![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Foundations of historical globalization worksheet |
- Printing press: faster book production, cheaper, more affordable, more people learned to read/write - trade: increased, more people worked, profit - sailing technology - Gold, God, Glory |
|
|
Mohandas Ghandi |
- Came up with the principle Shadeshi (Hindi for self sufficiency) - he lead India to independence in 1947 - when he came back from England he became a leader of the Indian National Congress Party - he said that in order for India to be self sufficient they needed to hand spin cotton so they wouldn't have to buy cloth from the British and also to help Indias unemployment |
|
|
Capitalism |
- Infinite wealth - economic freedom - money investments - founder: Adam Smith - happy individuals - a persons economic status can change |
|
|
Mercantilism |
- old imperialism - finite wealth - persons economic status cannot change - inequality of economic opportunity - government regulations - Hudson Bay Company - trading group - sit on money - happy nation |
|
|
Industrial Revolution |
- 1800 - Industrialization - Economic growth - Need for: resources and new markets - using machines instead of humans - Increased speed & production - changes economically, socially, & culturally - Britain was first country to do this |
|
|
The Silk Road |
- trade route - connecting East Asia, West Europe, - trading silk, spices, olives, wine, metals, plants, etc. - economic impact - trading ideas - disease |
|
|
Chapter 6 note taking assignment |

- Due to economic factors, in 1858, the British government took over India and began the period of Raj (Hindi word for rule) - Mohandas Ghandi came up with the principle Swadeshi (Hindi for self sufficiency) - he said that in order for India to be self sufficient they needed to hand spin cotton so they wouldn't have to buy cloth from the British and also to help Indias unemployment - he lead India to independence in 1947 |
|
|
Imperialism |

|
|
|
The White Man's Burden |
-The duty of Europeans to civilize savages - Europeans feel like they have to suffer - to civilize: convert to Christianity, educate, cure diseases, dress like Europeans, become farmers - poem by Rudyard Kipling |
|
|
Beothuk |
- Europeans cam to their land, when Beothuk tried to get them off, Europeans started killing - depopulation - migrated through necessity to the West - European diseases like smallpox, killing/murder, & starvation led to their extinction
|
|
|
Treaties |
- Goals: to assimilate First Nations - Results: loss of culture, dependence, verbal agreements during treaty negotiation not included in written and signed treaties - total 11 treaties |
|
|
Consequences of historical globalization worksheet |
Aztec Empire: - forced into slaves - assimilated - defeated Disease: - millions of people died - First Nations were not immune Slavery: - First Nations were treated as slaves - chattel: property of their owner, movable, permanent - indentured: property by contract, temporarily - Portuguese began slave trade Plantations: - Africans were usually used because they were experienced with agriculture, working in tropical conditions, and immune to tropical diseases - usually done in the South, not the North (couldn't keep slaves a love in harsh winter), also because it could support year round agriculture, warmer climate Abolition: - the stop of slavery (they were treated very badly |
|
|
Ethnocentrism/Eurocentrism |
Ethnocentrism: thinking that one country/group is better/superior than the rest Eurocentrism: European ethnocentrism |
|
|
Leopold & the Congo |

|
|
|
Scramble for Africa |
- the race for European countries to own parts of Africa & make colonies - colonies = power = wealth - Results include slavery & assimilation |
|
|
Indian Act |
- 1876 - Canadian government used to assimilate First Nations - Defining who was status Indian (they received certain benefits) - Banned traditions like the Sun Dance and Potlatch ceremony - Only those who moved off of reserves were allowed to vote in federal elections |
|
|
Residential schools |
- Government and Christian Church run schools in almost all of Canada - Used to assimilate First Nations children by removing them from their homes, moving then far away, not allowing them to speak their language, converting them to Christianity - loss of culture, identity, language - abuse, physical and mental, intergenerational trauma, deaths - federal government redress (official government apology) 2008 |
|
|
Potlatch Ceremony |
- spiritual traditions of various First Nations living on the Northwest Coast - Historically, the potlatch functioned to redistribute wealth in what some refer to as a gift-giving ceremony. Valuable goods were accumulated by high-ranking individuals over time, sometimes years. These goods were later bestowed on invited guests as gifts by the host or even destroyed with great ceremony as a show of superior generosity, status and prestige over rivals. Source: www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca |
|
|
Scramble for Africa map |
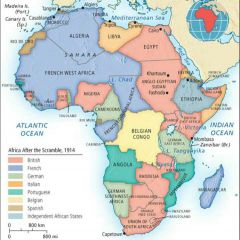
|
|
|
Cultural contact |
contact between peoples with different cultures, usually leading to change in both systems Source: www.britannica.com |
|
|
Industrialization |
- using machines instead of humans- increased speed & production- changes economically, socially, & culturally |
|
|
International trade |
Exchange of goods/services across international borders |
|
|
Colony |
A country's group of people move and settle to somewhere else (another country usually) |
|
|
Protectorate |
- a state that is controlled and protected by another greater one usually - Historically many countries, including Canada were protectorated by Britain Source: Google dictionary |
|
|
Sphere of influence |
- Who influences your opinions/decisions and to what level - examples: media, family, friends, work, school, politics, community |
|
|
Disaggregated |
Broke/separated something into smaller parts to make working with it easier/better |
|
|
World views |
A persons conception/opinion/philosophy on the world |
|
|
Civil strife |
- violent activity such as rioting, fighting, doing a demonstration, going on strike, or protesting in public places, especially involving many people against authority people Source: www.translegal.com |
|
|
Reconciliation |
- the restoration of friendly relations- synonyms: reuniting, bringing together (again), rapprochement Source: Google dictionary |
|
|
Depopulation |
- a group/country decreasing in population due to disease, starvation, war, climate, etc. |

