![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
NMR |
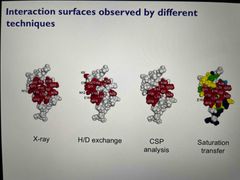
Allows identification of binding constants alongside structure for a wide range of affinities Spectra are residue specific Techniques include CSP analysis, chemical exchange measurement, H/D exchange, cross saturation |
|
|
Isothermal titration calorimetry |
Measuring heat changes upon ligand titrations into a protein sample Use of heat changes, sample volumes and concentrations to obtain enthalpy and binding constants Accurate measurements No reagent modification or immobilisation Large amounts of protein needed |
|
|
Surface plasmon resonance |
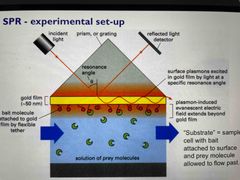
Plasmons on gold foil are excited by incident light Minimum detected intensity and maximum absorbance at a critical angle Ligand binding causes an increased refraction index Slopes from SPR association and dissociation plots directly give kinetic constants kon and koff Maximum height of signal on plot gives total mass bound |
|
|
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) |
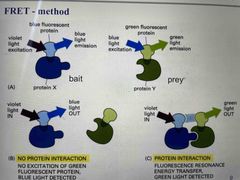
Label proteins with fluorophore Wavelength emitted by the donor fluorophore must be one that can be absorbed by the acceptor Emitted light from acceptor only if labelled proteins interact |
|
|
Fluorescence measurements |
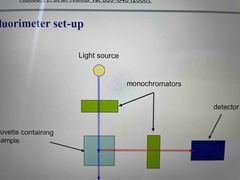
Measure fluorescence for free ligand, protein ligand complexes for various [P] and fully bound ligand Ensure fluorophore concentration remains constant so fluorescence changes are only due to binding |

