape : |
1.Taurodontism . 2.Accessory roots . 3.Pyramidal roots . |
|
|
Abnormalities of tooth structures |
Enamel defect . Dentin defect . Cementum defect . |
|
|
Supernumerary teeth classified morphologically into : 1.. 2.. |
Supplemental . Rudimentary |
|
|
Supernumerary teeth classified according to location into : |
Mesiodens . Para molars . Distomolars . |
|
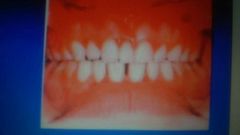
|
supplemental supernumerary |
|
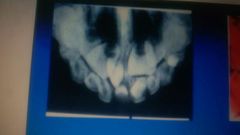
|
mesiodens |
|
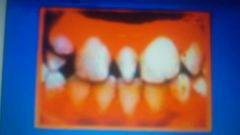
|
mesiodens |
|
|
Supernumerary teeth classified according to shape into : |
1.Conical . 2.Tuberculate ( multicusped ) . 3.Supplemental 4.Odontome like types . |
|
|
Tuberculate means?? (........ ) . |
multicusped |
|
|
Supernumerary teeth mostly impacted & never erupt & seen by radiograph |
T |
|
|
The commonest cause of delay eruption of a maxillary central incisors is ...... |
the presence of a mesiodens palatally . |
|

|
mesiodens |
|
|
Supernumerary teeth are more with 1... 2... 3.... |
1.Palatal clefts 2.Cleidocranial dystosis 3.Gardenn's syndrome |
|
|
Treatment of supernumerary teeth . |
1.Extraction 2.Surgical removal of impacted supernumerary teeth . |
|
|
Anodontia-means |
Absence of all teeth |
|
|
Oligodontia- means? |
Absence of most teeth |
|
|
Hypodontia in primary teeth is more in the ........ in permanent teeth occur in the 1.... 2.... 3.... |
★maxilla ( ( mostly lateral incisors )
3rd molar 2nd mandibular premolar maxillary lateral incisors ) |
|
|
congenital missing teeth |
8-2|2-8 8-5|5-8 |
|
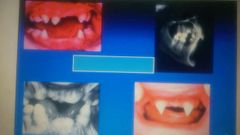
|
Hypodontia |
|
|
Hypodontia are mostly with : |
1.Ectodermal dyplasia 2.Cleft lip & palate . 3.Down's syndrome . |
|
|
Treatment of Hypodontia |
Prosthodontics . Orthodontics |
|
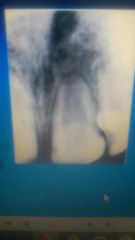
|
macrodontia |
|
|
1.Fusion and gemenation are the most common twinning abnormalities and both demonstrate enlarged teeth . 2.double teeth |
Macrodontia |
|
|
fused teeth can contain two separate pulp chambers |
T |
|
|
Fusion : Common in |
primary dentition . |
|
|
Represent incomplete division of single tooth bud that result in single pulp chamber |
gemenation |
|
|
To differentiate between fusion & gemenation by |
counting no of teeth in the arch if there's deficiency means fusion . |
|
|
Treatment of macrodontia : |
Extraction of double teeth & supernumerary teeth |
|
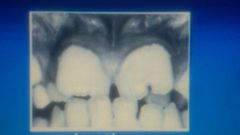
|
Double teeth gemination |
|
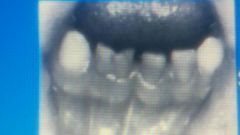
|
fusion |
|
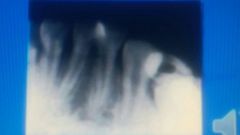
|
fusion |
|
|
Microdontia are common in... shape teeth? |
Peg shaped lateral incisor Down's syndrome . |
|
|
treatment of microdontia |
1.Extraction of primary teeth 2.Orthodontics . 3.Restoration by composite or porcelain veneer |
|
|
Accessory cusps More common in .... 1.primary dentition... 2.permanent dentition... |
1.More common in primary & permanent teeth.
