![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do straight line going up, horizontal line, curved line going up (reverse L), curved line going flat (upside down L), straight line going down mean on a distance time graph? What does a gradient show? |
Steady speed Stopped Accelerate Decelerate Steady Speed Speed (M/S) |
|
|
What do straight line going up, horizontal line, curved line going up (reverse L), straight line going down mean on a velocity time graph? How do you find distance? |
Acceleration Steady speed Increasing acceleration Deceleration The area under graph |
|
|
What is the formula for acceleration? |
Acceleration (M/s^2) = Change in velocity/Time |
|
|
What is the formula for weight? |
Weight = mass(kg)*gravitational field strength(g) It's caused by gravity so it changes if gravity is different. |
|
|
What is resultant force? |
The overall effect of forces acting along the same line. If there is a resultant force the object will change its state of rest/motion, so it will change the velocity. If the resultant force on a stationary object is 0 it remains stationary, if it's moving it remains at the same velocity. If there is a non zero resultant force it will accelerate. |
|
|
What is the formula for resultant force? |
Resultant force (N) = Mass (kg) * Acceleration (M/S^2) |
|
|
What happens when 2 objects interact? |
They exert equal and opposite forces, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. |
|
|
What is friction? What is drag? |
Acts in opposite direction to movement, for a steady speed, friction = driving force. Occurs between 2 surfaces or through a fluid (drag) Frictional forces in fluids increase with speed. |
|
|
How do you decrease resistance from fluids? |
Make the object streamlined |
|
|
What is terminal velocity? |
As speed increases so does gravity, so the object reaches a steady speed. Making a bigger surface area will decrease terminal velocity. |
|
|
What is stopping distance? What is thinking distance and braking distance affected by? |
Sum of thinking distance + braking distance. Speed, dopeyness Speed, good brakes, good tyres, good grip (surface, weather, tyre) |
|
|
What is work done? |
When a force moves an object through a distance, energy is transferred and work is done. Work done (j) = force (n) * distance (m) |
|
|
What is gravitational potential energy? |
Energy given because of vertical position in a gravitational field. GPE (j) = mass (kg) * g * height (m) |
|
|
What is the formula for kinetic energy? |
KE (j) = 1/2 * mass (kg) * speed^2 (m/s) |
|
|
How do car brakes work? |
To stop a car kinetic energy is converted to heat energy as friction. Kinetic energy = Work done |
|
|
How is energy conversion used in real life? |
Falling objects will convert potential energy to kinetic energy, some of this is converted to heat and sound. Space shuttles have heat shields which lose heat quickly. |
|
|
What is elastic potential energy? |
Work done to change the objects shape is stored then converted to kinetic energy when the force is removed. |
|
|
What is the formula for force with elastic potential energy? |
Force (n) = Spring constant (k) * extension |
|
|
What is the limit of proportionality? |
The maximum force the object can take + still extend proportionality. |
|
|
What is the formula for Power? |
Power (W or J/s) = (Work done/energy transformed(j))/(Time (s)) |
|
|
How do you calculate power output? |
Time run upstairs, Power = (mass*g*height)/time Time acceleration, Power = (1/2*mass*velocity^2)/time |
|
|
How do you calculate momentum? What is conservation of momentum? |
Momentum (kgm/s) = Mass(kg)*velocity(m/s) The total momentum before an event is the same as after the event |
|
|
How do you calculate momentum in a collision, and momentum in an explosion? |
Before total = momentum a + momentum b After total = (both masses) * total velocity Before total = no momentum After total = momentum a + momentum b |
|
|
What happens if a larger force interacts with an object? |
It will get a faster change of momentum. |
|
|
How do brakes work in cars? |
Reduce kinetic energy by transferring it to heat + sound Regenerative brakes - Put the motor in reverse and converts kinetic energy into electrical energy, that's stored as chemical energy in the battery. |
|
|
How do cars make crashes safer? |
By converting kinetic energy in a safe way. Crumple zone - Front + back of car, energy converted as it changes shape. Side impact bars - Strong metal tubes, directs energy to places like the crumple zone. Seat belts - Absorbs energy + increases time for user to stop. Air bags - Slow you down, stop hitting hard surface. |
|
|
What are power ratings? |
More powerful engine = faster top speed Aerodynamic cars are faster, more powerful |
|
|
What is static electricity? |
Electrons move from one object to another creating a negative and positive charge. Opposite charges attract and same charges repel. |
