![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What histologic features distinguish proliferative from nonproliferative fibrocystic change?
|
Nonproliferative changes include stromal fibrosis and cyst formation; proliferative changes include the nonproliferative changes plus epithelial hyperplasia and sclerosing adenosis
|
|
|
Does the presence of apocrine metaplasia increase the patient's risk for the subsequent development of breast carcinoma?
|
No.
|
|
|
How are apocrine metaplasia cells different morphologically from normal ductal cells?
|
Apocrine metaplasia cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large round nuclei with nucleoli.
|
|
|
Is the presence of ductal hyperplasia without atypia a risk factor for the subsequent development of breast carcinoma?
|
Yes, but there is only a slightly increased risk (1.5 to 2 times). Atypical ductal hyperplasia has a four to five times increased risk
|
|
|
List several risk factors for the development of breast carcinoma.
|
Risk factors include first-degree relatives with breast carcinoma, early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity, obesity, and proliferative fibrocystic disease. Five percent to 10% of breast cancers are believed to be related to the inheritance of mutations in the TP53 gene (Li-Fraumeni syndrome), BRCA1 gene, or BRCA2 gene. Individuals who inherit a mutant copy of one of these tumor suppressor genes develop carcinomas at a younger age
|
|
|
Are calcifications in the breast parenchyma diagnostic of carcinoma?
|
No, microcalcifications may be seen in benign disorders such as fibrocystic changes and in carcinoma. Radiologists examine the character of the microcalcifications to determine whether or not they are suspicious for being associated with carcinoma
|
|
|
What does the term scirrhous mean?
|
Hard.
|
|
|
Does the size of breast carcinomas have clinical significance?
|
Yes, size is important for staging purposes. Breast tumors 2 cm or less without regional or distant spread are in stage I. These tumors have a favorable prognosis.
|
|
|
define comedocarcinoma, or comedonecrosis
|
when the central portion of the duct contains necrotic debris
|
|
|
How does a high-grade intraductal comedocarcinoma differ in clinical behavior from that of low-grade intraductal carcinoma?
|
Recurrence or invasion occurs in approximately 40% of patients with high-grade comedocarcinoma after lumpectomy alone compared with only about 10% of patients with low-grade intraductal carcinomas after lumpectomy alone
|
|
|
How do invasive DUCTAL carcinomas differ in histologic appearance from invasive LOBULAR carcinoma?
|
Invasive DUCTAL carcinomas tends to form ductal structures, whereas invasive LOBULAR carcinomas invade as single cells, often arranged in a linear fashion.
|
|
|
Besides the axillary lymph nodes, what other organs are commonly involved by metastatic breast carcinoma?
|
Lungs, liver, and bone are commonly involved by metastatic breast carcinoma
|
|
|
What factors influence the prognosis of breast cancer?
|
Factors that influence prognosis are size of tumor, number of lymph node metastases, histologic type and grade of tumor, presence or absence of estrogen receptors, proliferative rate and DNA ploidy, and overexpression of HER2.
|
|
|
What age group is most commonly affected with fibroadenomas of the breast?
|
Young women (<30 years old) are most commonly affected
|
|
|
What are the typical physical examination findings of fibroadenomas?
|
Findings typically include well-circumscribed, mobile, rubbery nodules
|
|
|
What are the typical symptoms of an intraductal papilloma?
|
Typical symptoms include serous or bloody, unilateral nipple discharge, occasionally with an underlying palpable nodule
|
|
|
Why is serous and bloody nipple discharges often associated with intraductal papillomas?
|
The delicate papillae may produce an abundance of serous fluid or may fracture and bleed.
|
|
|
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is characterized by?
|
LCIS is characterized by the filling and expansion of the acini of a lobule by a uniform population of low-grade neoplastic cells
|
|
|
How does LCIS differ from ductal carcinomas in situ with regard to the subsequent risk for invasive breast carcinoma?
|
With long-term follow-up (approximately 24 years), 30% of patients with LCIS develop invasive carcinoma; however, the tumor may be ductal or lobular, in the same or opposite breast. Lobular carcinoma in situ is considered to be a marker of increased risk for invasive breast carcinoma, whereas intraductal carcinomas are considered precursors to invasive breast carcinoma
|
|
|
How does the prognosis of invasive lobular carcinoma compare with that of invasive ductal carcinoma?
|
Although there are conflicting studies, there is probably no significant difference in survival of invasive ductal and lobular carcinomas
|
|
|
35 yr woman, notices blood discharge from nipple of her right breast for the past 3 days. On PE, the skin of the breasts appears normal, and no masses are palpable. There is no axillary lymphadenopathy. patient has regular menstrual cycles and is using oral contraceptives. Excisional biopsy is most likely to show what lesion?
