![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Optimum |
Temp that organism grows best overtime |
|
|
Minimum |
Temp below which organism cannot grow |
|
|
Maximum |
Temp above which organism cannot grow |
|
|
Maximum |
Temp above which organism cannot grow |
|
|
Thermoduric |
Organisms that are usually mesophilic but that can also survive short bursts of high heat -pasteurization -listeria can survive in those short burst of high heat |
|
|
Water activity (osmolarity)- |
water activity: availability of water Closer to 1–> pure water; no solutes |
|
|
Water activity (osmolarity)- |
water activity: availability of water Closer to 1–> pure water; no solutes 0= high solute concentration |
|
|
Osmosis |
Movement of solvent molecules across semi-permeable membrane |
|
|
Isotonic |
Equal solute concentration in the environment and in the cell Net water movement is balanced |
|
|
Isotonic |
Equal solute concentration in the environment and in the cell Net water movement is balanced |
|
|
Hypotonic |
Lower solute concentration in the environment than in the cell NET WATER GOES INTO CELL Animals: swell and burst bacterial: swell but don’t burst |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Higher solute concentration in the environment than in the cell. NET WATER GOES OUT OF CELL Animal cells: shrivel Bacterial cells: comm membrane pulls away from cell wall |
|
|
Strict obligate aerobes |
Require the presence of oxygen to survive and produce ATP |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Higher solute concentration in the environment than in the cell. NET WATER GOES OUT OF CELL Animal cells: shrivel Bacterial cells: cell membrane pulls away from cell wall |
|
|
Strict obligate aerobes |
Require the presence of oxygen to survive and produce ATP |
|
|
Strict obligate Anaerobes |
Require the absence of oxygen to survive |
|
|
Facultative anaerobes |
Can live in the presence and or/absence of oxygen but PREFER to live in presence of oxygen. |
|
|
Facultative anaerobes |
Can live in the presence and or/absence of oxygen but PREFER to live in presence of oxygen. -aerobic cellular respiration -anaerobic respiration -fermentation |
|
|
Microaerophiles |
Can tolerate only small amount of oxygen |
|
|
Aerotolerant |
Can live in the presence or absence of oxygen. Preforms anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation. |
|
|
Opsonization |
Coats bacteria with complement and antibodies so that phagocytes can recognize attach and attack |
|
|
What are capsules and what are they made of? |
Polysaccharides Polypeptides |
|
|
What kind of stain is a capsule stain? |
Negative Capsule does not get stained Background does |
|

Front (Term) |
Monotrichous |
|

Front (Term) |
Lophotrichous |
|

Front (Term) |
Amphitrichous |
|
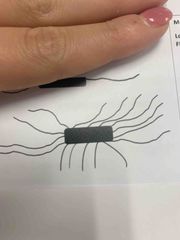
Front (Term) |
Peritrichous |

