![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
587 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following activities illustrates the administrative role assumed by an HR professional?
a. Filling out EEO reports b. Implementing the grievance process for an employee threatened with termination. c. Evaluating the bottom-line contribution of HR programs. d. Conducting an interviewing seminar for line managers.
|
a. Filling out EEO reports |
|
|
Which of the following activities illustrates the operations role played by an HR professional?
a. Ensuring currency of employee records. b. Conducting recruitment for new job openings. c. Forming contacts with key individuals outside the organization. d. Developing criteria for selecting supply chain partners. |
b. Conducting recruitment for new job openings. |
|
|
Which of the following examples illustrates the strategic role played by HR today?
a. Securing off-site backup and storage of employee transactions and records. b. Developing a system to track the number of people leaving the organization. c. Creating a training program for conducting safe and legal terminations. d. Working with senior and line managers to forecast workforce needs for the next five years. |
d. Working with senior and line managers to forecast workforce needs for the next five years. |
|
|
Which of the following best illustrates the way in which HR's strategic role has transformed its operations role?
a. Upgrading an HRIS system. b. Establishing relationships with key decision makers throughout the organization. c. Taking a more active role in responding to employee complaints. d. Analyzing job descriptions for changes to required skills that will affect recruitment and selection decisions. |
d. Analyzing job descriptions for changes to required skills that will affect recruitment and selection decisions. |
|
|
The impact of demographic changes on HR is best illustrated by which of the following?
a. Need to learn more about local legislation and rule-making process. b. Survey adequacy of existing organization communication vehicles for all employees. c. Establishment of employee self-service centers. d. Evaluating ethical liabilities posted by supply chain partners. |
b. Survey adequacy of existing organization communication vehicles for all employees.v |
|
|
Which of the following statements about SOX is true?
a. It applies to all companies, no matter their size or whether they are publicly or privately held. b. It relates primarily to compensation for high-level executives. c. It has little direct effect on HR. d. It addresses both insider training and whistleblowing activities. |
d. It addresses both insider training and whistleblowing activities. |
|
|
The supply chain is an example of:
a. flexible internal organization boundaries. b. a tendency to draw core competencies back into the organization. c. an extended organization. d. an organizational structural change required by lean manufacturing principles. |
c. an extended organization. |
|
|
A software company is considering the acquisition of a training company that will provide documentation and training support for its key customers. The company begins a due diligence investigation. Which of the following items will have the LEAST impact on the due diligence process?
a. Obligations to retirement plans b. History of OSHA complaints c. Strategies to integrate compensation and benefit systems. d. Cultural fit of the two companies. |
b. History of OSHA complaints |
|
|
HR can best prepare for a strategic role by
a. enhancing its ability to demonstrate return on investment. b. expanding the size of the HR function c. focusing on ways to cut production costs throughout the organization. d. centralizing HR activity for greater consistency and control |
a. enhancing its ability to demonstrate return on investment. |
|
|
Which of the following best describes a business case?
a. Cost-benefit analysis of business concept b. Market research into acceptability of a new service or product. c. Scenario-based test of a business plan. d. Analysis of a problem and of possible solutions. |
d. Analysis of a problem and of possible solutions. |
|
|
Which phase of a project's life cycle is most labor intensive?
a. Problem definition b. Project planning c. Implementation d. Evaluation |
c. Implementation |
|
|
The PRIMARY priority of a project manager who is exhibiting the interpersonal role is
a. disseminating information and helping team members. b. building team norms and fostering harmony c. allocating resources d. negotiating differences and monitoring project progress |
b. building team norms and fostering harmony |
|
|
Which of the following is the MOST important role HR can play in a major change initiative?
a. Communicate regularly with employees. b. Assume responsibility for implementing the change. c. Question whether the change is needed. d. Counsel people who are upset by the change. |
|
|
|
What is the FIRST step in locating a third-part vendor to handle an employee assistance program?
a. Create an RFP b. Conduct on-site visits c. Analyze needs and define goals d. Contact potential vendors |
c. Analyze needs and define goals |
|
|
Which one of the following HR activities should NOT be outsources?
a. Payroll administration b. Creation of online employee manuals c. Relocation programs for employees d. Development of goals and strategies for improving workforce skills. |
d. Development of goals and strategies for improving workforce skills. |
|
|
Which of the following trends in technology has occurred in business management in the last decade?
a. Mobile computing b. Stand-alone IT systems for functions within an organization c. Less vulnerability to exterior threats d. Less retention of data |
a. Mobile computing |
|
|
Which of the following is an example of strategy development?
a. A company allocates resources to enable it to reach a new market for its products. b. A company decides to market its products internationally c. A company motivates employees to increase international sales d. A company decides to cut back on its international advertising campaign. |
b. A company decides to market its products internationally |
|
|
A mission statement does NOT need to include
a. what the company does b. time frame for completion c. where the company is headed d. who its customers are |
b. time frame for completion |
|
|
An organization hires only experienced, top-performing people who tend to stay with the company for ten years or more. An organization would consider this situation a(n)
a. Strength b. Weakness c. Opportunity d. Threat |
a. Strength |
|
|
A paper products company divides its business into commercial and consumer divisions. The commercial division decides to expand its market share by forming key account teams to provide its most important customers with better service. This is an example of.
a. Organizational strategy b. Business unit strategy c. Corporate vision. d. Functional strategy. |
b. Business unit strategy |
|
|
A short-term objective is generally completed within
a. one month b. six months to one year c. one to two years d. three to five years |
b. six months to one year |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of strategy evaluation?
a. Take corrective action. b. Identify threats or opportunities c. Measure organizational performance. d. Determine which people are not performing well. |
b. Identify threats or opportunities |
|
|
An organization's debts are referred to as its
a. assets. b. liabilities. c. equities. d. receivables. |
b. liabilities. |
|
|
A company that increases recruitment and selection efforts to staff new positions is in which phase of organizational development?
a. Introduction b. Growth c. Maturity d. Decline |
b. Growth |
|
|
A company that emphasizes training to maintain workforce flexibility and improve productivity is in which phase of organizational development?
a. Introduction b. Growth c. Maturity d. Decline
|
c. Maturity |
|
|
Which of the following actions might be a likely way to increase employee engagement?
a. Promote a higher degree of managerial control b. Pay higher wages c. Explore employee values and needs d. Use a flat organizational structure |
c. Explore employee values and needs |
|
|
An employee who designs and develops sales training programs reports to both the executive vice president of sales and the vice president of HR. This is an example of what type of organizational structure?
a. Functional b. Divisional c. Matrix d. Task |
c. Matrix |
|
|
Which of the following describes the competitive strategies of an organization committed to differentiation?
a. Controlling costs, retaining key people, determining compensation strategy, and cross-training employees. b. Exploiting all economies of scale and focusing on low-cost production to the exclusion of everything else. c. Positioning unique product characteristics that customers will value and pay a premium price for. Formalizing policies, procedures, and rules and communicating them to all employees |
c. Positioning unique product characteristics that customers will value and pay a premium price for. |
|
|
Which of the following has the GREATEST effect on wages and pensions?
a. Consumer price index b. Amount of disposable income c. Trade agreements d. Inflation |
d. Inflation |
|
|
Which of the following statements about the global economy is NOT correct?
a. The combined economies of Brazil, Russia, India and China may eclipse the US economy by 2020. b. Western European economies will provides most of the economic growth in the coming decade. c. Global alliances among organizations will become more common. d. Growth in the global economy is fueled by middle class growth |
b. Western European economies will provides most of the economic growth in the coming decade. |
|
|
Considering technological developments, which of the following is true?
a. Employee productivity has decreased. b. The costnof Internet access will increase considerably in the future. c. Introduction of new technologies will lower the stress level of workers. d. Technology will allow organizations to provide 24-hour services to their customers. |
d. Technology will allow organizations to provide 24-hour services to their customers. |
|
|
Which of the following statements regarding labor force trends is NOT correct?
a. Lower birthrates in the 1960s and 1970s, combined with recent medical advances will leave us with an aging workforce. b. Generation X workers are fast becoming managers c. Entry-level jobs filled by immigrants and high school dropouts will require less training in the future. d An increasing number of service jobs will be created, while manufacturing jobs will decline. |
c. Entry-level jobs filled by immigrants and high school dropouts will require less training in the future. |
|
|
Which of the following is the BEST data to refer to when designing retention strategies?
a. Differences between Generation X and Generation Y. b. Advances in technology c. Turnover trends d. Unemployment rates |
c. Turnover trends |
|
|
Which of the following demographic trends is predicted?
a. More people with disabilities will be actively recruited to enter the workforce. b. Dual-career families will decrease c. Asians will become the largest minority group within the next five years. d. Unions will continue to focus on traditional membership sources. |
a. More people with disabilities will be actively recruited to enter the workforce. |
|
|
For which of the following situations would a cost-benefit analysis be an effective metric?
a. An organization wants to compare its productivity with that of similar competitors b. A function is seeking budget to hire new staff c. An investor is seeking information about a company's financial performance. d. An HR function wants to confirm that its complying with legal and regulatory requirements |
b. A function is seeking budget to hire new staff |
|
|
A major reason to use a balanced scorecard to measure strategic progress is that this approach
a. provides a more rounded assessment of the results of strategic activity. b. can be accomplished quickly. c. extends protection against legal risks to organizations. d. can be repeated periodically. |
a. provides a more rounded assessment of the results of strategic activity. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about audits is true?
a. They must conform to certain legal restrictions. b. They must be completed by objective third parties. c. They must be repeated to be reliable. d. They can produce legal implications due to findings and subsequent actions |
d. They can produce legal implications due to findings and subsequent actions |
|
|
A company requires job applicants to are applying for a position in their distribution center to take a lifting test. Test results are consistent, and the test measures what it is intended to measure. This test is considered
a. reliable b. valid c. neither reliable nor valid d. both reliable and valid |
d. both reliable and valid |
|
|
Which of the following reliability measures is most useful to an organization that requires managers to participate in assessment center activities?
a. Rater agreement b. Parallel forms c. Internal consistency d. Test/retest |
a. Rater agreement |
|
|
Which measure of variation shows how scores are spread out around a mean?
a. Range b. Percentile c. Standard deviation d. Mode |
c. Standard deviation |
|
|
If the correlations coefficient between two numbers is +1, it means that as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other
a. increases. b. decreases. c. stays the same. d. cannot be predicted. |
a. increases. |
|
|
An HR professional sends a survey to 500 of 10,000 employees. This is known as a
a. population. b. sample. c. standard deviation. d. normal distribution. |
b. sample. |
|
|
What is the PRIMARY benefit of appointing a chief ethics officer?
a. Other managers in the organization do not have to handle ethical issues. b. It reduces the number of employee complains and dispute resolution sessions. c. Legal counsel does not need to be consulted on ethical issues. d. It allows for consistent communication of values and standards to the organization. |
d. It allows for consistent communication of values and standards to the organization. |
|
|
You are an expatriate manager in a developing country and are having difficulty with timely shipments to the U.S. Local nationals explain that customs officials will expedite shipments if they are given cash payments. Your company has a policy against offering bribes. What is the BEST course of action?
a. Adhere to local practice and offer cash payments to customs officials. b. Have a local national handle all shipping arrangements. c. Adhere to your company's policies and look for other solutions to your problem. d. Ask the company for special dispensation from corporate policies. |
c. Adhere to your company's policies and look for other solutions to your problem. |
|
|
In light of SOX expectations of boards of directors, the following are all examples of poor practices EXCEPT
a. A director does not understand the detailed accounting tactics used in structuring an executive compensation package. b. A fellow director sleeps through many presentations at meetings. c. The CEO appoints a director not because of qualification but because she is a childhood friends d. A director cannot describe what the company does an how it makes money |
a. A director does not understand the detailed accounting tactics used in structuring an executive compensation package. |
|
|
The MOST effective corporate citizenship program is one that
a is tied to the company's strategic plan. b. requires involvement of less-senior employees. c. has no relationship to the company's bottom line. d. creates visibility for the company |
a is tied to the company's strategic plan. |
|
|
Early in its session, Congress passes a bill and sends it to the president. The president takes no action for ten days. What becomes of the bill?
a. It is automatically dead, since it has not been signed. b. The bill becomes law since Congress is still in session. The bill is sent back to Congress and passes if a two-thirds majority votes for it. d. The bill passes automatically if Congress adjourns immediately after passing it. |
b. The bill becomes law since Congress is still in session. |
|
|
Which of the following is the BEST example of a regulation?
a Civil Rights Act of 1964 b. Fair Labor Standards Act c. Interpretation of legal matters related to expatriation d. Process by which the Department of Labor clarifies the exempt status of employees. |
d. Process by which the Department of Labor clarifies the exempt status of employees. |
|
|
Process that helps an organization focus on how to succeed in the future by evaluating the organization's current status, where it would like to be, and how to get there. |
Strategic Planning |
|
|
These describe what is important to an organization, dictate employee behavior and create the organization's culture. |
Values |
|
|
This is a vivid, guiding image of an organization's desired future. |
Vision Statement |
|
|
This specifies what the organization does, who its customers are, and the priorities it has set in pursuing its work. |
Mission Statement |
|
|
This is the process for evaluating an organization's current strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. |
SWOT analysis |
|
|
These are specific results, to be accomplished in three to five years, that an organization seeks to achieve in pursuing its mission. |
Long-term objectives |
|
|
These provide the direction that enables an organization to achieve its long-term objectives. |
Strategies |
|
|
These serve a purpose similar to short-term objectives but are completed in one to two years. |
Mid-term objectives |
|
|
These are milestones that must be achieved, usually within six months to one year, in order to reach long-term objectives. |
Short-term objectives. |
|
|
These are detailed steps a unit, department or team will take in order to achieve short-term objectives. |
Action plans |
|
|
What are the four Organizational Development phases? |
1. Introduction 2. Growth 3. Maturity 4. Decline |
|
|
What are Michael Porter's 3 Competitive Strategies? |
1. Cost leadership 2. Differentiation 3. Focus |
|
|
An organization focused on _____________ strategy, is focused on optimizing processes for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness. |
Operational excellence |
|
|
By implementing the ________________ strategy, an organization achieves a competitive edge by always being out front -- having the newest and most innovative products and service. |
Product leadership |
|
|
Organizations that implement the _______ strategy offer a unique range of services, from education to personal help, so that the customer can get the most out of their products/services. |
Customer intimacy strategy |
|
|
__________ strategists believe that the most rewarding opportunities lie outside the conventional market boundaries -- in the middle of the deep, blue sea, far from familiar landmarks, with no one else around to bother your fishing. |
Blue ocean |
|
|
This advantage is common for organizations that rely on knowledge workers and rely on their employees knowing more, seeing more opportunities and acting faster. |
Human capital advantage |
|
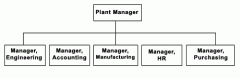
In this organization structure, departments are defined by what services they contribute to the organization's overall mission, such as marketing, sales, operations and HR. |
Functional structure |
|
|
The ________ structure is generally more decentralized than the functional one because divisions are separated on the basis of product, customer or market, or region. |
Divisional structure |
|
|
The ________ structure combines departmentalization by division and function to gain the benefits of both. It creates a dual rather than a single chain of command. |
Matrix structure |
|
|
This term refers to the number of individuals who report to a supervisor. If too large, organizations can be slowed and supervisors have difficulty making decisions quickly. Decisions, once made, can be communicated more quickly, however, |
Span of control |
|
|
________ serves an organization well when uniformity is imperative. Individuals are expected to follow policies and procedures; they have little discretion over how to perform their work. |
Formalization |
|
|
_________ is a process that involves a systematic survey and interpretation of relevant data to identify external opportunities and threats and to assess how these factors affect the organization currently and how they are likely to affect the organzation in the future. |
Environmental scanning. |
|
|
The seven factors that affect the external environment |
1. demographic 2. economic 3. employment 4. international 5. political 6. social 7. technological |
|
|
The balanced scorecard approach was designed to provide a concise yet overall picture of an organization's performance as measured against four key areas and from the perspectives of various stakeholders. The 4 key areas assessed in a balanced scorecard are: |
1. Finance 2. Customers 3. Internal business processes 4. Learning and growth |
|
|
KPI stands for |
Key performance indicators. These are quantifiable measures of performance used to gauge progress toward strategic objectives or agreed standards of performance. |
|
|
Revenue growth, cost reduction, growth in a particular division or capturing key accounts are examples of __________ KPIs. |
Financial |
|
|
A _________ KPI might be measured by factors like the number of return customers, error rates in fulfilling orders or customer satisfaction ratings. |
Customer |
|
|
For this KPI, key processes are monitored to ensure that outcomes will be satisfactory. Specific process measures will vary by business |
Internal business processes |
|
|
This KPI perspective looks at the ability of employees, the quality of information systems, and the effects of organizational alignment in supporting accomplishment of organizational goals. |
Learning and growth |
|
|
The 3 steps to implementing a balanced scorecard system are: |
1. Planning the process 2 Designing the scorecard 3. Employing and refining measures |
|
|
This measurement involves comparing the dollars spent on pay and benefits to an adjusted profit figure |
Human capital ROI |
|
|
The average cost when an employee leaves is: |
Turnover |
|
|
The percentage of an organization's revenues that are allocated to the direct costs of employees. It accounts for only on-payroll employees. |
Compensation as a percentage of operating expense. |
|
|
This measurement looks at the organization's total investment in building basic skills and improving individual productivity. |
Training investment factor |
|
|
This involves measuring the time from approval of requisition until someone is on the job. |
Time to start |
|
|
This is the organization's cost of finding and selecting quality human capital. |
Cost per hire |
|
|
The four steps HR must perform in the M & A process are: |
1. Prepare for M & A 2. Perform due diligence 3. Plan integration 4. Implement, monitor and measure |
|
|
The 4 steps in Project Management are: |
1. Define problem and gain support 2. Plan project 3. Implement project plan 4. Monitor, control and adapt 5. Evaluate outcomes |
|
|
The 3 roles of a Project Manager and examples are: |
1. Interpersonal: Leader/Liaison 2. Informational: Communicator/Information Disseminator 3. Decisional: Conflict resolver/Resource allocator |
|
|
This is an essential tool when competing for limited organizational resources. The steps to create one include a statement of the problem, objectives, potential solutions, project timeline and project metrics. |
A Business Case |
|
|
This project planning tool is also known as horizontal bar chart, milestone chart, or activity chart.
It plots the sequential steps of a project against time. |
Gantt Chart |
|
|
This project planning tool is an arrow diagram or road map identifying all major events.
Shows how much time is needed to complete a project. |
PERT Chart |
|
|
5 common steps in a Change Management model are: |
1. Create awareness of a need for change 2. Create vision 3. Facilitate change 4. Motivate employees 5. Incorporate change into culture and structures |
|
|
A company must immediately downsize its workforce by 15% due to shrinking markets. What important role will HR play during the process?
A. Form new work teams based on the gaps created by the layoffs. B. Summarize industry trends and communicate them to employees. C. Ensure that top management regularly communicates with employees. D. Launch a new quality initiative to preserve customer satisfaction. |
C. Ensure that top management regularly communicates with employees. |
|
|
The following are steps in what process?
Analyze needs and define goals. Define budget. Create RFP. Send RFPs to vendors. Evaluate vendor proposals. Choose vendor. Negotiate contract. Implement and monitor. Evaluate. |
The Outsourcing Process |
|
|
The four phases of the Strategic Planning Process are: |
Phase 1. Strategy Formulation Phase 2. Strategy Development Phase 3. Strategy Implementation Phase 4. Strategy Evaluation |
|
|
In this phase of strategic planning, HR must:
Develop vision and mission statements.
Define organizational values.
|
Strategy Formulation. Phase 1 |
|
|
In this phase of strategic planning, HR must:
Conduct a SWOT analysis, including an environmental scan.
Establish long-term objectives (three to five years).
Identify strategies. |
Strategy Development. Phase 2 |
|
|
In this phase of strategic planning, HR must:
Establish short-term objectives (six months to a year).
Develop action plans.
Allocate resources.
Motivate employees. |
Strategy Implementation. Phase 3 |
|
|
In this phase of strategic planning, HR must:
Review strategies.
Measure performance.
Take corrective action. |
Strategy Evaluation. Phase 4. |
|
|
This summarizes a firm's financial position at one point in time.
The basic form is Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
It only records transactions measured in money (excludes humans) |
Balance Sheet |
|
|
This compares revenues, expenses, and profits over a specified period of time.
The basic form of the statement is: Revenues – Expenses = Net income.