|
|
What is current, potential difference, and resistnace? |
Flow of electric charge around a circuit. Work done to push the current around Things which slow down the current. |
|
|
What is the formula for current? |
Current (A) = Charge (C) / Time (s) |
|
|
What is the formula for Potential difference? |
PD (V) = Work done (j)/ Charge (c) |
|
|
What does cell, battery, open and closed switch, filament lamp, fuse, LED, resistor, variable resistor, ammeter, voltmeter, diode, LDR, and thermistor look like? |
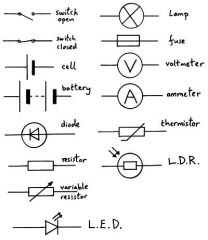
|
|
|
What is the standard circuit test? |
Use to find out the resistance of a component. Used to get resistance graphs. Voltmeter must be in parallel. Variable resistor allows you to get many readings. |
|
|
What do graphs for different resistors, filament lamp, and diode look like? |
Resistors - Straight line Filament lamp - S shape, as temperature increases so does the resistance. Diode - Reverse curved L, but only in the first quadrant, current only flows in one direction. |
|
|
How do resistors work? |
When charge flows through a resistor heat energy causes ions to vibrate more, making it harder for charge to pass through the resistor. |
|
|
What is the formula for potential difference? |
PD (V) = Current (I) * Resistance (R) |
|
|
What does a diode, LED, LDR, and thermistor do? What do LDR and thermistor graphs look like? |
Diode - semiconductor, regulates voltage, and current flows in one direction. LED - emits light when current goes in a forward direction. Used more as lighting as they have a smaller current (digital clocks, traffic lights, remote controls) LDR - resistance decreases as light intensity increases. Thermistor - Resistance decreases as temperature increases |
|
|
What are the properties of a series circuit? |
Everything must be connected. Potential difference is shared out (More cells = more voltage) Current is the same Resistance adds up to make the total resistance. |
|
|
What are the properties of a parallel circuit? |
You can remove components Potential difference is the same everywhere Current is shared between branches. |
|
|
What is the UK mains? |
AC, 230 volts, 50Hz frequency. |
|
|
What are Cathode ray oscilloscopes? |
Shows a trace, vertical height with AC is input voltage. With DC distance from the straight line trace is voltage. |
|
|
What is the formula for Frequency? |
Frequency (Hz) = 1/time period (s) |
|
|
What are electricity hazards? |
Long/frayed cables or in contact with something hot/wet. Water near sockets, shoving into sockets, damaged plugs, too many plugs in a socket, lighting sockets with no bulbs, appliances without covers. |
|
|
What are three core cables? |
Copper core + plastic coating. Live wire (AC), Neutral wire (0v). The earth wire protects wiring and works with the fuse to prevent shocks. It's attatched to the metal casing and carries the electricity to the earth. |
|
|
What are 3 pin plugs? |
Each wire is connected to a pin and screwed in. A cable grip is fastened over the cable outer layer. Thicker cables have less resistance (carry more current) Metal parts are copper/brass = conductors. Case, cable grip, cable insulators are rubber/plastic = insulators and flexible. |
|
|
What is double insulation? |
Has a plastic casing and no metal parts showing. Doesn't need and earth wire so it's a two core cable. |
|
|
What causes an electrical overload? |
Fault in live wire (touches metal case) because case is earthed too much current goes through the earth wire which melts the fuse/trips the circuit breaker if the surge is greater than the fuse rating - breaks the circuit. Stops fire and electric shocks and stops the rest of the circuit from frying. Fuses are rated slightly higher than normal current |
|
|
What is a circuit breaker? |
Break the circuit by opening a switch, you don't have to replace them but they're more expensive than fuses. Residual circuit breaker - Touch a live wire, less current goes through the neutral wire, difference is detected by the breaker and it opens a switch. They work faster an only need small current changes. |
|
|
What are components that transfer energy? |
Motors, light bulbs, hair dryers, and speakers. Filamnet bulbs work by passing a current through a thin wire so it glows. |
|
|
What is the energy efficiency between compact fluorescent bulbs, LEDS and filament bulbs? |
CFB + LED are much more efficient but they cost more. |
|
|
What is the formula for energy transferred? |
(kj) = Power (kw) * time (s) |
|
|
What is the formula for electrical power? |
(kw) = Current (a) * potential difference (v) |
|
|
What is the formula for energy transformed? |
(j) = Charge (c) * Potential difference (v) |
|
|
How does charge work? |