2.In primary dentition the most common teeth are Mesiobuccal aspects D¦D upper Mesiopalatal aspects E¦E upper
3.In permanent dentition cusps of carabelli of 1 " permanent molar . |
|
|
Permanent Incisor additional cusps arising from the lingual cingulum More in |
maxilla than mandible . |
|
|
Treatment of accessory cusps |
1. grinding of cusps .. 2. removal of cusp& pulpotomy |
|
|
invagenated teeth حاجه مميزه اسم غريب.. in.. more common in.... males or female clinical features..,...,.... patients complain of ...,... |
dens in dente More in upper permanent incisors particularly the lateral incisors . Males more affected than females 1.Enamel lining incomplete 2.dentine missing 3.bacterial spreading into the pulp . Patient complain of 1.acute facial cellulitis 2.acute dentoalveolar abscess |
|
|
treatment of invagenated |
Antibiotic therapy Endodontic treatment Surgical removal |
|
|
Evagenated teeth : seen in.... other teeth may affected...,... may lead to...,...,.. |
Seen in premolar teeth. molar or canine This may lead to 1.pulpal exposure - 2.periapical infection 3.necrosis infection |
|
|
treatment of evagenated teeth |
1.grinding of the tubercle . 2.Pulpotomy 3.Restoration of tooth . |
|
|
Dens evaginatus . Tuberculated teeth see in.... |
evagenated teeth |
|
|
Invaginated primary teeth are rare . |
T |
|
|
Taurodontism "" means "" common, uncommon found with...,... |
Multirooted teeth . Uncommon in primary teeth . = Permanent dentition molar more affected . Taurodontism found with a 1.amelogensis imperfecta , 2.ectodermal dysplasia |
|
|
Accessory roots means..... primary teeth.......,... permanent teeth....,... |
Excess in no . of roots . Branched roots in primary Accessory roots in maxillary primary incisors & molars . In permanent teeth _ upper incisor & upper canines . |
|
|
Branched roots in primary roots |
t |
|
|
Pyramidal roots means treatment....,... |
Fused roots RCT extraction |
|
|
Enamel defects 1...., 1...., 2.... 2.... |
1.Hypoplasia deficient matrix enamel thin , grooved , or pitted 2.Hypomineralization. poor mineralization mottled enamel |
|
|
other name of fluorosis? |
mottled enamel colorado stain |
|
|
شخص ياخد ف tetracycline لون سنونه iron |
yellow, brown |
|
|
الاخطر بين chronic and acute |
acute لانه sudden onset large does lead to toxicity to cardiac arrhythmia |
|
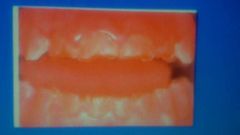
def more affect in.. than.. color |
dentinogensis imperfecta. primary bluish or brownish |
|
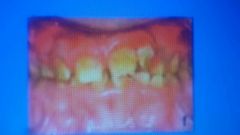
def color affect features |
amelogensis imperfecta
yellow to yellow brown
all dentition
hypoplastic Hypomineralization hard shiny |
|
|
Hypoplasia or hypomineralization of the enamel may affect the incisal portion of crowns of the primary teeth ( incisors ) . |
t |
|
|
Neonatal disorder in children born at term may lead to enamel defects in the primary dentition and 1st permanent molars . |
t |
|
|
Amelogenesis may be disturbed by the excessive Chronic ingestion of fluoride . |
tt |
|
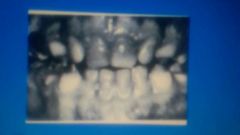
def |
enamel hypoplasia in primary dentition |
|
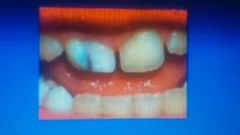
def causes |
localized enamel hypoplasia due to trauma in primary teeth |
|
|
Hypomaturation كأنها.... منو يلي اكتر والاسنان يلي تخبطهم.....،... |
Snow capped teeth . Incisal portion of anterior teeth are affected and to the occlusal portions in posterior teeth . The affected areas of the crown are mottled with opaque white enamel . Maxillary teeth more involved than mandibular teeth . the maxilla incisors & canine are commonly affected . |
|
|
precipitation factors of hyperthyrodism crisis |
1.infection 2.trauma 3.surgical 4.stress |
|
|
لو قسنا نبض البيبي ف بطن امه وطلع 120 شن بيكون عنده الطفل هذا؟؟ |
cretinism |
|
|
asthmatic patients avoid use asprin and ibrufen
|
لان بيدير v.c inter luken 1 |
|
|
hemophilia avoid aspirin شن نعطو افضل شي |
codeine |
|
|
disease all laperatory investigation abnormal |
polycythemia rubra vera |
|
|
الفرق بين coma, crisis |
coma means loss of consciousness crisis means exaggerated of attack |
|
|
Recognition of initial stage of hypothyroid ( myxedema ) coma |
- Hypothermia - Bradycardia - Hypotension - Epileptic seizures . |
|
|
Start immediate treatment of myxoedema coma |
1.Seek immediate medical aid 2.Hydrocortisone ( 100-300 mg ) 3.CPR as indicated . |
|
|
Oral Complications -hyperthyrodism |
Increased in tongue size • Delayed eruption of teeth • Malocclusion Gingival edema |
|