Owner withdrawals are distributions, not operating expenses.
|
Income statement |
|
|
This cornerstone of the federal antidiscrimination legislation was passed in 1964. |
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 |
|
|
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 makes it illegal to discriminate in employment on the basis of what 5 factors? |
race color sex religion national origin |
|
|
4 exceptions regarding the definition of discrimination for Title VII |
1. Work-related requirements: Ex. Physical requirements discriminate against women. 2. Bona-fide occupational qualification: Ex. Sex required to be woman for women's clothing model. 3. Bona-fide seniority systems: Seniority systems not designed to discriminate are lawful under Title VII. 4. Affirmative action plans: Targeted selection to fulfill a plan is acceptable. |
|
|
This act, passed in 1967, prohibits discrimination in employment against people age 40 or over. |
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 |
|
|
This act from 1978 prohibits discriminating against a woman because she is pregnant and treats pregnancy the same as any other temporary disability. |
The Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 |
|
|
Title 1 of the Americans with Disabilities Act does what? |
Passed in 1990, this prohibits discrimination against qualified individuals with a disability because of their disability. |
|
|
The ADA considers an individual disabled if they: |
1. Have an impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities. 2. Has a record of such impairment. 3. Is regarded as having such an impairment. |
|
|
Signed into law in 2008, this broadened the ADA's definition of a disability. |
ADAAA - American's with Disabilities Amendments Act |
|
|
From 1978, this covers all aspects of the selection process, including recruiting, testing, interviewing and performance appraisals. They recommend that employers be able to demonstrate that selection procedures that have an adverse impact upon minorities or women are valid in predicting or measuring performance in a particular job. |
Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures |
|
|
What percentage is used as the rule when determining if there is adverse impact? |
80% - The selection rate of the group with the lowest selection rate (minority) is divided by the rate of the group of the highest selection rate (majority). |
|
|
This is the practice in which employers make efforts to increase the presence of women, minorities, covered veterans, and disabled individuals in the workplace and take positive steps to correct their underutilization. |
Affirmative Action |
|
|
This order "prohibits federal contractors and federally assisted construction contractors and subcontractors who do over $10,000 in government business in one year from discriminating in employment decisions on the basis of race, color, religion, sex or national origin." |
Executive Order 11246 |
|
|
This requires federal government contractors and subs to take affirmative action to employe and advance in employment specified categories of veterans and prohibits discrimination against such veterans. |
Vietnam Era Veterans Readjustment Assistance Act (VEVRAA) |
|
|
VEVRAA applies to contracts in the amount of $25,000 or more and applies to those entered into before December 1, 2003. This amendment applies only to those entered into ON OR AFTER December 1, 2003. |
Jobs for Veterans Act (JVA) |
|
|
This act from 1973 prohibits discrimination based on physical or mental disabilities. |
Rehabilitation Act of 1973 Section 501 applies to the federal government Section 503 applies to their contractors with contract >= $10,000 |
|
|
This law (1952) addresses employment eligibility and employment verification. It defines the conditions for temporary and permanent employment in the US. |
Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) |
|
|
This act from 1986 addressed the need to curtail illegal immigration and is enforced by the Department of Homeland Security since 2003. |
Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) |
|
|
USCIS stands for |
US Citizenship and immigration Services |
|
|
The 3 kinds of IMMIGRANT Visas are: |
EB-1 (First preference) EB-2 (Second preference) EB-3 (Third preference) |
|
|
This is the most common NONIMMIGRANT work Visa andrd are issued for a period of 3 years. |
H-1B |
|
|
This is the streamlined process for obtaining labor certification and is the first stage of the green card process for foreign nationals seeking permanent residence. |
PERM - Program Electronic Review Management |
|
|
This act from 1988 requires some employers to give a minimum of 60 calendar days of advance written notice if a plant is to close or if mass layoffs will occur. |
Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) |
|
|
WARN applies to employers who employ: |
100+ full time employees or FT and PT employees who, in aggregate, work 4,000 or more hours per week. |
|
|
The 3 specific provisions of the WARN Act that require notices are: |
1. Employment loss 2. Plant closings 3. Mass layoffs |
|
|
Mass layoff as defined by the WARN Act is: |
A RIF during any 30-day period that results in 50+ FT employees losing employment if they compose 33% or more of the active workforce at the employment site or loss of employment for 500+ FT employees. |
|
|
Plant closings as defined by the WARN Act are: |
The closure, temporary or permanent, of an entire site or one or more facilities that results in employment loss during a 30 day period for 50 or more employees. The regulation requires aggregation of employment losses at a single site during a rolling 90-day period. |
|
|
The following exceptions still require notification under the WARN Act but do not require that notice be provided 60 days in advance. Notification must be given as soon as is practicable. |
1. Faltering company (applies only to plant closures) 2. Unforeseeable business circumstances (applies to closings and layoffs) 3. Natural disaster |
|
|
What company is using a corporate strategy of differentiation?
A. A company sells in volume and offers discounts to its best customers B. The finished product is sold at a lower price than that of the competition C. A company develops a product that is uniquely easy to use and charges a premium price D. A company orders large quantities of parts to get the greatest discount |
C
Differentiation focuses on setting a product or service apart by giving it unique characteristics that consumer's value and for which they'll pay a premium. The other options deal with ways to create a cost advantage. |
|
|
What financial document lists the revenues, expenses and profits of an organization for a designation period of time?
A. Balance sheet B. Income statement C. Financial statement D. Accounting entries |
B
The Income Statement shows revenues, expenses and profits for the organization. The balance sheet shows its assets, liabilities and shareholders' equty. |
|
|
What is the ESSENTIAL concept behind the stakeholder theory?
A. An organization affects and is affected by complex interests. B. True value must be determined by the increase in a firm's net worth. C. Organizations must see employees as partners rather than foes All stakeholders must receive value for a firm to be considered socially responsible. |
A.
The stakeholder concept proposes that any organization operates within a complex environment, in which it affects and is affected by a variety of forces or stakeholders, who all share in the value of the organization and its activities. |
|
|
Which of the following is a compensable factor?
A. Benefits B. Seniority C. Exempt Status D. Skills |
D
Compensable factors reflect how work is done and are supported by documentation such as job descriptions. The compsable factors flow from the work itself and not the employee holding the job. Therefore, seniority is not a compensable factor in determining the relative worth of a job. |
|
|
What is an example of implicit culture?
A. Language B. Food C. Communications Style D. Values |
D
Implicit culture includes such intangible factors as beliefs, attitudes and values. Dress, language and food are examples of explicit culture. |
|
|
What is the primary advantage of a balanced scorecard approach to measuring organization performance?
A. It allows organizations to assess intangibles B. It takes less time and effort to gather critical data C. It does not require a financial perspective D. It requires the involvement of the entire organizaiton |
A
A balanced scorecard approach focuses on finance, customers, internal processes, and learning and growth. Therefore, it goes beyond a traditional financial approach to managing the organization. It takes into consideration such intangibles as whether a business process has been improved or employees have learned new skills. It can be used in a single department or throughout the organization. |
|
|
What document is a formal statement describing a company's principles and the business practices that support those principles?
A. Code of conduct B. Mission statement C. Strategic plan D. Employee handbook |
A
A corporate code of conduct is a formal statement that describes a firm's principles and the business practices that support those principles. |
|
|
Which type of situation that could lead to workplace violence can be controlled by an organization?
A. Unstable economy B. Domestic problems C. Low employee self-esteem D. Pressure for increased productivity |
D
Conditions causing frustration and anger can lead to violence. Examples include pressure for productivity, rigid management style and layoffs. |
|
|
Which business function is likely to be closer to the end of the value chain?
A. Research and development B. Operations C. Sales and Marketing D. Fulfillment |
D
Fulfillment is the last function completed before the product reaches the customer |
|
|
What will increase the potential of reaching successful outcomes in global negotiation?
A Knowledge of cultural norms and behaviors B Consideration of prevailing interest rates C. Understanding of the political climate D. Focus on interests and positions of influence |
A
Effective negotiators prepare and plan well - beyond the basics (e.g. location, timing and attendance). Learning about the people, cultural characteristics, issues, options, common ground, differences, settlement ranges, and best approaches are all important. |
|
|
This act, passed by Congress in 1995, requires that federal employee relations legislation enacted by Congress apply to the employees of Congress as well. |
Congressional Accountability Act.
This requires that Congress must comply with the following 11 pieces of legislation: FLSA, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, OSHA, ADA, FMLA, Civil Service Reform Act, Age Discrimination in Employment Act, Employee Polygraph Protection Act, WARN Act, Rehabilitation Act, Veterans Reemployment Act |
|
|
USERRA |
Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (1994)
Enacted to protect the civilian employment, reemployment, and retention rights of persons who voluntarily or involuntarily serve or have served in the uniformed services. Many states provide more protection than federal law. |
|
|
Examples of penalties or damages that organizations may experience if they engage in discriminatory practices or violate EE rights legislation |
Prospective pay Back pay Compensation for emotional damage Punitive damages Loss of vendor contracts, government contracts, etc. Actual and hidden costs associated with employee turnover, morale and loss of productivity |
|
|
In general, how many days does an individual have to file a claim with the EEOC under Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act? |
180 days. Some states states have their own agencies that process and investigate charges (deferral states). In these states, a charge of discrimination may be filed with the EEOC within 300 days of the alleged discriminatory conduct. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 is true?
a. It prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex or national origin. b. It remove the limits, or "caps" on damages awarded for intentional discrimination on the basis of gender, religion or disability. c. It prohibits employers from giving temporary preference to any underrepresented protected class. d. It prohibits discrimination based on race, color, national origin, religion and age. |
a. It prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex or national origin. |
|
|
What federal agency was established to investigate charges of discrimination under Title VII.
a. NLRB b. Workers' Compensation Board c. EEOC d. ADA Board |
c. EEOC |
|
|
Which court ruling creates a safe harbor from punitive damages for employers with good-faith antidiscrimination practices?
a. Faragher v. City of Boca Raton b. Kolstad v. American Dental Association c. Meritor Savings Bank v. Vinson d. General Dynamics Land Systems vs. Cline |
b. Kolstad v. American Dental Association |
|
|
Which legislation prohibits mandatory retirement based on age?
a. Older Workers' Benefit Protection Act (1990) b. Age Discrimination in Employment Act (1967) c. Rehabilitation Act (1973) d. Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act (1990) |
b. Age Discrimination in Employment Act (1967) |
|
|
The Rehabilitation Act of 1973 prohibits discrimination on the basis of
a. age b. disability c. gender d. national origin |
b. disability |
|
|
Which of the following statements about the ADA is true?
a. It deals exclusively with employment issues for the disabled. b. A reasonable accommodation could include hiring an interpreter for a job interview with a deaf applicant. c. Employers can no longer claim "undue hardship" to escape making the workplace accessible to disabled workers. d. Current drug users are considered disabled under the definition of the act. |
b. A reasonable accommodation could include hiring an interpreter for a job interview with a deaf applicant. |
|
|
The Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 requires employers to treat pregnancy
a. under the provisions for protected classes b. the same as any other temporary disability c. under existing provisions for a long-term disability d. as a reasonable ADA accommodation |
b. the same as any other temporary disability |
|
|
Which of the following documents establishes a worker's identity and employment authorization for Form I-9?
a. US passport b. Driver's license with photo ID c. US birth certificate d. US military card |
a. US passport |
|
|
Under the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986, which of the following establishes employment authorization?
a. US military card b. Government ID card c. US Social Security card d. Driver's license with photo ID |
c. US Social Security card |
|
|
Under the EEOC's selection guidelines, adverse impact occurs when the selection rate for a protected class is less than what percentage of that for the group with the highest selection rate?
a. 20% b. 50% c. 67% d. 80% |
d. 80% |
|
|
Which legislation protects workers displaced in the merger of two corporations?
a. Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act b. Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures c. Executive Order 11246 d. Immigration Reform and Control Act |
a. Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act |
|
|
What is the MOST likely outcome if no reasonable cause is found during the EEOC complaint process?
a. the EEOC recommends private legal action b. the EEOC dismisses all charges c. the EEOC ends its involvement d. the EEOC mediates conciliation efforts |
c. the EEOC ends its involvement |
|
|
The Privacy Act (1974) protects the employment records of employees of private companies, the federal government or both? |
At this time, only the records of federal government employees. Some state legislatures and private employers have adopted guidelines regarding employee privacy and access to personnel files though. |
|
|
Who is exempt from the Employee Polygraph Protection Act (1988)? |
Federal, state and local governments. Also, lie detector tests administered by the federal government to employees of federal contractors involved in national security intelligence or counterintelligence are exempt.
Some private sector employers may administor with restrictions: employees suspected of involvement in a workplace incident resulting in economic loss to the employer, prospective employees of armored car, etc. and prospective employees of pharmaceutical firms, etc. that will come into contact with controlled substances. |
|
|
The Consumer Credit Protection Act limits what? |
It limits the amount of wages that can be garnished or withheld in any one week by an employer to satisfy creditors. |
|
|
This 1970 act requires full disclosure of consumer reports by consumer reporting agencies. It also requires written notice and authorization by the employee, pre-adverse action notification and adverse action notification. |
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) |
|
|
This amendment to FCRA removes the requirement that an employer using a third party to conduct a workplace investigation follow the same consent and disclosure requirements. When an investigation involves suspected misconduct, a violation of law or regulations, or a violation of preexisting written policies of the employer, written consent IS NOT required. |
Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (FACT) 2003 |
|
|
One of the requirements of this act is that employers requesting medical information about an applicant or employee obtain a specific written consent describing in clear and conspicuous language the use of the information. |
The FACT Act |
|
|
An employer can request that a polygraph test be taken by
a. an employee applying for a public relations position b. a clerical employee who has entered treatment for substance abuse c. an accountant whose department is under scrutiny for embezzlement d. a recovering alcoholic who is seeking a post as a newspaper reporter |
c |
|
|
Which statement best describes the provisions of the Consumer Credit Protection Act?
a. Employers are prohibited from terminating an employee for one single indebtedness b. Employees must provide a signed release authorizing payroll deductions c. Employers have strict legal obligations regarding disclosure of an employee's financial information d. Employees can set the amount of wages that can be garnished or withheld by an employer |
a. Employers are prohibited from terminating an employee for one single indebtedness |
|
|
According to the provisions of the Fair Credit Reporting Act, an organization may obtain credit information about an employee before offering a promotion if the individual
a. is a rehabilitated drug offender b. is provided written notice and gives authorization c. refuses to take a polygraph test d. volunteers information about being in arrears for child support |
b. is provided written notice and gives authorization |
|
|
Griggs v. Duke Power |
Precedent setting discrimination case where Willie Griggs applied for a coal handler position with Duke Power Company. He was denied on the basis of not being a high-school graduate and on the results of two preemployment tests that were requirements of the job. Grigg's position that the job requirements were discriminatory because they did not relate to job success prevailed.
Two points came out of this case: Employment discrimination need not be overt to be illegal and employment practices can be illegal even when applied to all employees. (DISPARATE IMPACT) |
|
|
McDonnell Douglas Corp. v. Green (1973) |
Established criteria for DISPARATE TREATMENT. The Supreme Court ruled that individuals can show a prima facie case of disparate treatment in a hiring situation if they can demonstrate that they:
Belong to a racial minority or other protected group under Title VII Applied for a job for which the employer was seeking applicants Were rejected despite being qualified Were rejected and yet the employer kept looking for people with their qualifications |
|
|
Albemarle Paper v. Moody (1975) |
The Albermarle Paper Company required job applicants to pass different employment tests, some of which were believed to be poor predictors of job success. The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the plaintiff, stating that items used to validate employment requirements must themselves be job-related. |
|
|
Washington v. Davis (1976) |
Police Dept. applicants in Washington DC were required to pass an examination on verbal ability, vocabulary, reading and comprehension.. This excluded a disproportionately high number of African-American applicants. The Supreme Court ruled that the procedures and written personnel test did not constitute racial discrimination under the equal protection clause. The test was considered valid to the training program. |
|
|
St. Mary's Honor Center vs. Hicks (1993) |
This ruling was in favor of the employer. It isn't enough for the plaintiff to prove the employer lied about the reason for termination. The plaintiff must also show that the lie was to cover up illegal discrimination. |
|
|
McKennon v. Nashville Banner Publishing Co. (1995) |
Established that the "after-acquired evidence defense" was invalid. Evidence of misconduct acquired after the decision to terminate cannot free an employer from liability, even if the misconduct would have justified terminating the employee. The evidence isn't entirely useless though and can be used to cut off some damages. |
|
|
Class-action racial discrimination lawsuit against Coca-Cola (2000) |
4 past and current African-American employees representing > 2,000 salaried employees since 1985 filed a lawsuit that they were offered fewer promotions, and were given lower performance evaluation scores than Caucasians. A $192.5 million settlement was agreed to and an independent task force was assigned to monitor Coca-Cola's progress. |
|
|
Employers with 100 or more employees and federal contractors with at least 50 employees and a federal contract or subcontract of >=$50,000 must submit this report of workforce data by September 30th each year. |
EEO-1 (for private businesses). Other businesses must submit the EEO-3, EEO-4, etc. |
|
|
A manager always hires young, attractive women as receptionists. This is an example of
a. disparate treatment. b. adverse impact c. reverse discrimination. d. sexual harassment |
a. disparate treatment. |
|
|
A psychological exam that tends to eliminate African-American applicants is an example of
a. disparate treatment. b. adverse impact. c. present effects of past discrimination. d. outmoded selection practices. |
b. adverse impact. |
|
|
In Washington v. Davis, the Supreme Court ruled that
a. a test that has an adverse impact against a protected class is legal if it is job-related. b. a test used for promotion or selection of employees must be a valid job predictor. c. an employer must demonstrate a lack of discriminatory intent. d. the burden of proof lies with the employee to show that any employment requirement is directly job-related. |
a. a test that has an adverse impact against a protected class is legal if it is job-related. |
|
|
An African-American is asked to fill out an EEO applicant flow form declaring race and ethnicity. Which of the following statements about this situation is true?
a. The request violates EEO regulations. b. Compliance is mandatory. c. The person making the hiring decision cannot be given the form. d. The form may be incorporated in the employee's file if the employee is hired. |
c. The person making the hiring decision cannot be given the form. |
|
|
Which of the following provides data on the proportion of current employees in protected classes by job title within a department or organizational unit?
a. Adverse impact analysis b. Affirmative action plan c. Availability analysis d. Workforce analysis |
d. Workforce analysis |
|
|
In which section of the AAP would a contractor report that it has 14% women and 28% minorities represented in its management team?
a. Organizational profile b. Job group analysis c. Placement goals d. Identification of problem areas |
b. Job group analysis |
|
|
Which of the following assesses the number of potential employees from protected classes?
a. Adverse impact analysis b. Affirmative action plan c. Availability analysis d. Workforce analysis |
c. Availability analysis |
|
|
Which of the following OFCCP activities focuses on the promotion of minorities and women to senior-level positions?
a. Desk audit b. Corporate management compliance evaluation c. Off-site review d. Workforce analysis |
b. Corporate management compliance evaluation |
|
|
Affirmative action plans (AAPs) are illegal when they
a. define underutilization of women and/or minorities. b. achieve placement goals within a particular affirmative action plan year. c. result in the discharge of qualified nonminority employees d. remedy a specific effect of past discrimination. |
c. result in the discharge of qualified nonminority employees |
|
|
Which of the following Supreme Court decision dealt with reverse discrimination?
a. Griggs v. Duke Power b. Albemarle Paper v. Moody c. Washington v. Davis d. General Dynamics Land Systems, Inc., v. Cline |
d. General Dynamics Land Systems, Inc., v. Cline |
|
|
A Caucasian manager who continually uses an ethnic slur for a person of color is an example of
a. quid pro quo b. adverse impact c. reverse discrimination d. harassment |
d. harassment |
|
|
Which of the following forms of sexual harassment occurs when an employee must give in to a supervisor's sexual demands or forfeit a pay increase?
a. Hostile environment b. Quid pro quo c. Whistleblowing d. Reasonable person |
b. Quid pro quo |
|
|
Which landmark harassment case established that employers are responsible for the discriminatory acts of their employees?
a. Meritor Savings Bank v. Vinson b. Faragher v. City of Boca Raton c. Harris v. Forklift Systems, Inc. d. Oncale v. Sundowner Offshore Service, Inc. |
b. Faragher v. City of Boca Raton |
|
|
During which of the following workforce analysis phases would HR analyze the organization as it currently exists?
a. Supply analysis b. Demand analysis c. Gap analysis d. Solution analysis |
a. Supply analysis |
|
|
Turnover analysis is a technique that
a. tracks the rate of employee separations b. utilizes information provided by individuals associated with an industry to project future industry needs c. predicts future employment trends based on marketplace data. d. determines if a relationship exists between two variables through the use of regression analysis and simulations. |
a. tracks the rate of employee separations |
|
|
Several HR managers are brought together to generate ideas about the impact of technology on HR management and staffing. This best describes which forecasting method?
a. Delphi technique b. Managerial estimates c. Multiple regression analysis d. Nominal group technique |
d. Nominal group technique |
|
|
Which forecasting method would be used to make a statistical comparison between gross sales and the number of employees in a retail chain?
a. Delphi technique b. Staffing ratio c. Turnover analysis d. Regression analysis |
d. Regression analysis |
|
|
In which organizational approach to international human resource management is it common to have all key executive positions held by personnel from the headquarters country?
a. Ethnocentric b. Polycentric c. Regiocentric d. Geocentric |
a. Ethnocentric |
|
|
Which of the following is the BEST example of an essential job function for a senior shipping specialist in an operations department?
a. Supervise shipping staff to ensure that procedures are followed. b. Oversee the use of the organization's van when needed. c. Accompany HR personnel at local recruiting fairs. d. Encourage shipping staff to participate in an organization-sponsored retirement planning. |
a. Supervise shipping staff to ensure that procedures are followed. |
|
|
A job analysis has identified several knowledge, skill and ability requirements for salespeople responsible for selling a product line to national accounts and government agencies.
