![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What dermatome is at the nipple line?
|
T4
|
|
|
What is the zone of partial preservation?
|
complete injury, intact sensory and motor above S5 and below level of injury
|
|
|
In Brown Sequard Syndrome, what is lost contralateral?
|
Pain
Temperature |
|
|
In Brown Sequard Syndrom, what is lost ipsilateral?
|
Reflexes
Proprioception Discriminitive Touch |
|
|
What is the Ashworth Scale?
|
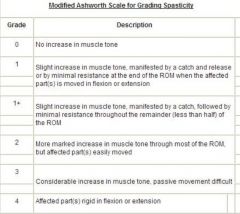
|
|
|
Which tract deals with pain and temperature?
|
Spinothalamic
|
|
|
Which tract deals with loss of reflexes and a positive babinski sign?
|
Corticospinal
|
|
|
How long does spinal shock last?
|
Several days to several weeks
|
|
|
What type of injury results in autonomic dyreflexia?
|
Complete and Incomplete
|
|
|
What is not a symptom of autonomic dysreflexia?
|
Tachycardia
|
|
|
By which mechanism can a man with a complete spinal cord injury have an erection?
|
Reflexogenic
|
|
|
How high does the chest raise during inspiration?
|
2.5-3 inches at the xyphoid
|
|
|
How frequent is optimal pressure relief?
|
10-15 seconds/10 minutes
|
|
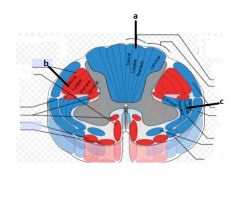
What is a, b, and c?
|
a- Medial Lemniscus
b- Lateral Corticospinal c- Lateral Spinothalamic |
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Absent Spasticity No movement |
Stage 1
|
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Developing Spasticity Weak associated movement that when attempted is in synergy? |
Stage 2
|
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Marked Spasticity All movements in synergy |
Stage 3
|
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Decreasing Spasticity Some deviations from synergy. |
Stage 4
|
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Further decrease in spasticity Almost free from all synergies |
Stage 5
|
|
|
What Brunnstrom stage has the following:
Free of synergy, slightly awkward Spasticity only during active rapid movements |
Stage 6
|
|
|
What is the most common stroke?
|
Ischemic
|
|
|
What is the 3rd leading cause of death?
|
Stroke
|
|
|
Does a hemorrhagic stroke have a higher or lower mortality than an ischemic stroke?
|
Higher
|
|
|
T/F History of CVA is modifiable
|
False
|
|
|
T/F Increased respiratory rate is a sign of ICP
|
False
|
|
|
What is defined as the transitional area surrounding the core and consists viable but metabolically lethargic cells.
|
Ischemic Penumbra
|
|
|
Following a stroke involving the middle cerebral artery, what is affected on the dominant side?
|
Aphasia
|
|
|
Following a stroke involving the middle cerebral artery, what is affected on the nondominant side?
|
Unilateral Neglect
Anosognosia Spatial Disorganization |
|
|
How long does a TIA last?
|
Less than 24 hours
|
|
|
What is the most common sight of a stroke?
|
Middle Cerebral Artery
|
|
|
T/F Lateral Medullary Syndrome will not have severe weakness
|
True
|
|
|
What is the position of the scapula with UMN syndrome?
|
Rectracted and downwardly rotated
|
|
|
Where does a stroke occur that causes Pusher Syndrome?
|
Posterolateral Thalamus
|
|
|
Where is Broca's Area?
|
Left prefrontal cortex
|
|
|
Where is Wernicke's Area?
|
Left Lateral Temporal Lobe
|
|
|
What affects proximal more than distal muscles, the head and trunk may be involved, emerges when the patient attempts to maintain a posture and may persist or worsen with goal directed movements of the limbs?
|
Postural Tremor
|
|
|
What is rhythmic oscillations of a limb about or on the way to the target. Usually perpendicular to the direction of movement and ceases on the target is reached?
