![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Strict aerobe |
Only grow with oxygen All bacteria gather at top |
|
|
Strict anaerobe |
Can not grow with oxygen Clear at top- bacteria will grow only at the bottom |
|
|
Aerotolerant anaerobe |
Tolerate oxygen ( cloudy tube ) grow through the whole tube |
|
|
Facultative anaerobe |
Adapt as needed. ( Grow at top but can go down in stab- lightning bolt (staph, E. Coli ) |
|
|
Media for checking oxygen? |
Thioglycolate |
|
|
Determining temperature range? |
Cloudy within that temperature range |
|
|
Bacillus-Stearothermophilus |
Thermophile- 55°C |
|
|
Mesophile |
E. Coli- 37° C |
|
|
Mesophile |
Staph 25°C |
|
|
Serratia Maseesens-Mesophile |
Red pigment @ 25° C Only make pigment at optimal temperature |
|
|
What is Viable count? |
Only living bacteria |
|
|
Generation time |
Time it takes for bacteria to double |
|
|
What is Gel Electrophoresis? |
Visualize and measure DNA Stain is ethidium bromide • Gel holds DNA in place Electro- electricity Phonesis- movement Black- negative Red-positive Ladder or marker= sizes out DNA |
|
|
Kirby Bauer Method |
Clear area-Zone of inhibition = measure diameter Chemical TSA plate- 4 circles L= lysol A= alcohol Q= qua Cp I= iodine |
|
|
Physical control- UV light |
Thymine Dimer 2 T's or C's glued together |
|
|
White light |
Photoreactivation- unglued fixes mutation |
|
|
Chemical plates |
Lysol- contains alcohol- kills gram - Ammonia kills gram + ( Quatermany compound) and bacteria Iodine- halogen -strong salt. Kills all |
|
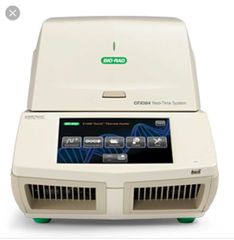
What is thermocycler used for? |
Used in PCR- polymerase chain reaction |
|
|
What are the steps of the chain reaction in PCR? |
Laboratory Replication(done with heat) Used to amplify and for copying DNA 1. Denaturation-Heat to 92°-97° which allows the DNA molecules to separate 2. Annealing- 45°C - 58°C - cool down which allows DNA primer to bind 3. Extension- Change heat to 70° - 73° which allows DNA Polymerase to bind and synthesis new DNA strands
Need to go through 15-20 cycles for millions of DNA replication |
|

What is this called? |
Gas pack jar |
|

What is this machine called? |
Gel- Electrophoresis |
|
|
What do the bands mean in the gel- Electrophoresis test? |
Band means you found the DNA and amplified it No band you did not find the DNA |
|
|
Is the antibiotic test quantitative, qualitative or both? |
Both quantitative and qualitative |
|
|
When do you need to do a gel- electrophoresis test? |
When looking for a genetic difference of strain |
|
|
What is thymine dimers? |
Used in Ultra violet light to glue t's or C's together |
|
|
What is a lawn of bacteria? |
Too much bacteria to count |
|
|
TSA- Type of soy agar |
None selective, inhibitor, differentiates, indicators |
|
|
Chart for TSA 5% sheeps blood |
Selects For-X Inhibitor-X Differentiates- hemolytic types Indicator- Blood |
|
|
Chart for PR Sugar |
Selects For-X Inhibitor- X Differentiates- Fermentation types Indicator- Phenol Red ( PH indicator ) |
|
|
Thioglcolate chart? |
Selects For-X Inhibitor- X Differentiates- Oxygen Req Indicator- Thioglcolate |
|
|
MSA Plate- Mannitol Salt Agar |
Selects For-Halophiles ( staph species ) Inhibitor- Salt concentration Differentiates- Mannose Fermentation Turns media yellow- Staph aureus No color change- Staph Epidermitis Indicator- Phenol Red |
|
|
PEA- B Phenylethyl Alcohol |
Selects For- Gram + Inhibitor- PE alcohol Differentiates- hemolytic types Indicator- Blood |
|
|
MacConkey |
Selects For- Gram - Inhibitor- Bile Salt Differentiates- Lactose Fermentation ( e. Coli ) turns magenta color NON- Lactose fermentation no color change Indicator- Neutral Red |
|
|
EMB- Eosin methylene Blue |
Selects For- Gram - Inhibitor- Dyes Differentiates- Lactose Fermentation ( E. Coli ) metallic green Indicator- Dyes |
|
|
What is Elisa? |
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay ( Fast Test ) Direct- Testing for antigen( cancer ) Indirect- Testing for antibodies ( virus ) |
|
|
What causes a weak positive on a elisa test? |
Time of exposure |