Which of the following is an example of a knowledge requirement?
a. Managing time effectively b. Overcoming customer resistance c. Maintaining good relations with customers d. Identifying product features and benefits |
d. Identifying product features and benefits |
|
|
A job analysis has identified several knowledge, skill and ability requirements for salespeople responsible for selling a product line to national accounts and government agencies.
Which of the following is an example of a skill requirement?
a. Understanding product advantages b. Demonstrating product features c. Knowing government procurement procedures d. Listing major competitors |
b. Demonstrating product features |
|
|
A job analysis has identified several knowledge, skill and ability requirements for salespeople responsible for selling a product line to national accounts and government agencies.
Which of the following is an example of an ability requirement?
a. Questioning for prospect need b. Maintaining friendly relations with suppliers c. Presenting proposals to decision makers d. Analyzing territory for market potential |
b. Maintaining friendly relations with suppliers |
|
|
An organization has decided to add a small group of direct salespeople to its current inside sales force and has asked an external consultant to conduct a job analysis to ensure that the direct sales position contributes to the organizational objective of increasing market share. Which of the following job analysis factors would help to establish the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities of the direct sales function?
a. Job context b. Job specifications/qualification c. Performance criteria d. New employee orientation |
b. Job specifications/qualification |
|
|
The PRIMARY purpose of a work log is to
a. compute the average time needed for key tasks. b. identify patterns that translate into job responsibilities. c. determine the attitude of incumbents toward the job. d. help supervisors rank employees' efficiency. |
b. identify patterns that translate into job responsibilities. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT included in the job description?
a. Primary duties and responsibilities b. Activities performed c. Rate of pay d. Working conditions |
c. Rate of pay |
|
|
A benefit of job posting is that it
a. provides a cost-effective way to reach the largest number of applicants at one time. b. provides an easy way to create a personnel database for job vacancies. c. allows individuals to maximize career opportunities within an organization. d. allows employees to indicate interest in a position that is currently filled. |
c. allows individuals to maximize career opportunities within an organization. |
|
|
A large employer generally has seven or more applicants per job. Recently, the firm was surprised by a lack of response to newspaper advertisements, resulting in several positions remaining unfilled for weeks. To expand their recruiting efforts, the firm should utilize all of the following steps EXCEPT
a. college and career fairs b. the state employment service c. employee referrals d. job bidding |
d. job bidding |
|
|
Which of the following recruitment methods allows candidates to talk to employers about an opening without making a formal job application?
a. Executive search firms b. Public employment agencies c. Employee referrals d. Career fairs |
d. Career fairs |
|
|
All of the following are good examples of employment branding on an organizational Web page EXCEPT
a. an offer to receive periodic updates about career development b. a link to information about balancing work and family life c. information about a pro bono engagement to help the Special Olympics d. a chance to win free flying lessons for submitting a qualified resume. |
d. a chance to win free flying lessons for submitting a qualified resume. |
|
|
Which of the following is a long-term consideration when evaluating the effectiveness of a recruitment program?
a. EEO implications b. Recruitment costs c. Relative performance on the job d. Quantity or quality of applicants |
c. Relative performance on the job |
|
|
An organization begins with 600 job applicants, narrows the field to 30 qualified applicants, and schedules 30 final interviews. They offer employment to ten applicants and hire six.
What is the yield ratio of qualified applicants to total applicants.
a. 5% b. 18% c. 20% d. 30% |
a. 5% |
|
|
An organization begins with 600 job applicants, narrows the field to 30 qualified applicants, and schedules 30 final interviews. They offer employment to ten applicants and hire six.
What is the yield ratio of offers to final interviews.
a. 10% b. 30% c. 33% d. 50% |
c. 33% |
|
|
An organization begins with 600 job applicants, narrows the field to 30 qualified applicants, and schedules 30 final interviews. They offer employment to ten applicants and hire six.
What is the yield ratio of hires to offers?
a. 10% b. 60% c. 70% d. 73% |
b. 60% |
|
|
An organization receives 250 responses to its job advertisement. They interview 95 qualified applicants, 20 of whom are African-American. Jobs are offered to two African-Americans from this group, but only one accepts the position.
What is the yield ratio of offers to African-Americans to qualified African-American applicants?
a. 5% b. 10% c. 15% d. 20% |
b. 10% |
|
|
An organization receives 250 responses to its job advertisement. They interview 95 qualified applicants, 20 of whom are African-American. Jobs are offered to two African-Americans from this group, but only one accepts the position.
What is the yield ratio of African-American new hires to qualified African American applicants?
a. 5% b. 10% c. 15% d. 20% |
a. 5% |
|
|
Floaters are BEST described as
a. employees scheduled to work less than a regular workweek on an ongoing basis b. self-employed individuals hired on a contract basis for specialized services c. people employed directly on an organization's payroll on a short-term basis or for a specific period of time to rotate among several positions or departments d. long-term temporaries assigned to a client organization |
c. people employed directly on an organization's payroll on a short-term basis or for a specific period of time to rotate among several positions or departments |
|
|
Under which flexible staffing option would a professional employer organization (PEO) be most likely to provide temporary workers with benefits?
a. Payrolling b. Master vendor arrangement c. Outsourced or managed services d. Temp-to-lease programs |
d. Temp-to-lease programs |
|
|
A potential advantage of a small firm outsourcing its payroll function is
a. increased continuity rather than having various staff members perform the function b. the outsourcing organization's employees will be paid only for time worked. c. less supervisory time on the part of the HR generalist d. the outsourcing organization's knowledge of payroll processing and administration |
d. the outsourcing organization's knowledge of payroll processing and administration |
|
|
Which of the following is a good reason applicant notification should take place in a timely fashion?
a. Organizations are legally required to notify applicants of their status in a timely manner. b. The recruitment process may have an impact on applicant reactions and subsequent attitudes toward the organization. c. It lets the applicant know the interview went well. d It keeps the recruitment process straight |
b. The recruitment process may have an impact on applicant reactions and subsequent attitudes toward the organization. |
|
|
Which of the following statements characterizes a nondirective interview?
a. The interviewer asks all applicants the same questions. b. The interviewer deliberately creates a high level of anxiety c. Each applicant is asked different questions about the same skill and ability areas d. The interviewer's next question is determined by the applicant's response to an open question |
d. The interviewer's next question is determined by the applicant's response to an open question |
|
|
A store is planning for expansion to a new geographic region, and applications for management-level transfers are being accepted from internal applicants. If internal recruiting efforts do not yield enough qualified candidates, a newspaper ad in the new geographic region will be run. In this situation, a structured interview process is better than an unstructured process because it
a. is possible to gather dissimilar information and compare qualifications of all candidates while reducing compliance concerns. b. fulfills EEO requirements about protected class biases and allows the interviewer to legally document subjective impressions of the candidates' nonverbal behavior. c. is possible to gather similar information from all candidates and ensure that the interview process is job-related and measure what is purports to measure. d. enables interviewers to measure the sample of behavior with a high degree of consistency by scoring/tallying numerical values assigned to given behaviors. |
c. is possible to gather similar information from all candidates and ensure that the interview process is job-related and measure what is purports to measure. |
|
|
Which of the following selection practices is illegal under federal law?
a. Obtaining information from references without an applicant's permission. b. Requiring a job-related test that has adverse impact on minority groups. c. Determining if an applicant has ever filed a workers' compensation claim. d. Requiring applicants to submit to a preemployment drug test. |
c. Determining if an applicant has ever filed a workers' compensation claim. |
|
|
Which interview question has the potential to be discriminatory under federal law?
a. I notice you use a white cane. Are you legally blind? b. Do you have any relatives who work for this organization? c. The job requires that you lift a 20-lb. weight and place it on an overhead shelf. Can you do that several times an hour, all day long? d. Are you over age 18? |
a. I notice you use a white cane. Are you legally blind? |
|
|
Which of the following preemployment tests has the best potential for measuring an applicant's integrity?
a. Ability test b. Personality test c. Honesty test d. Polygraph test |
c. Honesty test |
|
|
Which of the following selection practices is legal under federal law?
a. Taking age into consideration if an applicant volunteers the information. b. Requesting applicants to take a polygraph test c. Rejecting applicants on the basis of their credit record without telling them the name of the party that prepared the report d. Requesting proof an an applicant's eduation |
d. Requesting proof an an applicant's eduation |
|
|
Which of the following statements about a reliable employment test is true?
a. It determines how the applicant handled previous work situations b. It avoids linking the responses of successive questions. c. It must be job-related and measure what it purports to measure. d. It measures the sample of behavior with a high degree of consistency |
d. It measures the sample of behavior with a high degree of consistency |
|
|
An employment test is content-valid if it
a. sufficiently covers the area that it is intended to cover. b. relates the test to some external criterion, such as particular aspects of the job. c. establishes correlations between unrelated items d. adequately measures intangibles such as attitudes and behaviors |
b. relates the test to some external criterion, such as particular aspects of the job. |
|
|
Validation studies, such as predictive and concurrent validation, use which of the following?
a. Correlations b. Multiple means of assessment c. Multiple assessors d. Multiple regression |
a. Correlations |
|
|
A written test and a hands-on exercise that seek to assess the same criterion is an example of
a. content validity b. construct validity c. concurrent validity d. predictive validity |
c. concurrent validity |
|
|
Interviews with future co-workers is an example of a
a. stress interview technique b. realistic job preview c. specialized preemployment test d. method to establish equity |
b. realistic job preview |
|
|
Which of the following statements about medical examinations is TRUE?
a. Temporary workers can be required to submit to a medical exam before assignment b. Preemployment health checklists can be requested before an employment offer is made c. Exams must be job-related and may be required only after an employment offer is made d. The exam must be completed by the organization's medical staff or a referral. |
c. Exams must be job-related and may be required only after an employment offer is made |
|
|
An offer letter should be sent to a candidate immediately after
a. the hiring decision is made b. all contingencies are addressed c. both parties review the employment contract d. both parties verbally agree to any relocation agreement |
a. the hiring decision is made |
|
|
An appropriate retention practice for an internal transfer is to
a. offer a spot bonus for accepting the new job b. make a donation in the employee's name to the charity of his or her choice c. promise cross-training and partnering with more experienced workers d. provide a candid portrayal about the position and the opportunities, both short- and long-term, prior to the transfer's accepting the new position. |
d. provide a candid portrayal about the position and the opportunities, both short- and long-term, prior to the transfer's accepting the new position |
|
|
Which of the following statements is an example of voluntary turnover?
a. A high-performer quits to earn more money at another organization b. Employees are downsized due to organizational financial difficulties c. Departmental jobs are eliminated in a merger d. A supervisor is dismissed for committing quid pro quo harassment |
a. A high-performer quits to earn more money at another organization |
|
|
Systems that provide resources for line managers to increase a new hire's productivity and engagement during the first six months on a job describe
a. realistic job previewing b. orientation c. onboarding d. coaching |
c. onboarding |
|
|
An organization develops a plan to prepare select employees for positions that are key to achievement of the organization's strategic goals. This is an example of which type of program?
a. Socialization b. Mentoring c. Succession planning d. total rewards |
c. Succession planning |
|
|
An organization must significantly reduce its workforce because of increased costs resulting from changes in regulatory environment. What should HR do to help the retained employees cope?
a. Survey retained employees b. Disclose outplacement and severance terms c. Discount any rumors d. Explain the regulatory changes |
d. Explain the regulatory changes |
|
|
All of the following statement accurately describe employee records management EXCEPT
a. Requirements can vary based on the number of employees b. State requirements are always the same as federal requirements c. Employers are required to keep all relevant records until final disposition in a lawsuit d. Similar records may be required by more than one law |
b. State requirements are always the same as federal requirements |
|
|
What should an employer do if the requirements for the same record differ between three laws?
a. Keep duplicates of each record in multiple files according to the different requirements b. Make judgment about maximum retention based on the most important law c. Retain the information for the longest period of time required d. Keep the records for the shortest time required unless it involves a federal contractor |
c. Retain the information for the longest period of time required |
|
|
KSA stands for... |
Knowledge, skills and abilities |
|
|
These two supply analysis techniques use statistics to determine whether relationships exist between two variables. A manager may use these when looking at past performance as a predictor of the future. |
Trend and Ratio Analyses |
|
|
Labor productivity (Sales / Number of employees) has been the same for the past 4 years at $12,520. It is assumed that labor productivity will stay the same. However, sales are expected to increase to $5 million. $5mm / $12,520 = 399 employees needed. What kind of analysis is this? |
Ratio analysis |
|
|
Managerial estimates, Delphi technique and Nominal group technique are all examples of this type of Demand Analysis forecast that uses information from past and present to predict expected future conditions. |
Judgmental Forecast
These forecasts utilize information provided by individuals associated with the industry to project future industry needs. |
|
|
This forecasting approach progressively collects information from a group on a preselected issue. Participants list their ideas about the issue and return anonymously to the coordinator who then prepares and sends a second questionnaire to participants that contains all of the ideas sent in response to the first questionnaire. Participants refine each idea and resubmit. This process continues until it is clear that no new ideas are emerging. |
Delphi technique
This approach is designed to facilitate group involvement, problem solving and individual thinking but avoid "group think". |
|
|
This forecasting technique brings individuals together, face-to-face, to discuss issues in a session led by a moderator. |
Nominal group technique |
|
|
Regression analysis and Simulations are examples of this type of forecast used in demand analysis. |
Statistical Forecast |
|
|
This analysis technique compares Supply analysis to the demand analysis to identify the differences in staffing levels and KSAs needed for the future. |
Gap Analysis |
|
|
During this type of analysis, an organization decides whether to "build", "buy" or "borrow" talent needed to attain the staffing levels and KSAs required to meet organizational objectives. |
Solution Analysis |
|
|
In this type of Global Approach, headquarters maintain tight control over the international operations and subsidiaries have little autonomy. Key positions at home and abroad are held by personnel from the headquarters country. This means that talent and skills transfer essentially one way and the headquarters-country HR policies and practices are exported abroad. |
Ethnocentric Approach |
|
|
In this Global Approach, each international operation is treated as a distinct national entity. Local nationals are hired to manage functions but are rarely promoted to headquarters assignments. Headquarters-country personnel have little impact and talent acquisition policies are unique to each country. There is limited cross-border movement of talent and skills. |
Polycentric Approach |
|
|
In this Global Approach, operations are managed regionally and communications and coordination within a region are high but less so between regions. Employees circulate within regions, talent acquisition is developed and coordinated within regions and there is minimal interregion transfer. |
Regiocentric Approach |
|
|
In this Global Approach, the organization is viewed as a single international enterprise rather than a collection of individual headquarters-country and international operations. The strategic plan is global in organization and talent comes from any location. Employees circulate throughout the global organization and talent and skills are deployed globally. |
Geocentric Approach |
|
|
Which KSA is the body of information necessary for task performance? |
Knowledge |
|
|
Which KSA are the capabilities necessary to perform the job? |
Abilities |
|
|
Which KSA is the level of proficiency needed for task performance? |
Skills |
|
|
The following are all part of a what?
Job title and location Organizational relationships Duties and responsibilities Essential job functions Nonessential job functions Working conditions Level of financial accountability |
These are all part of a job description |
|
|
The following necessary qualifications for the job incumbent are examples of what?
Education Experience Training Mental abilities Physical efforts and skills Judgment Decision making |
Job specifications |
|
|
___________________ are the KSAs and other personal characteristics that work together to allow an employee to produce outstanding performance in a given area of responsibility. |
Job competencies |
|
|
(External Costs + Internal Costs) / Total number of hires in a time period = ? |
Cost Per Hire (CPH) |
|
|
((External Costs + Internal Costs) \ Total first-year compensation of hires in a time period ) x 100 = ? |
Recruitment Cost Ratio (RCR) |
|
|
The resource-based theory of the firm claims that an organization's competitive advantage is determined by its
a. Core capability b. Relationships with suppliers and buyers c. Superiority over rival firms d. Ability to limit new entrants into the industry |
a. Core capability
Although strategy focuses mostly on the external environment, internal conditions also play a major role in strategy formulation and implementation. This view, referred to as the resource-based theory of the firm, provides a very different focus on the sources of competitive advantage. According to Jay Barney, the person most frequently credited for the resource based view, sustained competitive advantage results from the ownership and control of resources that are rare, nontradable, nonsubstitutable, valued by the market, and difficult or impossible to imitate. |
|
|
Environmental uncertainty for an organization is a function of which two variables?
a. Costs and benefits b. Planning and forecasting c. Interest rates and inflation d. Complexity and stability |
d. Complexity and stability
Environmental uncertainty stems from two variables; (a) the complexity of the environment and (b) how rapidly the environment changes. |
|
|
A strategy that tries to gain a competitive advantage by providing exceptionally high quality is using which grand strategy?
a. Focus b. Differentiation c. Retrenchment d. Cost leadership |
b. Differentiation
|
|
|
Which form of departmentalization would be BEST if management wanted to avoid problems with duplication of personnel and facilities?
a. Customer classification b. Matrix c. Product-service d. Functional |
d. Functional
Functional departmentalization permits the maximum use of resources and encourages the use of specialists and specialized equipment, thereby eliminating the duplication of equipment and effort. |
|
|
What of these recommendations would MOST LIKELY result from an environmental scanning analysis?
a. Our prices should increase three percent next year to stay consistent with our competitors. b. The company can reduce its size through attrition without having to use layoffs if it acts now. c. Due to expected shortages in the labor force in the next five to ten years, the company will have insufficient workers to run at full capacity. d. Given last year's yield ratio, the company will need to recruit sixty college graduates to fill four vacancies in the design department. |
c. Due to expected shortages in the labor force in the next five to ten years, the company will have insufficient workers to run at full capacity.