|
intraductal papilloma
|
|
|
28 yr woman in 3rd trimester of preg discovered lump in her left breast. The physician palpated a 2cm, discrete, freely moveable mass beneath the nipple. After birth of a term infant, the mass appears to decrease slightly in size. The infant breastfeeds without difficulty. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenomas are common & may enlarge during pregnancy or late in each menstrual cycle. |
|
|
30 yr woman sustained a traumatic blow to her right breast. Initially, there was a 3cm contusion that resolved within 3 weeks, but she then felt a firm lump that persisted below the site of the bruise 1 month later. What is the most likely diagnosis for this lump?
|
fat necrosis
fat necrosis is typically caused by trauma to the breast - the damaged, necrotic fat is phagocytosed by macrophages, which become lipid-laden. The lesion resolves as a collagenous scar within wks to mos. |
|
|
55 yr man has developed bilateral breast enlargement over the past year. On PE, the enlargement is symmetric & is NOT painful to palpation. There are no masses. The patient is not obese & is not taking any medications. Which underlying condition best accounts for these findings?
|
micronodular cirrhosis
cirrhosis most often from chronic alcoholism & impairs hepatic estrogen metabolism, which can lead to gynecomastia |
|
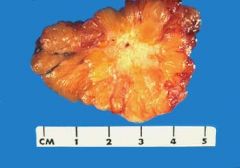
44yr woman sees her physician b/c she felt a lump in her left breast 1 week ago. The physician palpates a firm, irregular mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. There are no overlying skin lesions. The gross appearance is shown in picture. Which additional finding is most likely to be present on physical exam?
|
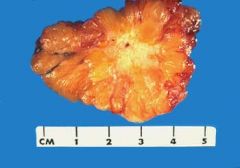
axillary lymphadenopathy
pic shows irregular, infiltrative mass = invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer. Breast carcinomas are most likely to metastasize to regional lymph nodes. By the time a breast cancer becomes palpable, lymph node metastases are present in more than 50% of patients. |
|
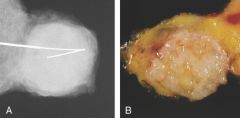
25 yr woman sees her physician b/c she has noticed a lump in her right breast. The physician palpates a 2cm, firm, circumscribed mass in the lower outer quadrant. The figure shows the excised mass and the mammogram. What is the most likely dx?
|
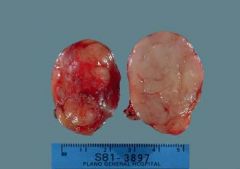
fibroadenoma
gross and radiographically, the lesion is a discrete mass that in a woman her age is most likely to be fibroadenoma. |
|
|
47 yr woman noticed a red, scaly area of skin on her left breast that has frown slightly larger over the past 4 months. On PE, there is a 1cm area of eczematous skin just lateral to the areola. Most likely dx?
|
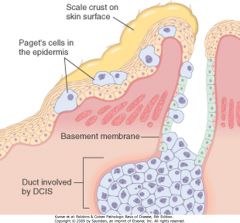
paget disease of the breast
|
|
|
3 wks after giving birth, 24 yr woman is breastfeeding and notices fissures in the skin around her nipple. Over the next 3 days, region around the nipple becomes erythematous & tender. Purulent exudate from a small abscess drains thru a fissure. Which organism is most likely to be cultered from the exudate?
|
Staph aureus
dx = acute mastitis |
|
|
27 yr woman feels a lump in her right breast. She has normal menstrual cycles, she is G3 P3 and her last child was born 5 yrs ago. The physician palpates a 2cm, irregular, firm area beneath the lateral edge of the areola. The mass is not painful & does not feel firm. There are no lesions of the overlying skin & no axillary lymphadenopathy. A biopsy specimen shows microscopic evidence of an increased number of ducts, which are compressed b/c of proliferation of fibrous connective tissue. Dilated ducts with apocrine metaplasia also are present. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
dx = fibrocystic changes
fibrocystic changes account for the largest category of breast lumps, statistically ~40% of all breast "lumps". These lesions are probably related to cyclic breast changes that occur during the monthly cycle. |
|
|
Fibrocytic changes include...?
|
ductal proliferation, ductal dilation (sometimes apocrine metaplasia) fibrosis
|
|
|
44 yr woman noticed a lump in her right breast. On exam, she has an ill-defined, 1 cm mass in the upper outer quadrant. The mass is cystic on ultrasound. An excision is done, and the mass shows predominately fibrocystic changes, but carcinoma also is present. FNA of both breasts reveal additional foci of similar malignant cells. Which type of carcinoma is most likely?