|
other name of thhrotoxic crisis |
thyroid storn |
|
|
Recognition of early stages of thyrotoxic crisis - |
1.Severe symptoms of thyrotoxicosis -2.Febrile 3.-Abdominal pain 3.-Delirious , obtunded or psychotic |
|
|
Oral Complications throtoxic crisis |
Osteoporosis Early eruption of permanent teeth Early shedding of deciduous teeth Early jaw development |
|
|
EACA DDAVP |
epsilon amino caproic acid حمض إبسيلون أمينو كابرويك 1 - desamino - 8 - darginine vasopressin ( DDAVP ) |
|
|
.anisocytosis - ...... Poikilocytosis- .... |
irregular is size
irregular is shape |
|
|
rapid screening methods |
1.Dextrostic - blood 2.Clinistix- glycosuria by the patient . 3.impaired fasting glucose - 110 < 126 mg / dl 4.impaired glucose tolerance - 140 < 200mg / dl |
|
|
.glycosylated hemoglobin : - |
< 7 % no diabetic 7-9 % patient control > 10 % patient not control |
|
|
شن المرض يلي يجي ل الاطفال وكل ما يكبر الطفل يختفي المرض؟؟ وكل التحاليل نورمال |
benign hemorrhagic telangiectasiasa |
|
|
other name of anemia 1... 2... 3... |
pulmmer vension syndrome patterson kelly syndrome microcytic- hypochromic anemia |
|
|
oral manifestation of deficiency anemia |
1.sore mouth 2.glossitis 3.In rare cases infection and bleeding complications → 4.pallor of oral mucosa . 5.slow wound healing 6.Angular cheilitis |
|
|
CBC |
complete blood coat |
|
|
Hg<10g/dl |
contraindications G.A |
|
|
addison anemia and addison disease |
★addison anemia malabsorption of vit b12 ★addison disease insufficiency of adrenal gland |
|
|
addison anemia اسمها تاني |
pernicious anemia |
|
|
schilling test used in |
pernicious anemia |
|
|
tourniquent test contraindications in..... and why?? |
SCA, precipitate crisis |
|
|
elliptic attack time?? last for |
30s to 2 minutes |
|
|
angina MI شن نعطوهم |
glycerin trinetrit sublingual morphen salfet 15mg im |
|
|
Best prolonged media for avulsion tooth?? |
green tea |
|
|
avulsion tooth?? means |
complete loss of tooth, displasment of tooth out alvolar or out scok |
|
|
وين نعطو L. A ف الاطفال |
below ooclusal plane in child |
|
|
لو خديت L. A وقعدت تنمل لفتره طويله شن تعطيه |
vit b12 & b complex 2 weeks |
|
|
material of choice for pulp capping is |
hard setting ca hydroxide |
|
|
formocrresol contraindications in child due to?? |
carcenogeni |
|
|
Formocresol used in pulpotomy causes |
mummification or fixation of all radicular pulp |
|
|
لو كنت ندير ف pulp capping وطلع دم هلبا هذر يعني فيه مشكله ف الجذر واللتهاب ويحتاج الى...؟ |
need to pulpotomy |
|
|
MTA ph def |
mineral trioxide aggregate 12.5 |
|
|
indirect pulp capping objectives, indications and contra |
objectives, indications and contra |
|
|
histological change after pulp capping?? |
. |
|
|
ph of ca |
12 |
|
|
final restoration in procedures of apecifications?? |
amalgam |
|
|
apexification & apexogenesis ?? وكيف تسكرهم |
non vital permanent teeth open apex.
apical closer by ca hydroxide, MTA vital pulp with open apex use splint&RCT. |
|
|
dental caries |
microbial disease due to destruction of organic and inorganic, demeniralization of tooth structure |
|
|
ideal restoration for pulpotomy |
stainless steel crown |
|
|
pt 5y badly decay treatment?? |
exto-space mentiner |
|
|
aspirin contraindications in child under 12y? asthmatic pt? pregnancy? Epola? |
1.ray's syndrome. 2.respiratory depression 3.obartion late dilevary. 4.toxic and bleeding |
|
|
oral manifestation of leukemia?? |
lymphadenopathy candidosis infection bell's palsy mobility of tooth enlarge of parotied gland trigemenal nurolgia gingival, bleeding, ulcers, enlargement ecchymosis, petechia |
|
|
CSC |
care for special child needs |
|
|
preferred material used in apexification?? |
non setting CA (OH) 2 |
|
|
material of choice in pulp capping |
hard setting ca hydroxide |
|
|
SSCs |
stainless steel crown |
|
|
most effective pulp capping agent |
ca hydroxide |
|
|
pulpotomy 3 processes |
one visit 2 visit 3visit نسموها mortal pulpotomy يعني بنحولوها من vital to non vital لو bleeding ما وقفش بعد 2m |
|
|
pulpoctomy procedure |
. |
|
|
partial pulpoctomy |
1.L.A with isolation by rubber dam
2.remove coronal pulp tissue زي pulpotomy
3.remove as much as possible form root canals with brabed broaches. proferation حاول ماديرش
3.irrigation canals by n/s
4.dry canals by sterile p.p
5.obturate the canal with ZOE used condenser to condens material in to canal
6.final restoration |
|
|
pulpoctomy امتى تشتغلها 1visit multi visit |
uncooperative patient. cooperative patient. |