Strategic HR planning is influenced by the overall state of the economy. |
|
|
An organization that calculates the cost of turnover using such measures as separation costs, replacement costs, training and development costs, and lost performance, is using
a. Outlay costs b. Cost accounting c. Budget prospective d. Key performance indicators |
b. Cost accounting
Cost accounting can be used to evaluate how much turnover costs an organization. The cost of turnover consists of 4 major cost categories: 1. separation costs, which includes exit interviews, administrative functions, separation pay and unemployment taxes 2. replacement costs 3. training costs 4. lost performance |
|
|
A useful model for analyzing the profit potential of a firm within its industry is called the
a. Strategy management model b. Five forces model c. Environmental scanning outline d. Resource allocation plan |
b. Five forces model
Michael Porter has developed a five forces model of competition that identifies the major environmental forces of an industry analysis. This five forces model suggests that an industry's profit potential is a function of the interactions among these five forces. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT one of Porter's five forces of competition?
a. Rival firms b. Buyers c. Supplies d. Technology |
d. Technology
The five forces are SUPPLIERS, BUYERS, RIVAL FIRMS, PRODUCT SUBSTITUTES and the threat of NEW ENTRANTS. |
|
|
Deontology defines right according to
a. What is best for society b. What is best for each individual c. What is fair and just d. What will harm versus help people |
c. What is fair and just
Deontology is based on the fundamental fairness of an action or the MEANS used to achieve the result. |
|
|
A company generally needs a separate staff position to handle HR functions when it reaches what size?
a. 25 employees b. 100 employees c. 1,000 employees d. 2,500 employees |
b. 100 employees |
|
|
An organization recently completed a merger and wants to develop competency models to enhance work accomplishment. What might HR professionals recommend as first steps in building relevant competency models?
a. Request that functional areas develop their own competency models as soon as possible so that employees understand expectations. b. Advocate that core competencies based upon strategic goals and objectives be developed for the organization as a whole. c. Develop models based on key competencies (that apply regardless of position or industry) for today's workers in general. d. Start the process from the ground up and have individuals prepare competency descriptions based on their own strengths and weaknesses. |
b. Advocate that core competencies based upon strategic goals and objectives be developed for the organization as a whole. |
|
|
To deal with aggressive global competition, an organization downsized and modified its strategic business plan. The most important thing the organization's training and development function must do to support the initiative is to:
a. identify training costs and cost-justifying training b. promote acceptance and change in employee behavior c. evaluate the effectiveness of current training programs. d. link training and development to the new strategic plan. |
d. link training and development to the new strategic plan. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT an example of a learning organization?
a. A software organization where employees are encouraged to join professional associations that increase their networking connections. b. A car manufacturer that introduces a new SUV in response to market changes c. A grocery store chain that sends one of its 30 managers to supervisory training. d. A bank that is implementing a strategic plan |
c. A grocery store chain that sends one of its 30 managers to supervisory training. |
|
|
Which of the following is MOST representative of a high-context culture?
a. Simple, direct speech b. Nonverbal communication c. Messages aimed at an individual d. Logical, linear explanation |
b. Nonverbal communication |
|
|
An article is in the public domain if
a. there is no effect on the value of the copyrighted work. b. it has already been reproduced by the copyright holder c. its period of copyright is still in effect d. it has been produced by the US government. |
d. it has been produced by the US government. |
|
|
A training specialist uses a properly cited paragraph from a novel in order to illustrate an important learning point in a training session. The training specialist has followed which of the following?
a. Fair-use provision b. Public domain c. Uniform Guidelines d. Reasonable accommodation |
a. Fair-use provision |
|
|
Under which of the following pieces of legislation must employers show that if they select certain individuals for a training session, they are not discriminating against a group of potential participants based on race, color, national origin, religion or gender?
a. Title VII, Civil Rights Act b. Americans with Disabilities Act c. Age Discrimination in Employment Act d. Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act |
a. Title VII, Civil Rights Act |
|
|
An organization surveyed its customers to determine their satisfaction levels with various operations within the organization. Findings show that there have been numerous delays in the response to customer inquiries and that the delays were the result of reporting structures limiting communications to "proper channels". Which organizational development approach should be evaluated to avoid future delays?
a. Interpersonal b. Procedural c. Structural d. Technological |
c. Structural |
|
|
Which of the following management consultants advocates a 14-point program and "four quality absolutes"?
a. W. Edwards Deming b. Joseph M. Juran c. Philip B. Crosby d. All three consultants |
c. Philip B. Crosby |
|
|
Which of the following prioritizes categories from most frequent to least frequent?
a. Control chart b. Process-flow analysis c. Pareto chart d. Scatter diagram |
c. Pareto chart |
|
|
Which of the following is an illustration of the relationship between two variables?
a. Control chart b. Process-flow analysis c. Pareto chart d. Scatter diagram |
d. Scatter diagram |
|
|
Which is a characteristic of an adult learner?
a. Directed by others b. Resistant to change c. Inflexible d. Focus on "real-world" issues |
d. Focus on "real-world" issues |
|
|
What is a benefit of incorporating knowledge of the characteristics of adult learners into an HRD program?
a. It allows participants to learn directly from the instructor. b. It accommodates the different learning styles of adults. c. It creates a structured environment in which it is easy for the instructor to teach. d. It tells participants what the best way is for them to learn. |
b. It accommodates the different learning styles of adults. |
|
|
Which learning curve is common when a trainee is learning a difficult task that also requires specific insight?
a. S-shaped curve b. Plateau curve c. Decreasing returns d. Increasing returns |
a. S-shaped curve |
|
|
According to Maslow, which of the following is an example of an esteem need?
a. Opportunities for growth b. Base salary c. Effective team work d. Recognition |
d. Recognition |
|
|
Which intervention strategy is used when a subject receives no response at all?
a. Positive reinforcement b. Negative reinforcement c. Extinction d. Punishment |
c. Extinction |
|
|
Needs assessments may not be conducted in organizations because
a. gaps between employees' skills and knowledge are already known. b. managers may prefer action over research c. there is no existing job description d. knowledge of what other organizations are doing precludes a costly study. |
b. managers may prefer action over research |
|
|
Which level is a needs assessment targeting when measuring what skills are required to perform a job effectively?
a. Individual b. Task c. Organizational d. Strategic |
b. Task |
|
|
To determine the cost of training per participant, the total cost of training is divided by which of the following?
a. Number of people actually trained b. Percentage increase in production c. Percentage decrease in turnover d. Number of people selected for training |
a. Number of people actually trained |
|
|
Which of the following should HR consider when defining the target audience for a training program?
a. Potential productivity gains b. Incentives for completing the training c. Peer group pressure d. Knowledge and skill of participants |
d. Knowledge and skill of participants |
|
|
Which of the following is an advantage of conducting a pilot program?
a. It allows you to evaluate the sequencing of content. b. Participants can be put at ease concerning the training. c. It provides the instructional designer with more time to design the program. d. It creates interest from key stakeholders |
a. It allows you to evaluate the sequencing of content. |
|
|
Which of the following is a primary advantage of conducting high-level managerial training off-site?
a. it will be easier to diagnose individual learning needs b. Participants will know exactly when the training will start and end c. A properly selected off-site location will be more conducive to effective learning. d. It will be easier to evaluate the extent to which the training objectives are achieved. |
c. A properly selected off-site location will be more conducive to effective learning. |
|
|
Which of the following evaluation methods provides the MOST valuable measurement information?
a. Reaction b. Learning c. Behavior d. Results |
d. Results |
|
|
The best way for managers to measure observable changes in behavior is through the use of
a. pre/post-measures b. performance tests c. performance appraisals d. questionnaires |
b. performance tests |
|
|
Which measurement process assesses complex performance that is difficult to evaluate by means of a questionnaire or interview?
a. Observation b. Simulation c. Critical incidents d. Reaction |
a. Observation |
|
|
The best way for managers to measure the results of training programs is to
a. compare the employees' performance against established performance standards. b. test employees to determine whether they understand the skills and knowledge presented in training c. ask employees to assess the effectiveness of the training d. ask trainers to evaluate the effectiveness of the training |
a. compare the employees' performance against established performance standards. |
|
|
Which of the following is the organization's responsibility in career management?
a. Assess career options inside and outside the organization b. Design a career path that matches organizational goals c. Match organizational needs with individual abilities d. Identify personal abilities and interests |
c. Match organizational needs with individual abilities |
|
|
An employee who is reappraising her early career plans, modifying those plans, and maintaining her work productivity is in which stage of the career development model?
a. Early career establishment and achievement b. Mid career c. Late career d. Occupational preparation |
b. Mid career |
|
|
In an executive coaching experience, the employee does all of the following EXCEPT
a. develop communication skills b. learn to produce results c. identify strengths and weaknesses d. design a new self-performance appraisal |
d. design a new self-performance appraisal |
|
|
Succession plans provide which of the following outputs?
a. Summaries of candidate availability b. Candidate data c. Compensation levels d. Position requirements |
a. Summaries of candidate availability |
|
|
An organization has defined a group of high-performing key managers in various departments. The organization has decided to provide special development for these individuals. Which career development program is this organization implementing?
a. Dual career ladder b. Coaching c. Fast-track program d Job enrichment |
c. Fast-track program |
|
|
A difference between management and leadership is that
a. management aligns people to the vision and strategies; leadership establishes structure for accomplishing plan requirements b management energizes people; leadership organizes people to solve problems c. management establishes the vision; leadership establishes detailed steps and timetables d. management delegates responsibility and authority for carrying out the plan; leadership communicates the direction by words and deeds. |
d. management delegates responsibility and authority for carrying out the plan; leadership communicates the direction by words and deeds. |
|
|
The two primary dimensions of behavioral theories of leadership are
a. intelligence and task-relevant knowledge b. consideration and self-confidence c. consideration and initiating structure d. initiating structure and intelligence |
c. consideration and initiating structure |
|
|
Which of the following exemplifies Hersey-Blanchard's situational leadership theory?
a. A leader's style must change over time as individuals develop and require a different type of direction and leadership. b. leaders don't necessarily need personal relationships with mentors to learn from them c. Leaders need to be charismatic because employees dislike rigid controls and inherently want to accomplish something d. A team leader is one equally concerned with people and production (task) to the maximum degree. |
a. A leader's style must change over time as individuals develop and require a different type of direction and leadership. |
|
|
In the contingency theory of leadership, which of the following refers to the degree of confidence, trust, and respect that followers have in their leader?
a. Task structure b. Position power c. Situational favorableness d. Leader-member relations |
d. Leader-member relations |
|
|
Emotional intelligence generally describes the ability to
a. subordinate the emotions of others in favor of oneself. b. empathize and manage emotions c. eliminate emotions from strategic decision making d. exhibit positive rather than negative emotions. |
b. empathize and manage emotions |
|
|
A forced-choice method of appraisal requires an appraiser to
a. measure employees against a five-point rating scale, with 1 being significantly below standard, 3 being standard and 5 being above standard. b. mark items on a checklist that describe that characteristics and performance of the employee c. check two of four statements: one that is most like the employee and one that is least like the employee. d. select key statements from a list of positive and negative statements and build two ranked lists of employee strengths and weaknesses. |
c. check two of four statements: one that is most like the employee and one that is least like the employee. |
|
|
Which of the following narrative appraisal methods is completed by a supervisor and a human resource professional?
a. Critical incidents b. Field review c. Essay d. Paired comparison |
b. Field review |
|
|
Which of the following appraisal methods includes the employee in setting goals?
a. 360-degree feedback b. Behaviorally anchored rating scale c. Behavior observation scale d. Management by objectives |
d. Management by objectives |
|
|
Which of the following performance appraisal methods was designed to combat the problems of category rating?
a. BARS b. MBO c. MOS d. 360-degree feedback
|
a. BARS |
|
|
An administrative assistant to the divisional manager of a major firm is extremely good with customers and does an excellent job of managing the schedule and keeping the boss informed of critical situations. Because of this, the employee receives consistently excellent appraisals in spite of the fact that paperwork is often incomplete and behind schedule. This is an example of which appraisal error?
a. Halo b. Horn c. Contrast d. Bias |
a. Halo |
|
|
A manager is tempted to rate an employee's performance as excellent based on the employee's strong performance during the last six months. By deciding that the employee's earlier performance must be considered as well, the manager has avoided which appraisal error?
a. Bias b. Leniency c. Recency d. Contrast |
c. Recency |
|
|
If an employee received an excellent rating because the employee was considerably more skilled than fellow workers, it would be an example of which appraisal error?
a. Bias b. Leniency c. Recency d. Contrast |
d. Contrast |
|
|
Which of the following is an example of a specific comment used to give feedback?
a. I like the way you relate to customers b. You could improve the way you relate to customers c. Your customer satisfaction index is rated 8.8 d. Customers seem to like you |
c. Your customer satisfaction index is rated 8.8 |
|
|
HR Management decides to create a shared services center for career development counseling. Several months later, management notes high turnover in HR offices throughout the organization. What is the most likely reason for this outcome?
a. Natural elimination of redundant positions b. Strategic workforce management c. Poor management of the extended effects of an organizations change d. Weak organizational communication |
c. Poor management of the extended effects of an organizations change |
|
|
A needs analysis identifies several department that are expanding or facing future challenges. In this case, the needs analysis was done at which level?
a. Individual b. Organizational c. Task d. Local |
b. Organizational
An organizational needs analysis anticipates knowledge, skills and abilities that will be needed by the organization in the future It identifies departments with high turnover or skill deficiencies. |
|
|
Over five years, an employee has been promoted from Scientist I to Scientist III and then laterally moved to the operations department as Engineer III, a position more routine than previous jobs. The employee performed well in previous positions but is clearly performing poorly in the current one. What action should the employee's manager consider?
a. Relocation b. Transfer c. Suspension d. Demotion |
b. Transfer
Transfer move employees to the area in which they will be of the most benefit to the organization. They allow employees with expertise to move within the company to improve operations or increase their satisfaction with work. In this case, the employee was bored with routine tasks of the new position, so the manager should consider transferring the employee to a position that matches his or her talents and benefits the company. |
|
|
What does an effective pre- and post-test training assessment measure?
a. Changes in knowledge before and after training b. Overall satisfaction of employees c. Effect of training on organizational goals d. Time needed to improve performance |
a. Changes in knowledge before and after training |
|
|
What is the difference between career planning and career management?
a. Career planning focuses on the organization's needs; career management focuses on the employee's needs. b. Career planning focuses on developing a career path; career management focuses on individual skill assessment c. There is no difference between career planning and career management d. Career planning responsibility lies with the individual; career management responsibility lies with the organization |
d. Career planning responsibility lies with the individual; career management responsibility lies with the organization |
|
|
What positive outcome will result from coaching high-potential employees?
a. Employees will change jobs less frequently b. Employees will contribute more effectively to the organization c. Employees will be less engaged in their current jobs d. Employees are more likely to leave the organization |
b. Employees will contribute more effectively to the organization |
|
|
What leadership theory maintains that performance depends on the interaction between situation favorableness and leadership style?
a. Situational b. Behavioral c. Contingency d. Trait |
c. Contingency |
|
|
How are OD intervention strategies generally characterized?
a. Task, individual or organizational b. Interpersonal, operational, or team c. Interpersonal, technological, or structural d. Functional, dynamic or static |
c. Interpersonal, technological, or structural
OD intervention strategies are generally characterized as interpersonal, technological, or structural |
|
|
An organization recently revised its strategic business plan to enter a new vertical market. What is the MOST important thing the training department can do to support the initiative?
a. Recruit salespeople with experience in the vertical market b. Identify the cost of training associated with the new business plan. c. Monitor the effects of the change on the workforce d. Determine how training can link to the business plan. |
d. Determine how training can link to the business plan. |
|
|
An organization wants to reduce its research and development time by 50%. Which of the following training events is MOST closely linked to this corporate goal?
a. Time management training b. Data collection and analysis training c. Leadership training d. Conflict resolution training |
b. Data collection and analysis training |
|
|
What are 4 characteristics of a Learning Organization? |
Learning is accomplished by the organizational system as a whole
Systems thinking is practiced
Employees network internally and externally
Change is embraced
Failures become opportunities to learn |
|
|
Knowledge Management focuses on |
Expertise sharing and organizational learning.
Knowledge retention and recovery of knowledge lost due to employee attrition. |
|
|
What is "Localization" in HRD? |
When programs are customized for the local population. |
|
|
What are Hofstede's Value Dimensions (5)? |
Power distance: extent to which less-powerful members of organizations accept that power is distributed unequally. High = Asia
Uncertainty avoidance: need for structrure
Individualism/collectivism
Masculinity/femininity
Long term/short term view |
|
|
Describe Low versus High-Context Cultures |
In Low-Context, communication is direct, structured and specific. A shared background is not assumed. A higher value is placed on words spoken rather than nonverbal communication. Behaviors and beliefs are spelled out explicitly.
High-Context is the opposite. Communication is less clear because of common understandings. Meanings are derived from nonverbal communication. Face-saving and tact are balanced with the need to communicate fully and frankly. |
|
|
What are the 9 SHRM HR Competencies? |
Relationship Management Ethical Practice HR Expertise Business Acumen Critical Evaluation Diversity and Inclusion Leadership and Navigation Consultation (in-house typically) Communication |
|
|
When is a work in the public domain? |
When published before 1/1/1978 and NOT COPYRIGHTED
Published between 1/1/78 and 3/1/89 without notice and without reasonable attempt to affix notice within 5 years.
Author is deceased +70 years
Produced by the US government |
|
|
Organizational culture is shared values and perceptions that... |
Give members an organizational identity
Facilitate commitment
Promote system stability
Shape behavior
Impact an organization's success or failure |
|
|
Three steps of the Organizational Development (OD) Intervention Process |
1. Diagnose the environment 2. Develop an action plan 3. Evaluate the results
Examples of interventions are training & team building, quality initiatives, diversity training, flexible work & staffing. |
|
|
What is Organizational Development? |
A planned organization wide effort to increase organizational effectiveness. |
|
|
Systems Theory is based on understanding the relationship between what three components? |
Inputs, Process and Outputs |
|
|
Three categories of OD intervention strategies are: |
Interpersonal: Deal with work relationships between employees
Technological: Process analysis, job design, specialization, work-flow analysis
Structural: Looks at how the org structure helps or hinders the organization. Span of control, reporting relationships |
|
|
Four examples of OD interventions are: |
team building, flexible work & staffing arrangements, diversity programs, and quality initiatives. |
|
|
What kind of chart illustrates variations from normal in a situation over time? |
Control chart |
|
|
What kind of chart is a visual map that lists out factors thought to affect a problem. It is used to show process failure. Also called "fish bone" or "Ishikawa". |
Cause-and-Effect Diagram |
|
|
What kind of diagram is used to see if a relationship exists between two variables? |
Scatter diagram |
|
|
What type of chart displays a distribution of a single type of measurement? |
Histogram |
|
|
This chart is based on the principle that 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. In this, the bar height reflects frequency or impact of causes. |
Pareto chart |
|
|
Which of the following acts requires organizations holding federal construction contracts to pay laborers and mechanics the prevailing wage of the employees in the locality where the work is performed?
a. Davis-Bacon Act b. Walsh-Healey Act b. Copeland Act d. Fair Labor Standards Act |
a. Davis-Bacon Act |
|
|
Under the FLSA, which of the following employees must be paid overtime?
a. A janitor who worked 30 hours during the workweek and was paid for 12 hours of vacation time. b. A vice president in charge of operations who worked 50 hours in a week. c. A nonexempt employee who worked 45 hours in a week. d. A security guard who worked 40 hours, including 10 hours on a holiday. |
c. A nonexempt employee who worked 45 hours in a week. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true under the provisions of the Fair Labor Standards Act?
a. Public employees may elect to accumulate comp time rather than be paid in cash for overtime. b. Private employers cannot limit the number of hours an employee works based on age. c. Severance and vacation pay are regulated by the FLSA. d. FLSA regulations take precedence over state regulations with regard to minimum wage when state wages are higher. |
a. Public employees may elect to accumulate comp time rather than be paid in cash for overtime. |
|
|
When calculating overtime, the employer must include the time for an employee who
a. spends two hours at home, waiting for a call to report to work. b. arrives one hour early for the shift and waits in the employee waiting area. c. arrives at 8:00 as scheduled but cannot begin work because the needed delivery doesn't arrive until 10:00 d. must commute one hour each way from home to the plant. |
c. arrives at 8:00 as scheduled but cannot begin work because the needed delivery doesn't arrive until 10:00 |
|
|
Which of the following issues is NOT a consideration when determining equal work under the Equal Pay Act?
a. Skills b. Gender c. Effort d. Responsibility |
b. Gender |
|
|
Which of the following acts sets minimum wages, child labor standards, and overtime pay provisions for workers?
a. Davis-Bacon Act b. Walsh-Healey Act c. Copeland Act d. Fair Labor Standards Act |
d. Fair Labor Standards Act |
|
|
Which legislation deters discriminatory compensation practices in the workplace and ensures that when discrimination does occur wronged employees can receive fair compensation?
a. Equal Pay Act b. Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act c. Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act d. IRS Intermediate Sanctions |
b. Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act |
|
|
Under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, publicly traded companies are required to
a. disclose the compensation of certain executives to shareholders. b. provide shareholders with a copy of the organization's compensation philosophy. c. demonstrate that pay discrepancies between executives and rank-and-file employees are grounded in statistical analysis. d. pay an excise tax on erroneously awarded incentive-based compensation paid to executives. |
a. disclose the compensation of certain executives to shareholders. |
|
|
Which of the following philosophies would an entitlement-oriented organization embrace?
a. Lifelong employment b. Individual rewards c. Bringing in new talent d. Performance-driven pay |
a. Lifelong employment |
|
|
What is a major advantage of an organization having internal equity?
a. It is a sure way to eliminate gender bias. b. It lowers the amount the organization spends on salaries. c. It guarantees that all employees have the same benefits. d. It allows organizations to fairly recognize unique jobs. |
d. It allows organizations to fairly recognize unique jobs. |
|
|
An HR manager reviews widely published salary data to ensure that the organization's compensation is superior to regional competition. A potential outcome of this lead compensation philosophy is
a. less likelihood of securing federal contracts b. improved ability to attract and retain scarce-skill employees c. increased need for pay openness in the organization d. fewer categories of nonexempt employees who will qualify for paid overtime. |
b. improved ability to attract and retain scarce-skill employees |
|
|
A salary offer based on widely published salary survey data for a less-skilled position in a locale with an abundant labor pool would most likely equate to which of the following market percentiles?
