![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ethics
(Book Def.) |
The study of right or wrong; good or bad "beliefs about right or wrong, that guide the way we think & Act"
Essentially being able to do the right thing; it is a simple concept, but also a complex chanellge at time. |
|
|
Ethics in PR
|
Ethical behavior forms foundation of PR...but ethical choice might not always be clear
|
|
|
Challenges to Ethical Behavior
|
-dilemmas
-Overwork -Legal/ethical confusion -cross-cultural ethics -short term thinking -virtual organizations |
|
|
Formalized Codes of Ethics
|
See PRSA p. 528
|
|
|
Key priciples of Ethics
|
-honesty
-fairness & accuracy -free flow of Information -fair competition -disclosure of sponsorships>celebraties have sponsor>questioned about their beliefs if they follow in what their sponsorship wants -respect for clients -safe guard confidences |
|
|
Examples of Ethical Problems
|
-dishonesty
-conflict of interest -representing unethical clients -false representation of information -bribes or inappropriate gifts -omitting important information -disclosing confidential information |
|
|
Arthur Page
|
* At&T; PR Executive & VP
- 1927- 1955 * Page's Principal - tell the truth - Prove truth w/ action - listen to the customer - manage for tomorrow - conduct PR as if company depended on it - Remain calm, Patient and good humored - Realized company's true character is expressed by it's people |
|
|
Philoshical prespective on ethical Decision Making
(Golden Mean) |
Aristotle
idea of finding an average solution > Happy Median |
|
|
Philoshical prespective on ethical Decision Making
(Categorical Imperative) |
Immanuel Kant
In situation to make decision > think universally will decision could be good or bad |
|
|
Philoshical prespective on ethical Decision Making
(Utilitarianism) |
Bentham Mill
choice that will do greatest good for greatest number of people |
|
|
Philoshical prespective on ethical Decision Making
(Social Justice) |
Jon Rowls
empower those with little or no power |
|
|
Potter Box
|
analytical tool for determining the ethical consideration in any decision
(helps deicide on an issue and show possible reaction) |
|
|
Potter Box points
|
-define situation
-identify values -select principles -choose loyalties to stakeholders |
|
|
PR research
|
research is valuable to PR but it is oftern underused
|
|
|
Research has value at every stage of PR Initiative
|
-idea generation
-conceptualization -planning -early implementation -execution -finalization -evaluation |
|
|
Arguements for research
|
-insure better focus
- better control resources, budgest etc. -help formulate strategy -test messages -size up competition -support positions -sway opinion |
|
|
Research can help organization to:
|
-avoid, or at least minimize errors in judgement
-learn from successes-> and mistakes |
|
|
Questions in Research
|
-what do i already know?
-how well do I know this -what do i need to know -How best can i get this information |
|
|
Areas of research
|
-client research
-stakeholder Research -Problem-opportunity research -Evaluation Research |
|
|
Types of research in PR
|
- secondary (library) research
- communication audit - feedback research - focus groups - survey research |
|
|
Secondary (library) research
|
- published material
- data bases - public records |
|
|
Communication Audit
|
Analysis of how well communications match mission and goals of an organization
|
|
|
Feedback research
|
- tallies of website "hits"
- media monitoring of mentions of organization (clipping services, etc) |
|
|
Focus groups
|
Small groups formed to provide answers to specific questions
- members share key attributes - 8-12 participants - moderator, or a facilitator - members respond to eachother - sessions observed and recorded |
|
|
Survey research
|
- sampling: non probability (convenience) / probability (random,etc)
- survey instrument-(questions pg: 220) -survey execution - analysis and conclusions |
|
|
PR Planning and Strategy
|
- Focusses on who, what, when, where & why
- MOSTLY WHY |
|
|
Strategies important for PR activity
|
- Events
- Programs - Campaigns |
|
|
Event
|
one time activity
|
|
|
Programs
|
ongoing, routine activity
|
|
|
Campaign
|
- special initiative
- time limited - focussed on specific issue or cause |
|
|
Types of Plans
|
- Ad Hoc Plan
- Standing Plan - Contingency Plan |
|
|
Ad Hoc Plan
|
- address specific situation
- short term, temporary response EX: crisis communication |
|
|
Standing Plan
|
- ongoing, long term
- intended to giude organization - reflects values in attempt to fulfill mission |
|
|
Contingency Plan
|
- "what if" plans
- meant to be used in event of change, or even crisis EX: Back up plan; Plan B |
|
|
Advantages of Planning
|
- provides guidance
- consistency with values, vision & mission - perspective and understanding-> forces to think whats a priority - commitment & consensus - appropriate resource use & allocation - focus on the future; not the past |
|
|
Strategy & Tactics
|
Strategy: More the why & What for
Tactics: more w/ the how; specific actions to carry out the plan; "techniques part" |
|
|
Planning & Strategy deals with problems and opportunities
|
Problem: something to be solved
Opportunity: a favorable circumstance, a chance to attain goal |
|
|
Goals & Objectives
|
Goal: a generalized aim or intent
EX: "for our company to become better known" Objective: more specific, milestones, that can be measured EX: "for 300 people to access our website be Dec. 20th" |
|
|
Values, Mission, Vision
|
- Underline everything an organization attempts to do.
