![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Flow Chart |
Schematic representation of a system or process
|
|
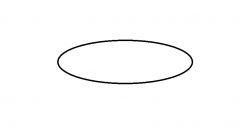
|
Start/Stop
|
|
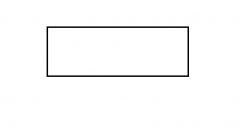
|
Process
|
|
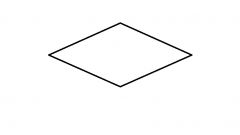
|
Decision (quality control), with a yes/no answer
|
|
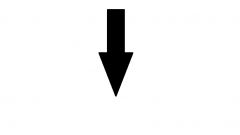
|
Arrow- indicate the flow of control |
|
|
Open-loop control system
|
no feedback information on quality, therefore the process will continue with no interference |
|
|
Disadvantage of open-loop control system
|
Cannot detect or correct any errors
|
|
|
Application of open-loop control system
|
Basic processes e.g. a light switch
|
|
|
Closed-loop control systems
|
Utilise feedbback, to make decisions about changes to a process |
|
|
Advantages of closed-loop control systems
|
Improved performance tracking throughout production process and early detection of faults that can be rectified |
|
|
Applications of closed-loop control system
|
More complex systems e.g. a light switch with a dimmer |
|
|
Flow chart sequence |
Start Input Perform Algorithm Output End |
|
|
Algorithm is.. |
The logic & calculations & how & when things are supposed to happen to produce the desired output using the input |
|
|
Inputs can sometimes be included with outputs? |
True! Outputs need a logical association with something the user can understand. Inputs placed with outputs have () placed around them to distinguish them |
|
|
3 types of output exist for flow charts |
Display Prompt |
|
|
What are the 3 kinds of flow charts? |
Sequential Selection / Decision Loop. Reptition, Iteration |