a. 25th percentile b. 50th percentile c. 60th percentile d. 75th percentile |
a. 25th percentile |
|
|
Which of the following statements regarding job evaluation methods is correct?
a. Quantitative methods are more easily explained to employees. b. Quantitative methods do not establish the relative order of jobs. c. Nonquantitative methods evaluate the whole job. d. Nonquantitative methods evaluate job worth. |
c. Nonquantitative methods evaluate the whole job. |
|
|
Which of the following job evaluation methods would provide a small organization with a quick and inexpensive way to compare one job to another?
a. Ranking b. Paired comparison c. Point-factor d. Factor comparison |
a. Ranking |
|
|
Which of the following job evaluation methods would be MOST appropriate for an organization that has a large number of people with similar, defined jobs?
a. Paired comparison b. Factor comparison c. Job ranking d. Job classification |
d. Job classification |
|
|
The HR group gathered salary data but was unable to analyze it until the following year. Is the data still considered usable?
a. Yes, if the data is leveled. b. Yes, if the data is adjusted for wage inflation c. Yes, if the jobs studied are still comparable d. No, salary data over six months old is unusable |
b. Yes, if the data is adjusted for wage inflation |
|
|
Which of the following measures uses number of incumbents and salary?
a. Weighted average b. Unweighted average c. Median d. Mode |
a. Weighted average |
|
|
What is the range spread for a job with a minimum salary of $60,000 and a maximum of $90,000?
a. 15% b. 33% c. 50% d. 67% |
c. 50% |
|
|
Which of the following job classes would typically have the greatest range spread?
a. Production b. Customer service c. Supervisor d. Executive |
d. Executive |
|
|
What is the compa-ratio for an employee who earns $15 per hour where the salary range has a midpoint of $12 per hour?
a. 0.03 b. 0.80 c. 1.25 d. 1.35 |
c. 1.25 |
|
|
Which of the following statements regarding payroll is correct?
a. Social Security taxes are matched and withheld by the employer up to a yearly amount. b. Medicare taxes are matched and withheld by the employer up to a yearly amount. c. Voluntary deductions are withheld from employee paychecks before involuntary deductions. d. Employers must retain paper copies of their payroll records. |
a. Social Security taxes are matched and withheld by the employer up to a yearly amount. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about flat-rate systems is true?
a. They are used most often for bargaining unit jobs. b. They are used most often for professional jobs. c. They are used most often in privately held organizations. d. They are the most cost-effective approach. |
a. They are used most often for bargaining unit jobs. |
|
|
A compensation method related to an employee's individual performance is known as
a. an incentive pay plan. b. a Scanlon plan. c. a step plan. d. a merit pay plan. |
d. a merit pay plan. |
|
|
Which compensation system guarantees an employee a base wage and then pays an additional amount for each unit produced?
a. Straight piece-rate system b. Differential piece-rate system c. Production bonus system d. Commission system |
a. Straight piece-rate system |
|
|
Which of the following statements about person-based pay systems is true?
a. They pay higher performers more aggressively. b. They pay more to employees with long service. c. They pay employees for what they are capable of doing, not for what they currently do. d. They work best in organizations with a few professional employees. |
c. They pay employees for what they are capable of doing, not for what they currently do. |
|
|
An employee has redesigned its pay structure, and a position has a pay range for the grade of $9.10 to $12.75 per hour. What term would apply to an employee in this position who is earning $8 per hour?
a. Red-circle rate b. Green-circle rate c. Broadbanded d. Career-banded |
b. Green-circle rate |
|
|
Two consecutive years of mandated 10% increases in the minimum wage would probably result in which of the following?
a. Compression between the lowest-paid workers and more skilled workers for a retail trade employer b. Less pressure on the available pool of discretionary funds to pay increases for most employers who have minimum-wage employees c. Reduced leverage of employees making one to two times the minimum wage in asking for larger pay increases. d. Increased pressure for larger pay increases among employees making one to two times the minimum wage. |
a. Compression between the lowest-paid workers and more skilled workers for a retail trade employer |
|
|
Gainsharing is a type of
a. profit sharing b. individual incentive plan c. group incentive d. commission |
c. group incentive |
|
|
An advantage of a stock-based (equity-based compensation plan is that it
a. encourages participants to think more like owners. b. provides certain income to participants. c. is preferred by participants over equivalent amounts of cash. d. has no cost; the equity market creates the value. |
a. encourages participants to think more like owners. |
|
|
What should be the compensation basis for a sales representative whose time is spent acquainting potential customers with the organization's product line and providing technical assistance?
a. Commission b. Volume (sales) incentive c. Base salary that represents a large percentage of compensation d. Sales of new products |
c. Base salary that represents a large percentage of compensation |
|
|
All pay decisions should satisfy these six objectives: |
Be legal Be adequate Be motivating Be equitable Provide security Be cost-benefit effective |
|
|
The four factors that influence pay levels are: |
1. External factors: market, unions, geographical pay differences, etc.
2. Organizational factors: Industry, union or nonunion, profitability, size, etc.
3. Job Factors: Skill, Responsibility, Effort and Working Conditions.
4. Individual Factors: Performance, Experience, Seniority, Potential, Desirability of the job, security, etc. |
|
|
What is a wage-level decision, wage-structure decision and an individual wage decision? |
Wage-level decisions concern the overall level of an organization's compensation when compared to another organization.
Wage-structure decisions concerns the pay awarded to different jobs WITHIN the organization.
Individual wage decisions concern individual incentives and merit pay. How much does an employee receive relative to another employee performing similar work? |
|
|
What are the three different Labor Markets (compensation)? |
Blue-collar and Nonsupervisory white collar
Professional
Supervisors and Executives |
|
|
What are the US Justice Department's Antitrust Safety Zone guidelines for how employers can exchange salary data without violating the law when conducting do-it-yourself surveys? |
Compensation surveys must be managed by a third party. Data must be more than 3 months old All salary data must be derived from at least five entities and no individual entity can represent more than 25 percent of the data. |
|
|
What are three different types of wage surveys? |
Government
Private Industry (Professional Organizations, etc.)
Company-Sponsored (most common) |
|
|
Name 5 different job evaluation methods and indicate which two are non-quantitative. |
1. Ranking (non-quantitative) 2. Classification (non-quantitative) 3. Point method 4. Factor comparison 5. Hay method (Guide Chart-Profile Method)
|
|
|
Describe the ranking method of job evaluation, its advantages and disadvantages. |
Jobs are ranked from highest to lowest value. This is the simplest and requires little time or paperwork. However, the differentials between the ranks are assumed to be equal when they usually are not. Evaluating each job as a whole is not conducive to a careful analysis and it is difficult to use when there is a large number of jobs. |
|
|
Describe the Classification/Grading job evaluation method. |
Typically used by the federal government (GS system). A number of grade with descriptions are set beforehand and then jobs are placed in each of the grades. Then each job is ranked from high to low. An advantage is that wages are standardized for similar jobs and pay differentials between jobs are maintained. However, its stability makes it unresponsive to factors such as regional wage differences and labor-market variances. |
|
|
Describe the Point Method of job evaluation. |
This is used most frequently because it is not difficult to administer and decisions are defensible. Content of jobs from written job descriptions is analyzed and points are allocated for specific factors. The number of points assigned to each job determines a range of pay. |
|
|
What are the six steps in the Point Method of job evaluation? |
1. Identify key jobs (12 - 20 jobs)
2. Identify job factors used to determine pay levels (responsibility, physical demands, etc.)
3. Weight the factors according to their contribution to the overall worth of the job.
4. Divide each job factor into degrees that range from high to low and assign points to each degree.
5. Reach a consensus about degree assignments.
6. Develop a wage curve using key jobs. |
|
|
Describe the Factor Comparison Method of job evaluation. |
This is similar to the Point Method but slightly more complex and less popular. Steps include:
1. Identify key jobs
2. Identify job factors
3. Rank jobs
4. Assign monetary amounts to each job on each factor.
5. Compare unique jobs with key jobs. |
|
|
What are the three compensable factors of the Guide Chart-Profile Method (Hay Method)? |
Know-how: Managerial and Technical.
Problem solving: The thinking environment and the thinking challenge
Accountability |
|
|
What are "key jobs" or "benchmark jobs"? |
These are jobs that are equitably paid. They are not necessarily the most important jobs in the organization, but should be jobs that are stable and well defined. They should be equitably paid because the wage structure for the entire organization will be based on these jobs. |
|
|
This is the process of placing a $ value on the worth of a job. |
Job pricing. Usually a pay range is assigned rather than a specific fixed amount. Job pricing involves making decisions about pay ranges and pay grades. |
|
|
Most pay grades have pay ranges that are ___% to ___% above and below the midpoint of each grade. This is called the range spread. |
10% to 20%
A wider pay range provides more incentive. |
|
|
How is a compa-ratio calculated? |
By dividing a person's wage rate by the midpoint of the pay range and multiplying by 100.
Example: Midpoint is $8 and individual earns $9. ($9 / $8 x 100) = 112.5. A pay range of + or - 20 percent would have compa-ratios between 80 and 120. |
|
|
What is a Scanlon gainsharing plan? |
This is a combination of a gainsharing plan and an employee suggestion system. This usually increases efficiency and productivity and is advocated as a means of reducing union-management conflict. Originally intended as an instrument for unionized companies. A normal cost of labor ratio is determined and if labor is reduced, then the savings go into a bonus fund. |
|
|
Describe the Rucker Share-of-Production plan. |
Similar to Scanlon but based on more sophisticated accounting analysis of "value added" that goes beyond just labor costs. The value added is the sales value of ouput less the cost of materials used. |
|
|
Describe an Improshare gainsharing plan. |
Improshare is similar to Scanlon and Rucker plans but they are tied directly to measures of productivity rather than the value of the product. "Improved Productivity through Sharing". This can be used in situations where a physical product is not produced, unlike the others. |
|
|
What is an ESOP and an ESOT? |
Employee Stock Ownership Plan: Where a trust is created where the company makes tax-deductible contributions of cash or stock. The proceeds are used to buy shares of the company's stock which are allocated to individual employee accounts.
Employee Stock Ownership Trusts are when organizations are wholly owned by their employees through and ESOT.
The idea is that employees who are stockholders will work harder to increase the value of the stock. However, stock prices and dividends are very removed from individual efforts and this doesn't work as intended. However, the monetary value can be motivating. |
|
|
How is money viewed from the various theories of motivation?
Maslow's Need Hierarchy McLelland's Learned Needs Herzberg's Motivator-Hygiene Theory Expectancy Theory Equity Theory Reinforcement Theory |
Maslow's Need Hierarchy: Money is not considered an effective motivator. McLelland's Learned Needs: Money does not have a strong motivating effect on the performance of high-need achievers but does motivate low-need achievers. Herzberg's Motivator-Hygiene Theory: Pay is a hygiene factor and frequent pay adjustments only keep a worker's mind focused on money, leading to dissatisfaction. Better to set pay and forget it. Expectancy Theory: Suggests money can be a powerful motivator if the proper relationships between effort, performance and rewards are perceived. Equity Theory: An individual compares their inputs with rewards to determine if they are equitable. Reinforcement Theory: An individual will perform the task as long as the money is considered an adequate reward and predicts that performance will improve as finance rewards become larger.
|
|
|
What factors should be considered in balancing base pay and incentive pay? |
Security, motivation and equity. |
|
|
Just Noticeable Difference (JND) |
The amount that is required to make a meaningful difference. At higher income levels, a much larger dollar amount is required to make a noticeable difference between income levels. |
|
|
The 1981 Economic Recovery Tax act provided for Incentive Stock Options (ISOs). Why did this increase the popularity of stock option programs? |
This allowed executives to defer paying tax on the appreciated value of their stock until they sold it and it was taxed at the capital gains tax rate of 20% instead of the ordinary income tax rate (usually more than 40%). |
|
|
What are the following controversial practices that companies used to make pay plans more profitable to executives?
Backdating Repricing Reloading Spring-loading Bullet-dodging |
Backdating: pretending an option was granted at an earlier date when the stock price was lower in order to make it more profitable.
Repricing: setting a new, lower exercise price for existing options, because the market price of the stock has fallen since the original award.
Reloading: automatically granting new options at current prices to replace some or all of those that are being exercised.
Spring-loading: awarding options just before releasing positive news likely to drive up stock prices.
Bullet dodging: waiting to award an option until after bad news has driven down the stock price. |
|
|
The popularity of restricted stock grants has increased, why? Also, what are the two different types. |
With the increased reporting required by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and difficulty in determining the fair market value of options, the restricted stock grants have become more popular. These have an absolute value when granted and are more easily accounted for. The two types are time-based shares (requiring executives to be with the company for a defined time) and performance-based shares (require certain performance goals be met). |
|
|
NQDC stands for: |
Nonqualified Deferred Compensation. These include stock options, severance pay plans, etc. These are used to provide additional tax-deferred compensation and retirement benefits to top executives as a recruiting or retention tool. |
|
|
What is a "rabbi trust"? |
A rabbi trust is a vehicle for holding assets set aside to support an employer's unfunded deferred compensation obligation. It is so called because the first IRS ruling on this form of deferred compensation involved a congregation that utilized such an arrangement to protect its retirement obligations for its rabbi. These funds cannot be used by the employer unless it becomes insolvent or enters into bankruptcy. The funds can be used to pay creditors. |
|
|
Perquisites are... |
"Perks" such as Chauffeur Service, Reserved Parking, etc. |
|
|
What are the three benefits that must be provided by employers and are intended to protect employees' incomes? |
Social Security (FICA), Workers' Compensation and Unemployment Compensation |
|
|
In addition to paying a worker upon retirement, Social Security benefits are also available for: |
survivor benefits when a worker has died
disability benefits (under the Old Age Survivors and Disability Insurance Act)
Medicare for individuals 65+ (if not disabled) |
|
|
The Rx benefit added in 2006 for people eligible for Medicare is know as what? |
Plan D |
|
|
Which tax is not capped? Social Security/FICA or Medicare? |
Medicare tax does not have a cap. |
|
|
What three benefits are provided by workers' compensation in most states? |
death benefits (one time lump sum) medical expenses wage replacement payments |
|
|
What is a traditional company-provided pension plan also known as? |
A Defined Benefit Pension Plan.
These use salary and years of service to determine the benefits that employees receive. Separate accounts are not maintained for each participant. |
|
|
What are some differences between Defined Benefit Pension Plans and Defined Contribution Plans? |
Defined Contribution Pension Plans require a separate account for each participant and the money put in these accounts comes from both employers and employees in most cases. An example is a 401(k). |
|
|
What is a Cash Balance Plan? |
This is a hybrid plan that combines aspects of both defined benefit and defined contribution plans. These plans allow employers to decide how funds will be invested and are more portable when employees want to move from company to company. There are three methods the ER can choose from for determining the interest credit rate. |
|
|
What are target date funds? |
Target-date funds, AKA life-cycle funds, automatically adjust their mix based on an employee's age. Example: Younger employees may have higher risk portfolios. |
|
|
What is a 403(b) plan? |
This is a retirement savings plan for tax-exempt organizations such as public schools, colleges, etc. |
|
|
When must minimum distributions to participants in employer-sponsored plans begin? |
No later than April 1st of the year after which the participant reaches the age of 70.5 or retires, whichever comes later. So, if an employee retires at 72, distributions are required April 1st of the following year. |
|
|
What section of the NLRA states that employees shall have the right to:
Self-organization Form, join, or assist labor organizations Bargain collectively through representatives of their own choosing. Engage in other concerted activities for the purpose of collective bargaining or other mutual aid or protection. Refrain from any or all such activities. |
Section 7 of the NLRA
|
|
|
Which Executive Order requires that contractors (unionized or nonunionized) entered into contracts with the federal government:
Post notices informing employees about their rights under federal labor law. Include provisions in their contracts that require their subcontractors to post the same employee notice. |
Executive Order 13496
|
|
|
What are three COMMON-LAW exceptions to Employment at Will?
|
Public policy: Employees cannot be fired for fulfilling legal obligations or for exercising their legal rights.
Implied contract: Employees cannot be fired when an agreement for employment is implied by the circumstances, even though there is no express contract. Implied covenant of good faith or fair dealing: A termination may be unjustified if it involves a lack of good faith or fair dealing by the employer; contracts oblige each party to act with honesty in the conduct of the transaction. |
|
|
This type of law serves to protect person' interests in their physical safety and well-being, in the possession and enjoyment of their property, in their financial resources, and in the intangible resource of reputation.
|
Tort Law
|
|
|
Examples of Common-Law Tort Claims include:
(5 examples) |
Negligent hiring/negligent retention: occurs when a person is harmed because an employer hired an employee who the ER knew or should have known posted a risk or retained employees who engage in misconduct that poses a threat to others both during and after work hours.
Defamation: Injuring someone's reputation by making a false and malicious statement; may be spoken (slander) or written (libel). Fraudulent misrepresentation: Intentional deception relied upon and resulting in injury to another person. Employee's duty of loyalty: Imposes on employees a duty to be loyal to the employer and not take actions that would harm the employer's business. Invasion of privacy: Strikes a balance between the individual's right to privacy and other important public interests. |
|
|
A properly written and enforceable noncompete agreement will contain language that:
(3 items) |
Limits the geographical area to which the agreement applies.
Limits the duration of time the agreement will be in effect. Details the scope of the activity that is prohibited. |
|
|
What is INEVITABLE DISCLOSURE?
|
The principle that an employee with knowledge of a former employer's trade secrets will inevitably disclose the secrets to a new, competitor employer.
|
|
|
What are 4 Common-Law Contract Law issues?
|
Express oral contract: Involves verbal promises made between employer and employee related to employment.
