![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
External Oblique |
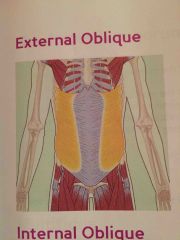
Back (Definition) |
|
|
A squat, curl, to two arm press exercise is an example of an exercise from which phase in the OPT model? |
Strength |
|
|
Periodization |
The dividing of a training program into smaller, progressive stages |
|
|
What is a goal of phase 5: power training? |
Enhance neuromuscular efficiency |
|
|
What is neuromuscular efficiency? |
Ability of neuromuscular systems to enable all muscles to efficiently work together in all planes of motion |
|
|
What is the best example of performing an exercise in a proprioceptively enriched environment? |
Dumbbell chess press on stability ball |
|
|
What is the immediate profession of the two-arm ball squat, curl to press exercise? |
Alternating-arm ball squat, curl to press. |
|
|
What is the proper method of progression for the stabilization phase? |
Proprioception |
|
|
Which is a regression of the two-leg, alternating-arm stable cable row exercise? |
Seated cable row exercise |
|
|
Metabolic specificity |
The energy demand placed on the body |
|
|
What are the three planes of motion? |
Frontal, Sagittal, Transverse |
|
|
What are the three planes of motion? |
Frontal, Sagittal, Transverse |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
Right and Left plane Forward and backward motion Flexion/extension |
|
|
Frontal Plane |
Front and Back Side to side or lateral motions |
|
|
Transverse Plane |
Top and bottom half Rotation motions |
|
|
Isotonic |
Force is produced, muscle tension is developed, and movement occurs through a given range of motion |
|
|
Isotonic |
Force is produced, muscle tension is developed, and movement occurs through a given range of motion |
|
|
Eccentric (muscle action) |
Moving in the same direction as the resistance. Decelerates or reduces force
|
|
|
Concentric (muscle action) |
Moving in opposite direction of force. Accelerates or produce force. |
|
|
Isometric (muscle action) |
No visible movement with or against resistance. Dynamically stabilizes force. |
|
|
Isokinetic (muscle action) |
The speed of movement is fixed, and resistance varies with force exerted |