* Values: the core belief that guides us * Mission: our purpose * Vision: what we strive for; our ideal - PR people often help to write statements. |
|
|
Reactive vs. proactive approaches
|
Reactive: acting in response to something
Proactive: trying to anticipate in order to act before something occurs; may prevent something from occuring |
|
|
Chapter 9: planning and tactics
Tactical considerations |
Tactics are like tools in a tool chest
Many possible tactics are available The strategic task: choose the right tactic for the purpose at hand |
|
|
Choosing a tactic
|
1. Public to reach
2. The goals 3. The messages 4. Resources available (money, time, skills) |
|
|
Tactics should be
|
- tied to values, mission, vision
- specific - targeted - based on research - constantly evaluated |
|
|
Particular tactics for particular publics
|

|
|
|
Types of tactics
|
Plant; facility tours
Considerations: Appropriateness Safety Privacy |
|
|
Tactic: institutional advertising
|
- advertising-like approach
- not directly related to selling products and services - paid for by organizations |
|
|
Four types of institutional advertisizing
|
- identity ad's
- image ad's - issues ad's - advocacy ad's |
|
|
Identity ad
|
Focuses on organizations name or key interest
EX:if company changes name or is merged with another |
|
|
Image ad
|
Focuses on the way the organization wants to be known
EX: may stress leadership or innovation |
|
|
Issue ad
|
Raises an issue and discusses it
Focuses on issues relevant to the organization Ex: may point to the need for a solution to energy problems |
|
|
Advocacy ad
|
Focuses on a point of view (specific solution, or answer)
EX: corn syrup producer may argue against its critics |
|
|
Tactics: publics service announcements
|
What are they?
Are promotional announcements Strictly for non-profit organizations Similar to ad's but time/ space is free Canberra printer broadcast |
|
|
PSA dynamics
|
Messages related to issues ex: quit smoking; vote; avoid drugs
Space is donated by media outlets as public service, saving non-profit $ ...time/ space may not be best |
|
|
Tactic: backgrounder
|
Usually single sheet of paper with background info about an organization or situation
Typically provides basic, useful info, largely for journalists |
|
|
Tactic: speeches
|
A talk to a public (internal / external)
- can be formal or informal - manuscript or extemporaneous - by CEO or spokesperson |
|
|
Tactic: special event
|
- planned happening with a public relations purpose
* pseudo event: - term used by critics - signifies a special event held only to attract media attention |
|
|
Tactic: annual report
|
- published by profit & non-profit
- published once a year - particularly important for publicly held corporations |
|
|
Tactic brochure
|
Printed message device
Typically a paper folded 3 times * characteristics - highly focused - written in a lean manner - highly informative * related concepts - flier (circular): single sheet, informal, inexpensive - leaflet: sheet folded over once (4 panels) - booklet: pamphlet: small book |
|
|
Tactic: house organ
|
A magazine or newspaper produced by the organization
|
|
|
Tactic: news letter
|
- a letter-like periodical
- contains news for publics - print or online |
|
|
The formal plan
|
Planning process typically generates a formal or written plan
- various elements in the plan: - goals & objectives - strategy - messages to convey - publics to address - tactics to employ - budget: resources - time frame |
|
|
Choosing a tactic
|
1. Public to reach
2. The goals 3. The messages 4. Resources available (money, times, skills) |
|
|
Communication channels
|
PR tactics accomplished through communication channels
Channels: pathways for information |
|
|
2 broad types of channels
|
1. Controlled channels
2. Uncontrolled channels |
|
|
Controlled channels
|
Under an organizations control
Advantage: control, determines content, style, slant, schedule, they have a final say Disadvantage: may have limited credibility and exposure (audience knows you call the shots info assumed to be self-serving |
|
|
Uncontrolled channels
|
Channels not under an organization control
Example: city newspaper, TV networks, consumer group newsletters Advantage: possibility of added credibility (endorsement) Disadvantage: you have to interest intervening public; lack of control over final say |
|
|
Media relations
|
Involves interaction w/people in the news media
- newspaper - magazines - TV - radio - current-event publishing |
|
|
People in the news media
|
- print journals
- broadcast journalists (reporters, editors, producers) |
|
|
Public relations people & media people
|
Relate to eachother
Rely on eachother Frequently get to know eachother well |
|
|
PR people
|
- PR people see media people as an intervening public
- the intent: messages sent to the media will be sent to other publics |
|
|
Media people
|
Media people see PR People as sources for news
- the intent: that relationships with PR people will yield ideas & resources that can be if interest to media audience |
|
|
PR characteristics
|
Value truth
Hard-working Professional Use journalistic (news style if writing) Voice a point of view Represent a particular organization |
|
|
Journalist characteristics
|
Value truth
Hard-working Professional Use journalistic (news style if writing) The ideal of of objectivity Audience focus Advertising/ supported |
|
|
News and PR MEDIA realtions hips
|
PR & media relationships based on the value of news
News=new; north, east, west, south |
|
|
Traditional journalistic criteria for evaluating news
|
To journalist, it may be news if it has:
- novelty - proximity - impact - prominence - tension - immediacy |
|
|
PR: news press release
|
- an essential written tactic used throughout oublic relations
- focuses on news of organization - written for news media - Hope: that media will use in articles, broadcasts - media rarely use whole release - usually edit or need more details - often ignore release (waste basket) |
|
|
Typical subjects of a news press release
|
- new products
- merger; acquisition - change in management - interesting developments - financial information |
|
|
News release functions
|
- relationship management
- addresses values & interests of the organization of targeted publics |
|
|
New release characteristics
|
- news story about an organization, written from sources point of view
- written in journalistic style |
|
|
Inverted pyramid
|
- most important info goes 1st
- least goes last - practical considerations |
|
|
Use of associated press style guide
|
- usage and grammar follow same guide
|
|
|
Use of summary lead
|
- who; what; when; where; why & how
- beginning of release same as beginning of standard news story - 1st couple sentences, 1st paragraph ( first 25 or so words) |
|
|
Elements of new release
|
- tightly written (every word counts)
- Highly focused - organization and address at top - contact person & contact information at top |
|
|
Elements of news release (cont.)