Unfair competition and noncompete agreements: Deal with employment contracts or employment agreements that contain covenants not to compete after the termination of the employment relationship and with the use of secret, confidential, or proprietary information that the employee obtained while working for the former employer. Inevitable disclosure: Enables an employer to prevent an employee from taking employment with a competitor when the current employer's trade secrets might "inevitably" be disclosed. Employee's duty of loyalty and confidentiality: Requires that employees not engage in conduct adverse to employers' best interests; obligates employees to maintain confidentiality of employer information, even after employment ends. |
|
|
What are the steps in the litigation process?
|
1. Notification
2. Answering the Complaint 3. Scheduling Conferences (Usually federal only) 4. Discovery Process 5. Motion to Dismiss 6. Summary Judgment 7. Pretrial and Trial |
|
|
What are the steps of an effective investigation?
|
Ensure confidentiality
Select an investigator Create a plan Conduct interviews Create a report, if appropriate |
|
|
An employer operates a customer service call center with 250 employees. It is a nonunionized workplace. The employer learns that a group of employees has been meeting regularly to compile a list of grievances about the conditions of employment, including both monetary and nonmonetary conditions. Which of the following actions is within the employer's and employees' obligations and rights under the NLRA?
a. The employer may fire the group of employees without cause. b. the group of employees may insist that other employees in the workplace share costs of seeking counsel from a labor attorney. c. The employees may join a union. d. The employer may make continued "concerted activity" grounds for dismissal. |
c. The employees may join a union
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about common law is TRUE?
a. It is a wrongful act, damage or injury done willfully. b. It is enacted by legislation. c. Its basic principles are found in every society. d. It is based on a history of court decisions and customs. |
d. It is based on a history of court decisions and customs.
|
|
|
After three months on the job, an employee is fired without cause. This situation is an example of
a. the disregard of reference checking by the employer. b. defamation. c. the violation of an implied contract. d. the common-law concept of employment-at-will. |
d. the common-law concept of employment-at-will.
|
|
|
A ten-year employee with a company as assured by the supervisor that the employee would always have a job. Three months later, the employee was called to jury duty and assigned to a trial that lasted six months The employer hired someone to take over the job and was then unable to find the employee a suitable position after the trial. This situation may violate all of the following exceptions to the doctrine of employment-at-will EXCEPT
a. express oral contract b. public policy c. implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing d. negligence |
d. negligence
|
|
|
The BEST way to avoid litigation over negligent hiring is to
a. administer personality tests b. check references c. include a disclaimer in the employment contract d. require a drug test |
b. check references
|
|
|
The common-law concept of defamation can be defined as
a. injuring someone's reputation in the community through slander or libel. b. denying an opportunity to a qualified individual due to protected class preferences. c. being liable for injuries caused by an employee who the employer knew or should have known posed a risk. d. being able to terminate an employee at any time, for any reason, unless prohibited by law. |
a. injuring someone's reputation in the community through slander or libel.
|
|
|
In deciding between two job offers, an individual decides to accept the lower salary offer because the interviewer stated that the organization would pay for graduate school. After six months on the job, the employee's request for tuition reimbursement is denied. Which common-law tort would apply if the employee chooses to file suit?
a. Invasion of privacy b. Negligence c. Fraudulent misrepresentation d. Implied covenant |
c. Fraudulent misrepresentation
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about a noncompete agreement is TRUE?
a. It prohibits a departing employee from ever finding employment in the same field. b. It is valid only in the employee's state of residence. c. It must be presented as a condition of employment at the time of a job offer is made. d. It must contain a clause limiting the length of time the agreement will be in effect. |
d. It must contain a clause limiting the length of time the agreement will be in effect.
|
|
|
Which of the following actions could be perceived as retaliation for an employee's complaint of discrimination?
a. A supervisor calls the employee into a private office and questions the employee closely about the complaint. b. An attorney questions coworkers about the employee's statements. c. Overtime for entire department, including the employee, is reduced. d. The employee's personnel records are provided to the organization's attorney. |
a. A supervisor calls the employee into a private office and questions the employee closely about the complaint.
|
|
|
An HR manager is informed that an employee has made a complaint to the EEOC regarding promotion and begins to write an e-mail to the employee's manager to describe the requirements of the necessary litigation hold. Which of the following directions BEST reflects these requirements?
a. Please locate and retain copies of performance reviews for this employee for 90 days past the usual document retention period. b. Contact IT to perform a thorough search of all electronic files related to this employee and retain them until further notice. c. Do not destroy any records related to this employee-oral, visual, document, data-filed as hard copies or stored on computers or other electronic devices. d. This hold pertains only to communications stored on the organization's premises or property (i.e., work computers). |
c. Do not destroy any records related to this employee-oral, visual, document, data-filed as hard copies or stored on computers or other electronic devices.
|
|
|
All of these factors support positive employee relations in nonunion organizations EXCEPT
a. skip-level interviews b. strong employee commitment to organizational goals. c. new and improved company newsletter d. use of sanctions to motivate desired behavior |
d. use of sanctions to motivate desired behavior
|
|
|
An entry-level employee expresses interest in applying for a possible Grade II position. This process is known as
a. job bidding b. job posting c. open-door communication d. balanced promotion |
a. job bidding
|
|
|
An employer in a nonunionized workplace becomes aware of widespread negative employee attitudes and decides to create an employee participation program that would work on improving workplace satisfaction. Which of the following actions might be problematic and construed under the NLRA as dominating a labor organization?
a. The employer tells members of the committee that they are not representing other employees. b. The employer does not inform the committee members of their right to form a labor organization before the committee begins its work. c. The employer promises to work with the committee, to respond to committee proposals, and to develop mutually agreed solutions. d. The employer tells the committee members to avoid issues related to wages and benefits. |
c. The employer promises to work with the committee, to respond to committee proposals, and to develop mutually agreed solutions.
|
|
|
Labor management cooperation is BEST supported by which action?
a. Preserving the traditional "us-them" environment b. Promoting high expectations for success c. Allowing committee members to defend their positions. d. Setting common goals on a united front |
d. Setting common goals on a united front
|
|
|
An employee at one plant in a large manufacturing company submits an idea to management that results in streamlining a distribution process. The suggestion saves the company about $500,000 in transportation costs and ensures continuous supply of product to customers. To recognize the employee contribution, senior management at headquarters immediately decides to give the employee a $100 bonus and to report the story in the next company newsletter. Why may this reward action prove problematic?
a. The reward may not be aligned with the value of the suggestion to the company b. Financial rewards don't affect employee engagement and motivation. c. Management should have waited for an end-of-year recognition program for all employee suggestions. d. Management may recognize the employee in private but should not provide details about the reward to the rest of the workforce. |
a. The reward may not be aligned with the value of the suggestion to the company
|
|
|
Which of the following describes task identity?
a. The amount of clear information received about how well or how poorly a job has been performed. b. The extent to which the job requires a whole, identifiable unit of work. c. The extent of individual freedom and discretion in the work and its scheduling. d. The extent to which the job has a substantial impact on other people. |
b. The extent to which the job requires a whole, identifiable unit of work.
|
|
|
Which of the following job design practices broadens the scope of a job by expanding the number of different tasks to be performed?
a. Job enrichment b. Division of labor c. Job rotation d. Job enlargement |
d. Job enlargement
|
|
|
A disadvantage of flextime is that
a. utility costs may be higher because of longer operating hours b. it provides more flexibility in handling uneven workloads c. the total number of employees to compensate increases d. one-day absences are reduced |
a. utility costs may be higher because of longer operating hours
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of an alternate work schedule?
a. Job sharing b. Self-directed work teams c. job rotation d. Task forces |
a. Job sharing
|
|
|
The significance of the Crown Cork NLRB decision is that it
a. discourage the use of project teams in unionized workplaces. b. strictly defines the use of incentives for employee creativity. c. allows some use of employee involvement committees. d. places strict guidelines on job definition |
c. allows some use of employee involvement committees.
|
|
|
Which of the following employer committees would follow under a safe-harbor provision for employee participation programs?
a. Employees within a work area select respected employees to present employees' ideas on increasing unit efficiency. b. A committee is organized to provide comments to management on the adequacy of the workplace safety procedures. c. Committee members poll fellow employees so that they can prioritize issues on workplace satisfaction in a report to management. d. A committee formed to improve attitudes meets with management to review its findings and develop final actions. |
b. A committee is organized to provide comments to management on the adequacy of the workplace safety procedures.
|
|
|
Employee attitude surveys serve which of the following functions?
a. Productivity improvement tool b. Job satisfaction improvement c. Intervention tool d. Supervisory feedback tool |
b. Job satisfaction improvement
|
|
|
When conducting evaluative research, the HR professional should
a. ignore extraneous factors. b. keep to the scheduled time line. c. establish base-line points against which changes can be compared. d. monitor employee behavior. |
c. establish base-line points against which changes can be compared.
|
|
|
Workplace dress code for casual days is generally an example of a
a. policy b. procedure c. work rule d. collective bargaining item |
a. policy
|
|
|
Which of the following best exemplifies a work rule?
a. Training employees to scan all e-mail attachments for viruses. b. Terms of paid sick leave for nonexempt employees. c. Method for authorizing departmental vacations d. Prohibiting employees from drinking alcohol on the job. |
d. Prohibiting employees from drinking alcohol on the job.
|
|
|
It is a good idea to regularly update an employee handbook because
a. job specifications must be modified to accurately reflect the chain of command. b. related laws, regulations and interpretive court decisions may change. c. discussion of job security legally needs to be translated for new minority employees. d. termination reasons need to be revised according to settlements reached in just-cause disputes |
b. related laws, regulations and interpretive court decisions may change.
|
|
|
An organization's handbook may create the appearance of "chilling" employees' rights to engage in concerted activities by
a. referring to union authorization cards. b. including a statement that the organization desires to remain union-free c. broadly warning employees against harassment in the workplace. d. making prohibitions that cannot be enforced consistently. |
c. broadly warning employees against harassment in the workplace.
|
|
|
An employee physically attacks another employee in a break room. The employer investigates the incident with witnesses and fires the violent employee without a hearing or the usual discipline process. This is an example of
a. termination with due process. b. termination because of a summary offense. c. termination as a result of a nonsummary offense. d. wrongful termination of an at-will employee. |
b. termination because of a summary offense.
|
|
|
A customer service representative is reported by a customer as having been rude during a recent call. The representative's supervisor checks the audio recording of the call, confirms the complaint, and meets with the representative to discuss the event. The supervisor says, "I'd like to understand better what happened and why you might have reacted this way. Then we can find a way to work on this and try to prevent it from happening again." This scenario is most likely an example of
a. progressive discipline b. punitive discipline c. nonpunitive discipline d. alternative dispute resolution |
c. nonpunitive discipline
|
|
|
A home health-care agency hires only experienced nursing assistants and because of this has not found it necessary to publish explicit work rules. A supervisor conducting a routine inspection finds that a new employee is not wearing the company-provided uniform and recommends that the employee be disciplined. The employee is told about the infraction at a meeting with management and explains that the uniform is uncomfortably tight and inhibits the employee's ability to lift patients. The employee is suspended for one day without pay. The employee protests that she has not received due process. What part of due process was violated here?
a. The requirement is unreasonable b. The penalty was inconsistently applied. c. The employee was not given the opportunity to defend herself. d. The employee was not informed of the requirement. |
d. The employee was not informed of the requirement.
|
|
|
Progressive discipline is best described as a system that
a. is based on feedback from peers b. imposes increasingly severe penalties for each violation. c. is based on the alternative dispute resolution process. d. improves two-way communication between manager and subordinate. |
b. imposes increasingly severe penalties for each violation.
|
|
|
Companies prefer to use alternative dispute resolution (ADR) because it
a. helps companies maintain their nonunion status. b. requires little training to institute the process. c. reduces the number of disputes that end up in court. d. keeps salaries competitive. |
c. reduces the number of disputes that end up in court.
|
|
|
Which of the following ADR options can be a binding resolution?
a. Ombudsperson b. Mediation c. Arbitration d. Fact finding |
c. Arbitration
|
|
|
The Railway Labor Act covers which of the following employees?
a. Railroad employees only b.Railroad employees and trucking employees c. Railroad employees and airline employees d. Railroad employees and maritime employees |
c. Railroad employees and airline employees
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about the Norris-LaGuardia Act of 1932 is true?
a. It guaranteed the employer's right to issue injunctions against union activities. b. It prevented union members from participating in strikes, picketing, and boycotting. c. It made yellow-dog contracts not enforceable in federal courts. d. It required employers to bargain in good faith with employees. |
c. It made yellow-dog contracts not enforceable in federal courts.
|
|
|
To improve employee relations, an organizationdecides to establish an alternative dispute resolution process. Which step would NOT be included in establishinga peer review program?
a. Decide if an HR professional will head the team. b. Determine what training will need to occur. c. Decide how to documentchanges in affected policies. d. Determine which employee will be on the team. |
c. Decide how to document changes in affected policies.
|
|
|
What payroll information needs to be kept in themaster file for a nonexempt employee?
a. Employee data,employment data, and tax and payroll information. b. Paper records of hire date, hours worked per dayor week, and regular rate of pay. c. Electronic records of Form W-4, allowancesclaimed, marital status, timecards, and Form W-2. d. Payroll records for the term of employment plusa specified period of time after employment endsnm��.��� |
a. Employee data, employment data, and tax and payroll information.
Although thereis no prescribed format, every employer is required to maintain a master filefor each employee with employee data, employment data, and tax and payrollinformation. This information may bestored on paper or electronically and must be made available within 72 hours ofrequest from any agency regulating payroll practices.m93LW] |
|
|
An employee files an EEOC complaint. The organization is mailed a copy of thecomplaint, along with a Waiver of Service Process form. The organization ignores the complaint anddoes not sign the form. What will happen?
a. They are tacitly admitting to the allegeddiscrimination. b. They have 20 days torespond to the complaint. c. They are held in contempt of court. d. The employee pays to have the complaintpersonally served. |
b. They have 20 days torespond to the complaint.
If the waiveris not signed, the organization has 20 days to respond; if the waiver issigned, they have 60 days to respond. Inaddition, the complaint will be personally served and the employer will incurthose costs. |
|
|
4. An organization must shift the rising costs of health-care benefits to their employees. Management is concerned that some top performers will seek employment elsewhere. Which action is the best way to sustain employee loyalty?
a. Education employees about how much their benefits are worth. b. Launch a social media campaign. c. Enhance work/life balance opportunities. d. Provide employees with industry trend analysis data. |
a. Educate employees about how much their benefits are worth.
As employerscontinue to shift the rising costs of benefits to their employees, employeesneed to know the price components of their benefits package. While most employees value their benefits,many underestimate the percentage of premiums their employer covers. Employees need to understand the value ofbenefits so they can make informed choices about who they work for and thebenefits they select. |
|
|
Under the NLRA, which of the following practices is illegal?
a. Allowing the union to represent nonunion workers in the bargaining unit. b. Establishing company-sponsored labor organizations. c. Contributing to a charity in lieu of union dues. d. Allowing employers to file union unfair labor practice charges. |
b. Establishing company-sponsored labor organizations.
Dominating or interfering with the formation or administration of any labor organization, financially or otherwise, violates the NLRA. |
|
|
When utilizing the services of third-party administrators (TPA’s) for COBRA, which of the following is the most important consideration?
a. Monitor reports and documentation provided by the vendor. b. Renegotiate the contract each year based on feedback from periodic reviews. c. Routinely assess whether the vendor’s culture is compatible with the organization. d. Ensure that the vendor’s service does not diminish the value of internal HR professionals. |
a. Monitor reports and documentation provided by the vendor.
Complying with COBRA is a complex endeavor. Organizations utilizing the services of TPAs for COBRA should vigilantly monitor reports and documentation provided by the vendor to ensure legal compliance and accuracy and to review the fiscal impacts of the outsourced program. |
|
|
Concerned about a potential organizing campaign, an organization hires an outside consultant to conduct an employee relations audit. This audit may result in
a. A union charge that an unfair labor practice has been committed. b. Audit data being requested during discovery in a future complaint case. c. A decrease in employee engagement. d. The organization being charged with violating employee privacy. |
b. Audit data being requested during discovery in a future complaint case.
An employee relations audit examines how well HR and the organization fulfill legal requirements and meet employee expectations. It can help identify areas of discontent so that they can be addressed before a unionizing campaign, but the data may also be subject to discovery in the event that an employee files a complaint against the employer. |
|
|
Which of the following health-care funding mechanisms contains the greatest amount of financial risk for an employer?
a. Partially self-funded b. Self-funded c. Fully insured d. Administrative-services-only |
b. Self-funded
If an organization has a self-funded health-care plan, the employer assumes the role of the insurance company and assumes some or all of the risk. Self-funded arrangements are subject to annual nondiscrimination testing requirements to ensure that the plan is not discriminating in favor of highly compensated employees. |
|
|
A new accounts payable policy, procedures, and work rules have been in effect for six months. The accounts payable team is frustrated because the policy is not being followed. This is resulting in lower morale in their department. What is HR’s role?
a. Support the accounting staff by listening to them but asking them to be patient in waiting for the shift in behaviors. b. The human resources team does not have a role at this moment. c. Endure that the managers are clear on the intent of the policy, that they are complying with it, and that they are enforcing it. d. Enforce the policy through progressive discipline of the employees who are not following it. |
c. Endure that the managers are clear on the intent of the policy, that they are complying with it, and that they are enforcing it.
HR needs to support both the accounting department and the managers by ensuring that the policy is understood and followed. |
|
|
Safety and illness prevention programs are BEST developed
a. After an organizational needs analysis. b. As a result of an OSHA inspection. c. In response to a company incident. d. When OSHA laws and regulations change. |
a. After an organizational needs analysis.
A needs assessment creates a snapshot of the organization’s safety strengths and weaknesses and should be done on a regular basis, before an OSHA audit or a safety incident. A regular audit will include changes necessary due to new or enhanced regulations. |
|
|
A manager in the organization consistently avoids dealing with employee attendance problems. One of the employees with an attendance problem has spoken in a hostile manner to the manager in a staff meeting. The manager now wants to start corrective action for attendance at the final warning stage for this employee. What should the HR manager NOT do?
a. Help the manager write a final warning for poor attendance for the employee. b. Meet with the employee for the problem-solving step of corrective action regarding the hostile language. c. Announce to the employees that the manager will start consistently applying the attendance policy. d. Work with the manager to reestablish the attendance policy. |
a. Help the manager write a final warning for poor attendance for the employee.
Since the attendance policy has not been enforced, the organization should not retaliate for hostile language with a final written warning for attendance. |
|
|
Which of the following characteristics is MOST important for an HR professional evaluating an organization’s compensation and benefits system?
a. The ability to understand the organizational culture b. An understanding of the current and emerging workforce c. Knowledge regarding competitors d. An understanding of current state and federal laws |
d. An understanding of current state and federal laws
All of the options presented are important characteristics for HR professionals working with compensation and benefits. However, the most important feature is that state and federal laws are satisfied. These regulations change at the direction of Congress and state legislatures; therefore, remaining current is a special challenge. |
|
|
Which common-law concept protects an employee from being fired for reporting a criminal activity committed by an employer?
a. Implied contract
b. Public policy
c. Constructive discharge
d. Implied covenant of fair dealing |
b. Public policy
The public policy exception to employment at will states that employees generally cannot be fired for disclosing illegal or illegitimate practices under the control of their employers to organizations that can take corrective action. The other concepts do not deal with the situation described above. Implied contracts hinge on statements implying that employment will be continued. Constructive discharge occurs when an employer makes conditions so intolerable that an employee must resign. The implied covenant of fair dealing comes into play when an employer treats an employee unreasonably and arbitrarily, for example, firing a sales employee who is due to collect a big commission. |
|
|
A manufacturing organization’s office employees are arriving late to work on a consistent basis. A focus group survey is conducted, and it appears that the employees’ morning commute has changed significantly due to highway construction and the opening of new businesses. Which is the BEST strategy the organization should use to correct the problem?
a. Enforce the tardiness policy consistently. b. Introduce a flextime policy with bandwidth hours. c. Introduce a job rotation plan to broaden the scope of the job. d. Establish a telecommuting policy. |
b. Introduce a flextime policy with bandwidth hours.
Since this is a manufacturing organization, employees need to be at the organization’s facility. Therefore, allowing employees to work on a flextime schedule is the best answer. |
|
|
An organization has grown quickly, and its culture has consequently changed. Its founders have directed HR to develop a skip-level interview policy. What concern most likely prompted this action?
a. Fear of a disconnect between upper levels of management and lower-and entry-level employees. b. Desire to manage the risk of employee litigation. c. Desire to facilitate the process of filing and resolving grievances. d. Belief in developing employees’ skills and promoting from within. |
a. Fear of a disconnect between upper levels of management and lower-and entry-level employees.
Rapidly growing organizations must often add layers of management, increasing the gap that lower-level employees feel they must bridge to communicate with management. A skip-level interview policy requires managers to spend time with each employee two levels below the manager on an annual basis. |
|
|
The HR director and the management team of a small resort hotel are developing a strategy to remain union-free. The union’s representatives are talking with the employees. What action should management take?
a. Conduct a joint presentation with the union representative for hotel employees. b. Ensure that the hotel’s pay structure and benefits package lag those of its direct competitors. c. Present the company’s position to the employees, but do not mention the union. d. Present the company’s position and the union’s strategy to the employees honestly. |
d. Present the company’s position and the union’s strategy to the employees honestly.
Be honest with the employees. Being dishonest will play into the union’s potential future organizing campaign. |
|
|
What is the difference between replacement planning and succession planning?
a. Replacement planning focuses on developing backups for key positions; succession planning develops a pool of candidates capable of filling several assignments. b. Replacement planning is based on a formal development plan; succession planning is more informal and is usually based on oral discussions between manager and employee. c. Replacement planning focuses on mid-level positions; succession planning focuses on executive-level positions. d. Replacement planning has a long-term focus; succession planning has a short-term focus. |
a. Replacement planning focuses on developing backups for key positions; succession planning develops a pool of candidates capable of filling several assignments.
