![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition |
a market in which there are many buyers & sellers, the products are homogeneous & sellers can easily enter/exit from the market |
|
|
Characteristics |
- large number of buyers & sellers - homogenous/standardized product - free of entry & exit - role of non-price competition - perfect knowledge of the market - absence of transport cost |
|
|
Price determination |
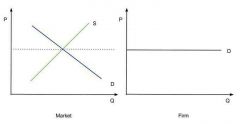
- intersection of the market supply curve & market demand curve - since firms are price takers, they face a horizontal demand curve (perfectly elastic) |
|
|
Profit maximization in the SR: economic profit |
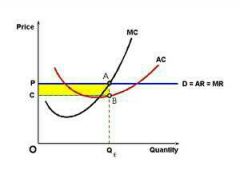
- TR > TC - P > ATC - profit maximization point is when MR=MC - TP = TR - TC = (P × Q) - (ATC × Q) - profit area is PABC |
|
|
Profit maximization in the SR: economic losses |
- TC > TR - ATC > P, firm would not be able to cover its costs - it can still continue its operation until P=minimum AVC (shut down point) - if P < AVC, firm will stop the production & exit the market since it will be unable to cover its fixed cost |
|
|
Profit maximization in the LR: effect of entry |
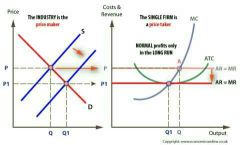
- normal profit in long run (effect of free entry & exit) - economic profit in SR attracts newcomers - adjustment of price continues until profit is eliminated |
|
|
LR supply curve: constant-cost industry |
- input prices are constant as the output increases or industry expands in LR - firm increases output where MR=MC - firm earns economic profits that attracts newcomers & increase the market supply - LR supply curve is horizontal |
|
|
LR supply curve: increasing-cost industry |
- input prices increase as the output increases or industry expands - firm increases output where MR=MC - firm earns economic profits that attracts newcomers & increase the market supply - in the increasing-cost industry, input prices rise as the output expands, ATC shifts upwards - LR supply curve is upward sloping |