|
- summary news leads
- text starts 1/3 -1/2 down page - short sentences - news - inverted pyramid format - "more" at end if page - "boilerplate" as last sentence - at the very bottom of release: "end"; "###"; "-30-"; |
|
|
Examples of student press releases
|
- PR& cyberspace
- computer-mediated communication system |
|
|
Types of media
|
Website: wiki; podcasts
Blog: social network |
|
|
Website
|
Internet based collection of files organization or individual
|
|
|
Blog
|
Internet based journal or log
Subject driven; authored |
|
|
Wiki
|
Website that can be edited by users
|
|
|
Social network
|
FB;interactive; opinion/ informative
|
|
|
Podcasts
|
Downloadable audio/ visual/ video
|
|
|
New media characteristics
|
- electronically based
- time flexibility (send/receive instantly) - space flexibility (5- 5,000 miles away) distance irrelevant - digital (integrative technologies |
|
|
Problem v. Crisis
|
Problem: an "ordinary" challenge; fairly predictable; relatively manageable
Crisis: an "extraordinary" challenge; harder (sometimes impossible to predict); affects an organization at its core |
|
|
Good crisis communication
|
Not about:
- denial - putting on a "happy face" About: - promoting understanding - sensitivity to publics - candor: natural - helping - clarifying issues |
|
|
Crisis dynamics & evolution
|
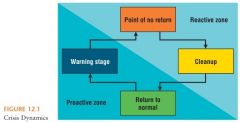
|
|
|
Notable crisis communication cases
|
- BP oil spill
- hurricane Katrina - china toys - Chernobyl - 3 mile island - Tylenol tampering - vioxx - Exxon Valdez |
|
|
Pro-active
|
Helping to prevent a crisis
* pr people as: - trend spotters - analysts - counsels to top decision makers |
|
|
Crisis predictability
|
The inst. of crisis management says...
- 14% of crisis are truly sudden, accidental & unexpected - 86% are more or less predictable |
|
|
Roles for PR IN crisis communication
|
- spotting potential problems /issues
- planning & coordinating - advising management - linking with key publics - drawing from lessons |
|
|
Elements of Crisis communication
|
A. Crisis prevention
- identify potential crisis risks - maintain solid relations with publics - ask "what if." |
|
|
Elements of Crisis communication
(Cont) |
B. develop crisis response plan
- procedures for responding - decision makers; spokesperson - capabilities ready |
|
|
Elements of Crisis communication
(Cont) |
C. If crisis occurs
- implement crisis plan - alert all organization leaders - mobilize crisis response teams - provide information quickly - inform all relevant publics (ESP. Employees and media - express concern (apology) - respond with candor - Verify & recheck as crisis unfolds - communicate quickly, consistently and truthfully - have materials as needed - have service, equipment as needed - be available |
|
|
Elements of Crisis communication
(Cont) |
D. In the wake of a crisis
- identify lessons for the future - move forward |
|
|
Integrated marketing communication (IMC)
|
Combination of PR, Marketing and advertising
- brand-focused - relationship building - identities retained, but work together |
|
|
Goal of Integrated marketing communication
|
To send well- defined interactive messages to individual consumers
|
|
|
Challenge of integrated marketing communication
|
To gain synergy without compromising identity and integrity of each area
|
|
|
Characteristics of IMC
|
Focus is often on "brand" centered
- uses coordinated and consistent message - draws on joint strengths of PR, marketing and advertising - geared to individual consumers: not mass market - emphasis on consumer preferences - meeting consumer needs through favorite media channels - relies on information about consumers and preferences - information often collected through use of new information technology and databases - adaptable to different situations - can be used for coordinated campaigns - may incorporate social issues - as in other aspects of PR, must stress ethics |
|
|
IMC strategy issues
|
- playing to strengths of PR and other fields
- determining which situations are appropriate for IMC treatment - choosing a consistent message - marshaling resources effectively - addressing consumer publics in a genuine and effective way - being sensitive to special consumer concerns, such as privacy |