Replacement planning is focused on a single functional area and on finding backup candidates who are ready to assume a position within the short term, usually 12 months. Succession planning focuses on developing a pool of talented employees who will be capable of filling a variety of positions within the long-term, usually 12-36 months. Replacement planning can be done at all levels, not just for mid-level executives. Generally speaking, replacement planning is more than succession planning. |
|
|
The term "closed shop" refers to a(n)
a. employer who refuses to hire employees who are union members. b. employer who requires employees to be union members at the time of hiring. c. union that limits the number of employees who may join the union. d. employer who establishes company-sponsored unions. |
b. employer who requires employees to be union members at the time of hiring.
|
|
|
A union shop clause states that
a. workers who take a job in a bargaining unit are not required to join the union. b. workers who take a job in a bargaining unit must pay union dues but are not required to join. c. workers must join the union to be considered for a job in a bargaining unit. d. workers who take a job in a bargaining unit must join the union within a certain period of time. |
d. workers who take a job in a bargaining unit must join the union within a certain period of time.
|
|
|
The Labor-Management Reporting and Disclosure Act of 1959 was enacted to
a. protect employees from corrupt or discriminatory labor unions. b. excuse union officers from reporting financial transactions. c. allow the construction trades to make hiring decisions based on union membership. d. uphold the unions' right to require membership as a condition of employment. |
a. protect employees from corrupt or discriminatory labor unions.
|
|
|
The purpose of organizational picketing is to
a. obtain employer recognition of the union as a bargaining representative. b. gain public support for the union and its goals. c. induce employees to accept the union as their representative. d. identify key issues and union complains prior to an election. |
c. induce employees to accept the union as their representative.
|
|
|
Before the NLRB will order an election, what percentage of the eligible employees must sign authorization cards?
a. 20% b. 25% c. 30% d. 35% |
c. 30%
|
|
|
In determining if a proposed bargaining unit is appropriate, the NLRB will consider whether the
a. proposed unit is the best unit to represent workers. b. employees have sufficient common interests. c. union has a reputation for fairness. d. size of the union will affect its ability to bargain efficiently. |
b. employees have sufficient common interests.
|
|
|
Which of the following are customarily excluded from a bargaining unit?
a. Supervisory employees b. Government employees c. Part-time employees d. Seasonal employees |
a. Supervisory employees
|
|
|
A consent election agreement occurs when
a. the union and the employer disagree on voter eligibility requirements. b. the issue of union recognition is the only outstanding dispute. c. the employer and the union disagree on the composition of the bargaining unit. d. a representation question concerning interstate commerce becomes an issue. |
b. the issue of union recognition is the only outstanding dispute.
|
|
|
An Excelsior List is a listing of
a. organizations that campaign against unions. b. names and addresses of all eligible bargaining unit employees. c. acceptable unions filed with the NLRB. d. union officials eligible to vote. |
b. names and addresses of all eligible bargaining unit employees.
|
|
|
A number of union employees at a company have become dissatisfied with the union due to major concessions the union made during the last several bargaining sessions. The FIRST step these employees must take to remove the unions as their bargaining agent is to
a. request temporary leave from the union. b. request an investigation by the NLRB c. inform union leaders of their dissatisfaction. d. request a decertification election. |
d. request a decertification election.
|
|
|
According to the NLRB, a company can legally
a. refuse to bargain with a union that represents a majority of employees after good-faith bargaining. b. bargain with individual employees in the bargaining unit. c. protect their property. d. refuse to bargain with a bargaining unit specified by the NLRB. |
c. protect their property.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is an example of a threat of reprisal by an employer?
a. Employees do not need unions b. Employees will lose existing benefits. c. Employers can provide anything employees need. d. The organization is successful and will continue to be successful. |
b. Employees will lose existing benefits.
|
|
|
Which of the following does NOT constitute an employer unfair labor practice?
a. Refusing to bargain with an NLRB-recognized union. b. Interfering with, restraining, or coercing employees. c. Campaigning against the union through speeches. d. Dominating or unlawfully supporting a labor organization. |
c. Campaigning against the union through speeches.
|
|
|
According to the NLRB, a union
a. must represent all workers in a bargaining unit equally, union or not. b. can insist that all employees in a bargaining unit use the union grievance procedure. c. can legally attempt to get a worker fired if that employee seeks to decertify the union. d. must expel a union member for failure to pay union dues. |
a. must represent all workers in a bargaining unit equally, union or not.
|
|
|
Which of the following does NOT constitute an unfair labor practice by the union?
a. Charging workers a service charge for representation during grievance proceedings. b. Fining employees for crossing a picket line after they resigned from the union. c. Causing an employer to discharge employees because they disagreed with union policy. d. Insisting on the inclusion of a closed shop contract provision. |
a. Charging workers a service charge for representation during grievance proceedings.
|
|
|
All of the following may happen after a preliminary NLRB investigation EXCEPT
a. a waiver of the right to a public hearing. b. a written statement of the facts underlying the charge. c. resolution of the dispute by the charged party without admitting guilt. d. appeal to one of the United States Courts of Appeals. |
d. appeal to one of the United States Courts of Appeals.
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a category of collective bargaining subjects?
a. Mandatory subjects b. Reserved subjects c. Voluntary subjects d. Illegal subjects |
b. Reserved subjects
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of a voluntary collective bargaining subject?
a. Rates of pay b. Overtime c. Hot cargo classes d. Neutrality agreements. |
d. Neutrality agreements.
|
|
|
A union that concentrates on negotiations with one employer and then negotiates similar contracts with competitors is using what type of collective bargaining?
a. Pattern b. Coalition c. Coordinated d. Focused |
a. Pattern
|
|
|
When more than one employer negotiates with the union, it is known as what type of collective bargaining?
a. Pattern b. Coalition c. Coordinated d. Focused |
b. Coalition
|
|
|
When an employer bargains with several unions simultaneously, it is known as what type of collective bargaining?
a. Pattern b. Coalition c. Coordinated d. Focused |
c. Coordinated
|
|
|
Which of the following types of bargaining would MOST likely be used for bargaining over wages?
a. Distributive b. Integrative c. Attitudinal d. Variable |
a. Distributive
|
|
|
Which of the following types of bargaining would MOST likely be used for bargaining over issues such as workplace health and safety?
a. Distributive b. Integrative c. Attitudinal d. Variable |
b. Integrative
|
|
|
Unlawful circumvention refers to an employer's
a. refusal to provide relevant information for the negotiation process. b. refusal to furnish information that would violate employee privacy. c. attempt to discuss with employees any proposals not presented during negotiations. d. attempt to go around the union by hiring temporary replacement workers. |
c. attempt to discuss with employees any proposals not presented during negotiations.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about a union negotiating a collective bargaining agreement in a right-to-work state is true?
a. The union may include an agency shop clause. b. The union may substitute a maintenance of fees clause. c. The union may charge the employer for nonunion member dues and fees. d. The union may not require employees to join a union or pay dues or fees if the employees choose not to join. |
d. The union may not require employees to join a union or pay dues or fees if the employees choose not to join.
|
|
|
A company that wants to change an existing collective bargaining agreement must notify the other party how many days before the expiration of the contract?
a. 30 b. 60 c. 90 d. 120 |
b. 60
|
|
|
Under Weingarten rights
a. a union employee has the right to have another employee present during certain investigatory interviews. b. the immediate supervisor must attempt to accurately determine the reason for a grievance and try to solve the problem. c. an ombudsperson may be present with a union employee during the highest level of a progressive discipline sequence. d. the employer must be willing to bargain with a union representative throughout the disciplinary process. |
a. a union employee has the right to have another employee present during certain investigatory interviews.
|
|
|
What is the final step in the grievance process under a union contract?
a. Discussion of grievance with manager. b. Third-party determination c. Supervisor intervention d. NLRB court ruling |
b. Third-party determination
|
|
|
Which of the following may be a protected union activity?
a. Primary picketing b. Wildcat strikes c. Secondary boycotts d. Shutdowns |
a. Primary picketing
|
|
|
Employees of a printing company are on strike, effectively shutting down the operation. The company owner transfers work to a neutral third-party employer, effectively using the neutral employees as strike breakers. In this situation, the union
a. has no legal course of action since the employer has the right to use other workers to keep the business operating. b. can extend its primary picketing to the neutral employer. c. can file an injunction against the neutral employer. d. can petition employees of the neutral employer to join the strike effort. |
b. can extend its primary picketing to the neutral employer.
|
|
|
Double breasting is defined as
a. an employer who has separate operations, both of which are union. b. an employer who has a union operation and a network of nonunion allies. c. an employer who has both union and nonunion operations. d. employers who have an agreement to provide labor to each other during strikes. |
c. an employer who has both union and nonunion operations.
|
|
|
Hot cargo clauses were agreements that allowed union workers to
a. expedite the shipment of perishable nonunion goods. b. refrain from picketing goods that were made by nonunion labor. c. refrain from handling good made by nonunion labor or plants on strike. d. set up separate shipping entrances that would not be picketing. |
c. refrain from handling good made by nonunion labor or plants on strike.
|
|
|
In the face of a strike threat, management is most interested in
a. arranging for union security b. informing local law enforcement officers c. assigning supervisors to replace striking workers d. arranging continuation of health insurance for employees. |
c. assigning supervisors to replace striking workers
|
|
|
An employer is required to displace workers hired on a temporary basis and reinstate striking workers when a strike
a. is a sympathy strike
b. is the result of a ULP
c. is declared illegal by the NLRB
d. lasts less than 48 hours |
b. is the result of a ULP or Unfair Labor Practice. |
|
|
Which of the following is a strike that occurs without the approval of the union
a. Economic strike b. Wildcat strike c. Secondary strike d. Spontaneous strike |
b. Wildcat strike
|
|
|
Some union-free organizations use EPPs. What are these?
|
Employee Participation Programs. Also called employee councils, quality circles, peer grievance review panels, etc. They have a common purpose of improving communication between employers and employees. They can also run an employer afoul of the NLRA if they are seen as dominating or interfering with a labor organization.
|
|
|
What is a safe harbor?
|
Safe harbors are provisions in a law or regulation that provide some measure of protection from liability if certain conditions are met. |
|
|
What is the key outcome of Elton Mayo's Hawthorne Studies, or the "Hawthorne Effect"?
|
The Hawthorne Effect is the discovery that individual behaviors are altered when workers are involved and management shows interest in their work.
This work began the human relations movement and the study of industrial sociology, which advocated job design as a way to direct work groups toward the goals of the organization. |
|
|
What are the 3 core characteristics of job design?
|
1. Tasks: a piece of assigned work activity.
2. Duty: Composed of a number of tasks and is a larger segment of work performed by one person. 3. Job Responsibilities: obligations to perform certain tasks and duties. |
|
|
Employees will be more motivated to work and satisfied with their job if the job design accounts for the following core characteristics:
|
Skill variety
Task identity Task significance Autonomy Feedback |
|
|
What is Task Identity?
|
The extent to which the job requires a "whole", identifiable unit of work - doing the job from start to finish with a visible outcome. Sewing a whole pair of pants as opposed to just the pocket.
|
|
|
What is task significance?
|
The extent to which the job has a substantial impact on other people. Is it meaningful?
|
|
|
What is Job Enlargement?
|
This is an attempt to relieve the boredom and low morale associated with excessive job simplification. It refers to broadening the scope of the job by expanding the number of tasks performed.
|
|
|
What is job rotation?
|
Breaks the monotony of routine jobs by shifting people between comparable but different jobs.
AKA "Horizontal Integration" |
|
|
What is job enrichment?
|
Increases the depth of a job by adding responsibility for planning, organizing, controlling and evaluation.
AKA "Vertical Integration" |
|
|
What are the 4 "safe harbors" for employers using Employee Participation Programs (EPPs)?
|
Performance of a management function
Brainstorming: Must be non selective and cannot reach a consensus about a specific proposal's merit. A suggestion box: Committee can organize comments but cannot prioritize them. Operational jurisdiction: Committee can make proposals related to operational issues but NOT to terms or conditions of employment. |
|
|
What is a "Consent Election"?
|
A consent election is an agreement between an employer and the union to waive the preelection hearing.
If the parties agree on preelection issues (including NLRB jurisdiction, bargaining unit composition, balloting procedures and voter eligibility), they may waive their right to a preelection hearing. |
|
|
What is a "Directed Election"?
|
A directed election is an election ordered by the NLRB regional director when the parties are unable to consent to an election and after a preelection hearing on the unresolved issues.
|
|
|
Who are ineligible as voters when forming a union?
|
Certain categories of workers are excluded, such as managers and supervisors, domestic workers, some agricultural workers and confidential employees.
|
|
|
The Control of Hazardous Energy standard requires an employer to a. maintain an inventory of hazardous chemicals in the workplace. b. attach signs or labels to all pieces of equipment. c. implement lockout/tagout procedures. d. provide employee training programs on hazardous materials. |
c. implement lockout/tagout procedures. |
|
|
The Confined Space Entry standard may require which of the following? a. Rescue procedures b. Injury history of all entrants c. Ergonomics analysis of the space d. Knowledge of infectious diseases |
a. Rescue procedures |
|
|
Which of the following OSHA forms is posted at the end of the year? a. OSHA Form 200 b. OSHA Form 300 c. OSHA Form 300A d. OSHA Form 301 |
c. OSHA Form 300A |
|
|
Which of the following must be reported to OSHA? a. An employee who leaves work with a migraine headache. b. A first-aid treatment given by the plant nurse. c. A work-related employee death. d. An employee who suffers the flu. |
c. A work-related employee death. |
|
|
In response to an employee complaint of an alleged violation, an OSHA compliance officer arrives unannounced at a manufacturing plant to conduct an inspection of an assembly line. The plant manager refuses to allow the compliance officer on the premises. The appropriate and legal OSHA response is to a. give 24-hour notice and return the following day. b. file and OSHA citation pending inspection. c. subpoena relevant accident and inspection records. d. obtain a court-ordered search warrant. |
d. obtain a court-ordered search warrant. |
|
|
Based on an OSHA workplace inspection, an organization receives a citation for inadequate ventilation of potentially toxic fumes. The organization may challenge the citation by a. requesting judicial review within 30 days. b. filing a Notice of Contest with the OSHA Area Director within 15 working days. c. requesting an informal conference with the OSHA Area Director. d. appealing to the OSHA Area Director. |
b. filing a Notice of Contest with the OSHA Area Director within 15 working days. |
|
|
Which of the following situations has the highest priority for an OSHA inspection? a. An employee's complaint of extremely long hours at a computer terminal without breaks. b. Employee exposure to dust and noise. c. An on-site accident that results in the hospitalization of seven employees d. An employee's complaint of improper ergonomics. |
c. An on-site accident that results in the hospitalization of seven employees |
|
|
A hazardous condition in the workplace that is causing or is likely to cause death or serious physical harm is an example of a a. serious violation b. willful violation c. repeat violation d. de minimis violation |
a. serious violation |
|
|
An employer that has a federal contract of $350,000 employs a carpenter who has been convicted of a criminal drug offense committed while on the job. Which of the following actions must the contractor take upon receipt of notice of the conviction? a. Fire the employee within 30 days. b. Provide the employee with drug treatment. c. Notify the employee's supervisor of the conviction. d. Notify the federal contracting agency within ten days. |
d. Notify the federal contracting agency within ten days. |
|
|
Reducing the risk of infection in the workplace is accomplished by all of the following EXCEPT a. education b. exposure control plans c. selective hiring d. personal protective clothing |
c. selective hiring |
|
|
According to the ADA, the appropriate action for an employer dealing with employees who are HIV-positive is to a. terminate or transfer the HIV-positive employees if related workplace productivity and/or efficiency losses among other employees are documentable. b. require the HIV-positive employees to seek counseling. c. give the HIV-positive employees six months' termination notice. d. retain HIV-positive employees as long as they are able to perform their jobs. |
d. retain HIV-positive employees as long as they are able to perform their jobs. |
|
|
An employer can reduce liability in the area of fetal protection by fully informing female employees of a. exercise/physical fitness b. teratogens c. nutrition eduction c. stress management |
b. teratogens |
|
|
A formerly excellent production line employee has displayed a marked change in behavior during the past month, characterized by outbursts of emotion and frustration and frequent requests to leave work early. In discussing the situation with the employee, the supervisor learns that the employee's child is terminally ill. This employee would benefit from which employee assistance program? a. Substance abuse counseling b. Wellness counseling c. Family and/or marital counseling d. Financial counseling |
c. Family and/or marital counseling |
|
|
Which of the following behavior changes might an organization expect from the implementation of a physical fitness program? a. Fewer losses due to accidents b. Less absenteeism c. Improved blood pressure d. Lower workers' compensation costs |
b. Less absenteeism |
|
|
An organization requirement that employees show their badges on entering the building would be considered part of which security measure? a. Investigation b. Identification and external control systems c. Theft and fraud d. Personal employee information security |
b. Identification and external control systems |
|
|
Which of the following is the FIRST step in conducting a security risk analysis? a. Develop an emergency response plan. b. Determine the ratio of the cost of protection to the cost of loss. c. Determine the organization's security risk factors. d. Determine the cost of replacing lost or damaged assets. |
c. Determine the organization's security risk factors. |
|
|
The economic rationale for most security programs is based on which of the following cost considerations? a. Risk containment requirements b. Lost investment income incurred in a loss c. Insurance or other indemnity available d. Protection costs versus cost of losses incurred without the protection |
d. Protection costs versus cost of losses incurred without the protection |
|
|
OSHA mandates having an emergency response plan for industries that a. use toxins. b. are located on a fault line. c. have experienced workplace violence. d. employ minors. |
a. use toxins. |
|
|
Which of the following is an internal cause of workplace violence? a. Working with the public. b. Insensitive terminations. c.Guarding valuable property. d. Working in a high crime area. |
b. Insensitive terminations. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a strategy for protecting organizational proprietary information? a. Remind workers not to discuss organizational activities or display sensitive documents in public places. b. Have all employees promise to safeguard organizational secrets. c. Place all organizational information on the intranet and Web sites. d. Have contractors and employees sign confidentiality and nondisclosure agreements. |
c. Place all organizational information on the intranet and Web sites. |
|
|
With regard to technology security risks, which action would be most helpful? a. Focus on protecting only the most confidential and proprietary information. b. Monitor employee use of the organization's e-mail system. c. Restrict access to certain computer information to personnel with a need to know. d. Ensure that information technology personnel have the necessary qualifications. |
c. Restrict access to certain computer information to personnel with a need to know. |
|
|
This type of insurance provides coverage for claims that aren't covered by a general insurance policy. Examples include protection against claims of discrimination, wrongful termination, sexual harassment, and some other employment-related issues made by employees, former employees or potential employees. |
Employment practices liability insurance (EPLI) |
|
|
This kind of insurance is available for directors, officers, employees and the organization to protect against claims of negligence in the performance of professional services. |
Professional liability insurance |
|
|
This insurance protects directors, officers and the corporation from claims such as shareholder class actions and SEC violations for fraud and mismanagement and other inaccurate or improper accounting practices. |
Directors' and officers' liability insurance |
|
|
OSHA provides for health and safety research through what institute? |
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) |
|
|
What are some examples of employees rights under OSHA (8 examples)? These are covered by the GENERAL DUTY CLAUSE. |
The right to demand safety and health on the job. The right to request inspections. The right to have an authorized employee representative accompany an inspection. The right to file a complaint The right to be informed of workplace hazards. The right to request action from the employer to correct hazards or violations. The right to file a discrimination complaint. The right to receive training. |
|
|
What are employer rights under OSHA (4)? |
Monistor OSHA's announcements of its intent to propose new regulations and participate in the rule-making process by attending public hearings on the proposed rules and submitting comments on the rules to the extent that they affect their workplace.
Be active in their industry association's involvement in job safety and health and take and active role in developing safety and health standards through participation in OSHA Standards Advisory Committees.
Apply to OSHA for a temporary variance from a standard if unable to comply because of the unavailability of materials, equipment, or personnel to make the necessary changes within the required time.
Apply to OSHA for a permanent variance from a standard if the employer can furnish proof that the facilities or method of operation provide employee protection at least as effective as that required by the standard. |
|
|
Provides guidelines for preparing an emergency action plan and includes specifications regarding exits and maintenance of emergency systems; also known as Means of Egress standard. |
Emergency Exit Procedures |
|
|
Requires employers to provide for effective engineering or administrative controls to reduce unsafe noise levels in the workplace; also known as Hearing Conservation standard.
|
Occupational Noise Exposure |
|
|
Provides general requirements for all machinery to protect operator and other employees. |
Machine guarding |
|
|
Requires use of labeling, MSDS, training, orientation for new and transferred employees, and written hazard communication programs to inform employees of hazardous chemicals in the workplace; also known as Employee Right-to-Know Law. |
Hazard Communication |
|
|
Require action so equipment cannot be activated (lockout) and signs or labels (tagout) are attached to dangerous equipment that should not be activated. |
Control of Hazardous Energy |
|
|
Requires employers to protect employees from potentially infectious materials; Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act revised the standard to require employers to minimize employees' exposure to blood through sharps injuries through annual reviews and employee input. |
Bloodborne Pathogens |
|
|
Addresses concerns over adequate oxygen content in the air, toxic or flammable substance exposure, and physical exposures for workers in confined spaces. Requires space-entry restrictions, rescue procedures, and written safe-entry program. |
Confined Space Entry |
|
|
Protects employees from environmental, process, chemical, mechanical, or radiological hazards capable of causing injury or impairment and sets criteria for acceptable equipment designs. |
Personal Protective Equipment |
|
|
Aimed at preventing or minimizing the effect of catastrophic releases of toxic, reactive, flammable, or explosive chemicals. |
Process Safety Management. |
|
|
An organization conducts a pay survey and finds that some of its key employees are underpaid. They want to raise the pay for these employees but are concerned about adding to their salary burden. Which of the following is their BEST option?
a. Incentive pay b. Step-rate adjustments linked to performance c. Market-based increases d. Cost-of-living adjustments |
a. Incentive pay
By definition, incentive pay is paying for performance beyond normal expectations. Employees receive the incentive pay only if specific goals are met. As long as incentive pay and base pay are not commingled, employees should perceive it as a reward (and not entitlement) and the employer will benefit from a greater return on investment for performance beyond normal expectations. |
|
|
An HR director’s compensation team is trying to integrate a centralized compensation model across multiple offices. Employees are having trouble understanding what the changes in compensation mean to them, and the eastern office location does not want to be a part of the centralized model because they believe that changes to compensation and bonuses will drive employees away. The organization is also dealing with other companies trying to poach their best employees by offering them higher salaries and more perks, so they cannot afford any additional turnover.