|
Intention Tremor
|
|
|
What is: Speech flows smoothly but auditory comprehension is impared (auditory association cortex of the left lateral temporal lobe)
|
Wernicke's
|
|
|
What is: Flow of speech is slow, hesitant, vocabulary limited, syntax impaired (premotor area of the left frontal lobe)
|
Broca's
|
|
|
What are right brain injury characteristics?
|
Visual-perceptual impairments
Quick, impulsive behavioral style • Often unaware of impairments • Poor judgment • Inability to self-correct; increased safety risk Rigidity of though Difficulty with abstract reasoning |
|
|
What are left brain injury characteristics?
|
Speech and language impairments
Low, Cautious behavioral style • Often very aware of impairments • Anxious about poor performance Difficulty with processing delays |
|
|
T/F Shoulder pain with a CVA are not edemic
|
True
|
|
|
What is function gait speed?
|
2.75 mph
|
|
|
What is the ideal height of a stair?
|
Less than 7 inches
|
|
|
What is the ADA height for handrails?
|
34-38 mph
|
|
|
What is ADA grade for a ramp?
|
1:12
|
|
|
What is ADA compliant ramp width?
|
36 inches
|
|
|
Which is ADA compliant door width?
|
32 inches
|
|
|
What is the most dangerous area of the house for a wheel chair bound person?
|
Bathroom
|
|
|
Change in stance and swing becomes progressively ________ as speed slows.
|
greater
|
|
|
If a person has an excessive positional plantarflexion, what would you expect?
|
Achilles contracture
|
|
|
What would you expect with genu recurvatum?
|
Flaccid/weak quad
Fixed ankle PF deformity |
|
|
Hip hiking is compensating for what?
|
Lack of knee flexion
Lack of DF Extensor spasticity of swing leg |
|
|
What is the velocity needed to cross a street?
|
3.8 ft/sec
|
|
|
What is the normal width of base of support?
|
1-5 inches
|
|
|
What is the average walking velocity?
|
3 mph
|
|
|
What are the 2 goals with postural control systems?
|
Stability and Function
|
|
|
What do you test when testing coordination?
|
Mobility
Stability Controlled Mobility Skill NOT Flexibility |
|
|
What does the CNS feedback do?
|
Monitor and adjust output
|
|
|
What does CTSIB stand for?
|
clinical test for sensory integration and balance
|
|
|
Conditions 5 and 6 on the CTSIB deal with what?
|
Vestibular
|
|
|
What is factitious disorder by proxy?
|
Munchausen
|
|
|
What percent of hysteria end up showing organic causes?
|
60%
|
|
|
Does an intention tremor increase or decrease once the target is reached?
|
Decrease
|
|
|
What is the percentage of people in the clinic that present with conversion disorder?
|
14%
|
|
|
Depression and substance abuse is _____ times higher in people with disability.
|
3
|
|
|
What are common defense mechanisms?
|
Humor
Acting Out Denial Intellectualization |
|
|
What isn't a primary vital sign?
|
PO2
|
|
|
What will indicate variations in vital signs and physiological status?
|
Aerobic activity
Endurance |
|
|
Long term hypoxia results in what?
|
Clubbing
|
|
|
Input to effector organs is via what?
|
Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems
|
|
|
What controls thermoregulation?
|
Vascular
Metabolic Skeletal Muscle Sweating NOT respiratory |
|
|
What is normal HR?
|
70
|
|
|
How do you monitor HR?
|
Volume
Rate Rhythm |
|
|
What are parameters to observe/measure with respiration?
|
Rate
Depth Rhythm Sound NOT forcefulness |
|
|
What are the two components of BP?
|
Cardiac Output
Peripheral Resistance |
|
|
What factors influence BP?
|
Volume
Arm Position Exercise Age NOT time of day |
|
|
What percent of parkinson's patients manifest with tremors?
|
70%
|
|
|
What are the dominant symptoms of parkinsons?
|
Tremor as main feature
Posture in stability and gait dynamics NOT bradykinesia |
|
|
What is a composite impairment with parkinson's?
|
Balance Disturbances
|
|
|
What area is not affected by plaque from MS?
|
Brain Stem
|
|
|
What is the first line therapy for clinical treatment of MS?
|
Symmetrel
|