When a charge goes through a voltage charge energy is transferred, it is supplied at the power source to raise it through a potential. Charge gives up the energy when it falls through a potential drop. Battery with more voltage supplies more energy (charge is higher at the start) |
|
|
What did Rutherfordd and Marsdon do? |
Democritus said matter was tiny spheres. JJThomson discovered electrons could be removed so they must be positive spheres with electrons stuck in. Fired alpha particles at gold foil (would be slightly deflected), they went straight through one came straight back. Mass was just a tiny positive nucleus. |
|
|
What are the masses and charges of particles? |
Proton - 1, +1 Neutron - 1, 0 Electron - 1/2000, -1 |
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Same number of protons (same atomic number) Different number of neutrons (different mass number) Radioactive isotopes are unstable and decay into other elements |
|
|
What is radioactivity? What is background radiation? |
Random, unaffected by physical conditions (temp, chemical bonding) Unstable isotopes (air, food, rocks), cosmic rays, nuclear things |
|
|
What is radiation dose affected by? |
Some rocks cause higher levels at the surface High altitudes (more cosmic rays) Underground (more rocks) Nuclear industry workers are exposed to a lot more Radiographers wear lead aprons and stand behind lead screens |
|
|
What are the properties of alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays? |
Ap - 2 neutrons + 2 protons, big, heavy, slow moving (Strongly ionising). Don't penetrate far into materials, stopped quickly even in air. BP - 1 electron, fast, small (moderately ionising) Penetrate moderately, have a long range in air GR - Penetrate far into materials, pass straight through air (weakly ionising) |
|
|
What do you do with nuclear equations? |
Alpha decay - Atomic mass -4, Atomic number -2 Beta decay - Atomic mass (same), Atomic number +1 |
|
|
How are radioactive particles affected by electric + magnetic fields? |
Alpha + beta are deflected in opposite directions because of their opposite charges. Alpha has a large charge and feels a greater force but is large so deflects less. |
|
|
What is half life? |
Average time it takes for the number of nuclei in a radioactive isotope sample to halve. (The count rate falls to half its initial level) |
|
|
How is radiation used in real life? |
Smoke detector - alpha creates a current between electrodes, smoke absorbs radiation, current stops + alarm sounds. Tracers - gamma/beta emitters are injected into the body + followed with external detector, radioactivity disappears quickly. Radiotherapy - Gamma rays kill cancer cells Sterilisation - Gamma rays kill microbes, sterilise medical instruments and fresh food. |
|
|
What happens to living cells with radiation? |
Collisions cause ionisation, low doses will cause cancer but high doses can cause radiation sickness. Outside body - (Beta + gamma dangerous) - get into organs Inside body - (Alpha dangerous) - damage in localised area |
|
|
Safety precautions you have to take with radiation? |
Short time as possible Use tongs Hold at arms length Keep away from body, avoid looking at Store in lead box, lead aprons, lead screens |
|
|
What is nuclear fusion? |
2 light nuclei join, releases a lot of energy (occurs in stars) It doesn't leave much waste, and we have lots of hydrogen, but needs a really high temperature To hold the hydrogen you need a strong magnetic field |
|
|
What is nuclear fission? |
Split up atomic nuclei, used in nuclear power stations since it releases heat energy, uranium-235 or plutonium-239 A neutron is absorbed into the nucleus, makes it unstable so it splits. This spits out more neutrons so a chain reaction occurs. It releases a lot of energy but the products are radioactive so are waste. The fuel is cheap but it's expensive because of setting up and decommissioning the power plant, there's the risk of radiation leaks. |
|
|
What is the life sequence of a star? |
Protostar, main sequence star, giant Red giant -> white dwarf -> black dwarf Red super giant -> supernova -> black hole or neutron star |
|
|
What is a protostar? Main sequence star? Red giant? Red super giant? |
P - Formed from clouds of dust + gas. Gravitational energy goes to heat energy increase temperature. Once high enough fusion occurs so heat + light are given out. MSS - Heat created provides an outward pressure to balance the force of gravity this stable period lasts billions of years |
|
|
What happens to a red giant? Red super giant? |
Hydrogen runs out so heavier elements are made so it swells and surface cools. RG - Will become unstable + eject outer layer as a planetary nebula. Then goes to white dwarf as a hot dense solid core which becomes a black dwarf. RSG - It begins to glow again, undergoes more fusion and explodes in a supernova, leaving a neutron star or black hole |