Which of the following is the best move to socialize the eastern office into the new compensation program? a. Propose that the average compensation rate in the organization be the base line for the eastern office’s new compensation rate. b. Suggest that upper management meet with the eastern office about the need to align their compensation with the centralized model. c. Research the maximum proportion of total salary that bonuses should account for by industry. d. Conduct a market analysis of compensation rates in the eastern region for comparison to the eastern office rate. |
d. Conduct a market analysis of compensation rates in the eastern region for comparison to the eastern office rate.
|
|
|
An HR director’s compensation team is trying to integrate a centralized compensation model across multiple offices. Employees are having trouble understanding what the changes in compensation mean to them, and the eastern office location does not want to be a part of the centralized model because they believe that changes to compensation and bonuses will drive employees away. The organization is also dealing with other companies trying to poach their best employees by offering them higher salaries and more perks, so they cannot afford any additional turnover.
What is the best way for the HR director to respond to the other organizations poaching their employees? a. Execute on the company’s vision to be an employer of choice by creating a document summarizing all of the benefits of working in the organization. b. Solicit solutions from managers who are experiencing the greatest losses due to poaching. c. Conduct a compensation analysis to benchmark against the market, implementing appropriate responses to further the company’s mission to be an employer of choice (e.g., retention bonuses, adjustment to compensation policy). d. Hold a meeting with top-level executives to discuss the need to increase salaries to remain competitive. |
c. Conduct a compensation analysis to benchmark against the market, implementing appropriate responses to further the company’s mission to be an employer of choice (e.g., retention bonuses, adjustment to compensation policy).
C is the best option because, through Business Acumen, it demonstrates an understanding of the industry and competitive environment within which the organization operates. B is the second-best option because HR uses the Consultation competency to gather information and investigate the issue, which can result in strategy development. |
|
|
An HR director’s compensation team is trying to integrate a centralized compensation model across multiple offices. Employees are having trouble understanding what the changes in compensation mean to them, and the eastern office location does not want to be a part of the centralized model because they believe that changes to compensation and bonuses will drive employees away. The organization is also dealing with other companies trying to poach their best employees by offering them higher salaries and more perks, so they cannot afford any additional turnover.
What is the best way to handle the confusion regarding changes to the compensation model? a. Create a presentation that can be used by HR managers across the organization to communicate changes in compensation and bonuses. b. Encourage senior leadership to make a public effort to promote the new compensation model. c. Meet with managers at all regional offices to develop a strategy to announce the new compensation model. d. Send an e-mail to the staff including frequently asked questions about the new compensation model. |
a. Create a presentation that can be used by HR managers across the organization to communicate changes in compensation and bonuses.
A is the best option because it provides proactive communication on critical information to stakeholders. D is the second-best option because it provides clear and concise information to employees to clarify ambiguity. Both show the use of the Communication competency. B and C are unacceptable because they do not efficiently deliver information. |
|
|
Which of the following determines the relative worth of each job in an organization?
a. Job specification b. Job study c. Job evaluation d. Job analysis |
c. Job evaluation Job evaluation determines the relative worth of each job by establishing a hierarchy of jobs within an organization. It is intertwined with a concern for internal pay equity. |
|
|
What is the advantage of nonqualified deferred compensation plans?
a. They provide incentives for key executives to stay with the organization. b. They are not subject to ERISA and are protected from creditors. c. They allow all company employees to contribute more than the limits prescribed by qualified plans. d. They provide more-favorable tax advantages to employers than qualified plans. |
a. They provide incentives for key executives to stay with the organization.
Nonqualified deferred compensation plans allow organizations to provide additional benefits to a select group of key executives, which motivates them to stay with the organization. |
|
|
Chain of command refers to the
a. Extent to which policies and procedures govern the rules of the organization. b. Number of individuals who report to a supervisor. c. Line of authority within an organization. d. Balance between standardization and localization. |
c. Line of authority within an organization.
Chain of command refers to a line ofauthority within an organization. Authority relates to the scope of responsibilities that define the areain which a manager is empowered to make decisions. It is growing less distinct in manyorganizations today.\U |
|
|
After conducting a reference background check, HR discovers that a leading candidate misrepresented dates of previous employment both on the resume and the job application. What is the most probable outcome of the learning this information?
a. Check criminal records for felonies or misdemeanors. b. Conduct a credit history check with a consumer reporting agency. c. Ask for references about the employee’s professionalism. d. Do not extend an offer of employment. |
d. Do not extend an offer of employment.
|
|
|
What type of strike occurs without the approval of union leadership?
a. Jurisdictional strikes b. Wildcat strikes c. Sympathy strikes d. Economic strikes |
b. Wildcat strikes |
|
|
Do heterogeneous teams generally outperform homogeneous teams?
a. Yes, but only if they are well managed. b. No, they are too difficult to manage and coordinate. c. No, there are too many different perspectives. d. Yes, they get off to a faster start and maintain an advantage. |
a. Yes, but only if they are well managed.
|
|
|
During a non-work group lunch, an HR person overhears an HR colleague discussing a recent new hire’s previous job experiences. The information is not sensitive, nor was the intention malicious. What should the HR person do?
a. Ignore the occurrence since it was harmless. b. Issue a written warning to protect the organization from potential liability under the Privacy Act. c. Warn the employee in writing that this information has been divulged. d. Remind the colleague later that it is not ethical to divulge confidential information. |
d. Remind the colleague later that it is not ethical to divulge confidential information. |
|
|
An organization is faced with the challenge of offering robust benefits to retain top talent while staying within budget or cost constraints. Why is a benefit needs assessment a valuable undertaking?
a. Assessment results help align the benefits strategy with the organizational brand. b. Data collected helps the organization address employee financial or health problems impacting productivity. c. A benefit needs assessment would determine employee willingness to pay an increasing portion of the plan coverage. d. A benefits package can have a positive impact on attracting, motivating, and retaining talent. |
d. A benefits package can have a positive impact on attracting, motivating, and retaining talent. |
|
|
A mid-sized software organization is preparing to acquire two smaller software firms. The organizations that are being acquired will work both individually and collaboratively on new product lines with multiple dual roles. All three organizations are currently competitors with strong opinions about their competitions’ competencies. Which OD intervention strategy should be used to manage the change to dual reporting roles post-acquisition?
a. Structural strategy b. Interpersonal strategy c. Technological strategy d. Strategic management strategy |
a. Structural strategy A structural strategy helps identify reporting relationships as well as span-of-control issues. |
|
|
A multinational organization allows its labor relationship to be managed entirely by the local subsidiary. This relationship is referred to as
a. Standardized b. Laissez faire c. Centralized d. Hands-off |
d. Hands-off
|
|
|
A vice president and the HR director observe an employee focus group facilitated by HR staff. Both take notes, but their perceptions of employees’ priorities and the strength of employee feelings on certain topics differ enough that both are reluctant to act on the group responses. What would be the BEST solution that the HR director could propose?
a. Rerun the focus group with an outside facilitator and a different group of employees. b. Ask focus group participants to complete an anonymous survey that calls for numerical responses to specific questions. c. Assemble another focus group, keeping conditions the same, and see if the disagreement persists. d. Set aside areas of disagreement and focus on areas where the VP and the director heard the same messages. |
b. Ask focus group participants to complete an anonymous survey that calls for numerical responses to specific questions.
The best strategy would be to clarify participants’ attitudes in a way that can be analyzed objectively. The responses in the focus group can be used to develop an effective survey to gather this focused data. Rerunning the focus group, even with a different group or outside facilitator, may present the same issues. A greeting to ignore areas of disagreement may mean agreeing to ignore critical areas of employee dissatisfaction. |
|
|
An organization must make labor reductions to reduce its costs. Several long-term employees havebeen offered early retirement packages. One employee has decided to decline the opportunity to takeearly retirement. The manager reassigns the employee to another job with a lower profile that theemployee clearly finds intolerable. The employee quits.
What action could the employee claim in a lawsuit against the organization? a. The employee could claim an unemployment violation to the EEOC against the manager. b. The employee could claim organizational harassment in the workplace against themanager. c. The employee could claim the right to work due to the individual’s long-termemployment with the organization. d. The employee could claim that the organization’s actions created a constructivedischarge situation. |
d. The employee could claim that the organization’s actions created a constructive discharge situation. |
|
|
An organization must make labor reductions to reduce its costs. Several long-term employees havebeen offered early retirement packages. One employee has decided to decline the opportunity to takeearly retirement. The manager reassigns the employee to another job with a lower profile that theemployee clearly finds intolerable. The employee quits.
What must the employee prove to prevail in this case? a. The employee must prove that a reasonable person in the employee’s place would havefelt forced to resign or that there was intent on the part of the employer to force theperson to leave. b. The employee must prove that any employee working in the same department andworking conditions would have felt forced to resign or a lack of concern for the wellbeingof the employee. c. The employee must prove that there was organizational harassment in the workplacethat forced the resignation or that there was intent on the part of the employer todefame the person’s reputation. d. The employee must prove that there were many employment-at-will exceptions thatwould have forced the resignation or that there was intent on the part of the employerto defame the person’s reputation. |
a. The employee must prove that a reasonable person in the employee’s place would have felt forced to resign or that there was intent on the part of the employer to force the person to leave. Some courts hold that the standard for determining whether an employee has been constructivelydischarged is whether a reasonable person in the employee’s place would have felt forced to resign.In other courts, a specific intent to force the person to leave must be proven. |
|
|
Which type of organizational structure creates a dual chain of command? a. Line & staff b. Functional c. Divisional d. Matrix |
d. Matrix Matrix organizations have a dual chain of command, where an employee reports to two managers,with neither manager assuming a superior role. |
|
|
A company fires a minority employee, who responds by filing a discrimination suit. Early in thelitigation process, the employer discovers that the employee falsified information on theemployment application. Assuming that discrimination has occurred, the court is MOST likely to a. Free the employer from all liability in the discrimination case. b. Fine the employee for falsifying information. c. Require the employee to pay court costs. d. Consider the employee’s misconduct when awarding damages or back pay. |
d. Consider the employee’s misconduct when awarding damages or back pay. In the McKennon v. Nashville Banner Publishing Co. case, the Supreme Court held that evidence ofmisconduct acquired after the decision to terminate cannot free an employer from liability, even if themisconduct would have justified terminating the employee. This evidence, referred to as afteracquiredevidence, is not a complete defense to a claim brought under any of the federalantidiscrimination laws. The Court went on to state that such evidence may be used to cut off certaindamages, including damages suffered after the prior misconduct was discovered. The court may alsoconsider such evidence when awarding back pay. |
|
|
An HR professional would develop a business case to a. Secure budget and resources for a proposed project. b. Report on the success of an HR strategic initiative. c. Train the organization’s managers and supervisors in applying ethical guidelines toworkplace situations. d. Help senior management choose a competitive strategy. |
a. Secure budget and resources for a proposed project. Many organizations now require their members to complete business cases when requestingorganizational resources in order to increase accountability. A business case describes a problem tobe solved, desired outcomes, the advantages and disadvantages of different solutions, and what willbe needed to implement the best solution. |
|
|
Which of the following job analysis methods would be MOST appropriate for a position wherethe job tasks are short in duration and it’s important to obtain firsthand knowledge andinformation about the job being analyzed? a. Observation b. Interview c. Open-ended questionnaire d. Work diary or log |
a. Observation The observation method of job analysis is well-suited for jobs in which the work behaviors are short induration and readily observable in a short period of time. The method allows direct observation ofthe work environment, the tools and equipment used to perform tasks, the interrelationships of theincumbent(s) with other workers, and the complexity of the job. |
|
|
HR would like to implement an organizational policy regarding the use of the organization’semail system. Senior management is wary about adding yet another policy. What would be thestrongest argument in support of HR’s initiative? a. The new policy would relieve managers of the responsibility for monitoring employeebehavior in this area. b. The new policy would increase employee productivity. c. The new policy would reduce the amount of risk posed to the organization byemployees’ use of the email system. d. The new policy would save the organization money. |
c. The new policy would reduce the amount of risk posed to the organization by employees’ use of the email system. HR, along with other members of the organization, has a responsibility to do what it can within itsarea of authority and expertise to help the organization manage potential risks. This policy could helpdecrease the organization’s legal liability in the event of misuse of email communication, with itsattendant economic and non-economic costs (e.g., tarnished image, damaged relations with externalgroups). |
|
|
After conducting a reference background check, HR discovers that a leading candidate misrepresented dates of previous employment both on the resume and the job application.What is the most probable outcome of learning this information?
a. Do not extend an offer of employment.
b. Check criminal records for felonies and misdemeanors.
c. Conduct a credit history check with a consumer reporting agency.
d. Ask for references about the employee’s professionalism. |
a. Do not extend an offer of employment.
Every employer has a legal duty to exercise due diligence in hiring. In certain circumstances, anemployer may give the candidate the opportunity to explain the results of their reference backgroundcheck that might have an adverse effect on an employment decision. However, most job applicationsinclude a statement that signing the job application attests to truthfulness of the informationcontained in the document. Some employers even advise candidates at the onset of the applicationprocess about the potential negative consequences of providing any false or intentionally misleadinginformation. |
|
|
The balance sheet is most helpful when HR needs information about a. Production costs versus the selling price. b. Transactions regardless of monetary value. c. Organizational assets, liabilities, and equity. d. Corporate value reflected as net income. |
c. Organizational assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet summarizes the financial position of a company at a given time. It lists the assets andliabilities of the organization and includes only transactions measurable in money. |
|
|
To attract Generation Y workers, organizations will need to a. Offer more management-related responsibilities. b. Provide collaborative work opportunities. c. Provide health-care benefits that extend to their aging parents. d. Coach intensely to instill motivation. |
b. Provide collaborative work opportunities. Members of Generation Y are inclusive in their working relationships and enjoy a work environmentwhere everyone pulls together. This desire for collaboration feeds their desire to be highly creative intheir work. While the generations before them deal with advanced career issues like assumingmanagement roles and interest in elder-care benefits, Generation Y members are focused on findingorganizations to support their determined yet inclusive work ethic. |
|
|
A city council is holding hearings on a proposed statute preventing employers from conductingcertain types of pre-employment screenings. What is the role of HR in this situation? a. Attend hearings and submit comments on the employer’s behalf. b. Change screening practices proactively. c. Prepare documentation for a legal challenge. d. Survey employees for positions on the issue. |
a. Attend hearings and submit comments on the employer’s behalf. As employment specialists, HR professionals should testify at hearings and in comments as to theimpact of the proposed action on their own organizations. Changing practices and preparing achallenge would be hasty actions at this stage. Employee opinions are not of primary importancehere |
|
|
An HR professional knows the organization is planning a downsizing in two months and that afriend who is currently considering an offer from another organization will be one of thoseaffected. In this situation, the HR professional should a. Attempt to change the company’s decision to eliminate the friends position. b. Keep the workforce reduction information confidential. c. Encourage the friend’s manager to inform the friend of the company’s plans. d. Inform the friend of the company’s plans. |
b. Keep the workforce reduction information confidential. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about job posting is true?
a. Jobs must be posted internally before advertised outside the organization.
b. Jobs can be posted electronically or in employee newsletters.
c. Job posting permits employees to express interest in a position before it becomes available.
d. Job posting generally decreases adverse impact on protected groups. |
b. Jobs can be posted electronically or in employee newsletters.
Job posting allows current employees the chance to respond to announcements of positions. This procedure once consisted largely of posting notices on a bulletin board. Today it involves the use of other forms of communication, such as newsletters, memos, electronic bulletins, recorded job lines,or the organization’s intranet. |
|
|
Certain bona fide executives are partially exempt from the protections of which of the followingacts? a. Rehabilitation Act b. Age Discrimination in Employment Act c. Title VII d. Americans with Disabilities Act |
b. Age Discrimination in Employment Act Certain bona fide executives may be exempt from the protections of the Age Discrimination inEmployment Act and can be required to retire at age 65 if they are entitled to receive companysponsoredretirement benefits of at least $44,000 per year, in the aggregate, and have held theirposition for two years immediately prior to retirement. |
|
|
A hearing to resolve an unfair labor practice charge is conducted before a(n) a. Labor law judge. b. Administrative law judge. c. Arbitrator. d. Circuit court judge. |
b. Administrative law judge. The hearing is conducted by an administrative law judge (ALJ), who is an individual knowledgeableabout labor law and practices but not necessarily admitted to the bar. A staff attorney of the NLRB’sregional office is responsible for prosecuting the case, but the party who files the ULP charge may alsopresent evidence at the hearing. Both parties are entitled to representation at the hearing. |
|
|
An organization’s competition has implemented an HRIS program that is credited withfacilitating recruitment of its top candidates. The organization wants to gain a competitiveadvantage as well as boost productivity, improve service, and save time by matching thecompetitor’s strategy. What advantages might the organization realize by adding an HRIS? a. Staff reductions, cost reductions, and fast access to accurate information b. Staff organization, cost increases, and secure access to accurate information c. Staff increases, cost reductions, and more access to accurate information d. Staff education, cost increases, and more access to accurate information |
a. Staff reductions, cost reductions, and fast access to accurate information Numerous organizations have managed to significantly reduce staff, cut costs, and offer fast access toaccurate information through technology innovation. |
|
|
A mature software organization is planning to launch a new product line to satisfy its largestcustomer base. How can HR link its actions with the organization’s strategy? a. Understand the plan through a SWOT analysis and study of the planned product linelaunch. b. Stabilize the research and development workforce through high technology sourcingand retention policies. c. Complete an environmental scan through a solid understanding of the organization andthe competition. d. Stabilize the entire organization through solid implementation of department policiesand procedures. |
b. Stabilize the research and development workforce through high technology sourcing and retention policies. The company will need to rely on its R&D and product development staff to complete the productlaunch. HR can link its actions with the organization’s strategy by ensuring that an adequate R&Dstaff is in place. |
|
|
The HR director in a manufacturing organization is engaged in strategic planning. The CEOwants to analyze the competition, current safety legislation, supervisor strengths, and assemblylineoperations. Which of the following should the HR director recommend to the CEO toaccomplish this? a. Needs analysis b. Environmental analysis c. SWOT analysis d. Job analysis |
c. SWOT analysis The SWOT analysis reviews internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities andthreats. Leadership capability and operations are internal concerns, while legislation and thecompetition are external concerns. An environmental analysis examines only external information. |
|
|
For many years, an electronics company has used financial measurements such as the balancesheet and the income statement to plan and measure organizational performance. What is thebenefit of implementing the balanced scorecard approach? a. It enables companies to save money on accounting personnel and practices. b. It drops financial measurement in favor of more process-oriented measurement. c. It provides feedback around both internal business processes and external outcomes. d. It eliminates the need to share financial information with managers. |
c. It provides feedback around both internal business processes and external outcomes. Traditional financial measures of performance are important, but the balanced scorecard offers astrategic performance measurement. The balanced scorecard integrates four related perspectives(finance, customers, internal business processes, and learning and growth) and gives a more completeand balanced look at how a company is doing. |
|
|
How would an organization’s use of zero-based budgeting affect the human resources budget? a. All expenditures must be justified. b. Balances for continuing projects from the previous period are carried over. c. New projects must be postponed. d. The function’s budget will see no growth in this period. |
a. All expenditures must be justified. |
|
|
An organization operates on the basis of a product leadership strategy. Which of the followingHR objectives should receive highest priority? a. Roll out training on lean manufacturing techniques. b. Work with the information technology department to increase sharing of customerdata. c. Develop programs to attract and retain talented individuals. d. Implement a rewards system for eliminating product defects. |
c. Develop programs to attract and retain talented individuals. |