|
Lobular carcinoma
among primary malignancies of the breast, lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is most likely to bilateral. LCIS may precede invasive lesions by several yrs. Lobular carcinoma may be mixed with ductal carcinoma, and it may be difficult to distinguish them histologically. |
|
|
56 yr woman sees her physician for a routine health exam. There are no remarkable findings on physical exam. A mammogram shows 0.5-cm irregular area of increased density with scattered microcalcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. Excisional biopsy shows atypical lobular hyperplasia. The patient has been on post-menopausal estrogen-progesterone therapy for the past 10 years. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day for the past 35 years. Is she at risk for invasive carcinoma?
|
yes, atypical lobular hyperplasia and atypical ductal hyperplasia increase the risk of breast cancer 5-fold; and the risk of is higher in premenopausal women
|
|
|
54 yr woman sees her doc after feeling a lump in her breast. Doc feels a firm, irregular mass in lower outer quadrant just beneath the lateral margin of the areola. Mammogram shows 2-cm density with focal microcalcifications. Excisional biopsy shows intraductal and invasive components of breast carcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining shows cells are (+) for HER2/neu expression, but neg for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor expression. When combined with doxorubicin, which drug would be useful for this patient?
|
Trastuzumab
|
|
|
55 yr woman has felt a poorly defined lump in her right breast for the past year. On exam, she has a nontender, firm, 6cm mass in the upper inner quadrant. There are no lesions of the overlying skin and no axillary lymphadenopathy. needle biopsy is done, and microscopic exam of the specimen shows cellular stroma protruding into spaces lined by a single-layer cuboidal epithelium. The mass is excised with a wide margin, but recurs 1 yr later. After further excision, the lesion does not recur. What is the most likely dx?
|
Phyllodes Tumor
- similar to fibroadenomas grossly and under the microscope, but occurs at an older age, are larger, and are more cellular. They can recur locally but rarely metastatic. |
|
|
51 yr woman has noticed an area of swelling with tenderness in her right breast that has worsened over the past 2 months. On PE, the 7 cm area of erythematous skin is tender & firm. There is swelling of the right breast, nipple retraction, and right axillary lymphadenopathy. Excisional biopsy is most likely to show?
|
infiltrating ductal carcinoma
nipple retraction and axillary lymphadenopathy + the gross appearance of the skin is consistent with invasion of dermal lymphatics by a carcinoma = inflammatory carcinoma. |
|
|
39 yr woman has noticed an enlarging mass in her left breast for past 2 yrs. Physical palpates 4cm firm mass. A simple mastectomy is performed with axillary lymph node sampling and plastic reconstruction of the breast. On gross sectioning, the mass has a soft, tan, fleshy surface. Histologically, the mass is composed of large cells with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli. There is marked lymphocytic infiltrate within the tumor, and the tumor has a discrete, noninfiltrative border. No axillary node metastases are present. The tumor cells are neg for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor. What is the most likely dx?
|
medullary carcinoma
medullary carcinomas account for ~1-5% of all breast carcinomas. They tend to occur in women at younger ages. Despite poor prognostic indicators, such as absence of estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors (ER-PR) medullary carcinomas have a better prognosis than most other breast cancers. |
|
|
47 yr woman has routine exam. There are no remarkable findings except for a barely palpable mass in her right breast. A mammogram shows irregular, 1.5-cm area of density in the upper outer quadrant. Scattered microcalcifications are present in the density. A biopsy shows atypical ductal hyperplasia. Which is the most appropriate advice to give to the patient?
|
there is risk of cancer in the opposite breast, but radical or simple masectomy is not needed at this time
- atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasias increase risk of breast cancer 5-fold |
|
|
25 yr Jewish woman sees her physician after finding a lump in her right breast. On PE, a 2cm firm, nonmovable mass is palpated in the upper right quadrant. No overlying skin lesions and no axillary lymphadenopathy are present. The family hx indicates that the patients mother, aunt, and grandmother have similar lesions. The physician should do a genetic test to look for a mutation in which gene?
|
BRCA1
|
|
|
a study of women with breast carcinoma is done to determine the presence and amount of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) in the carcinoma cells. Large amts of ER and PR are found in the carcinoma cells of some patients. These receptors are not present in the cells of other patients. The patients with (+) ER-PR are likely to exhibit which traits?
|
higher response to therapy
can tx with antiestrogen compounds such as tamoxifen |
|
|
79 yr old, prev healthy woman feels lump. Doc palpates 2cm firm mass. Lumpectomy with axillary lymph node dissection is performed. Microscopic exam shows mass is infiltrating ductal carcinoma. 2/10 axillary nodes contain mets. Immunohistochemical tests shows cells are (+) for estrogen receptor, neg for HER2/neu expression , and (+) for cathepsin D expression. What is the MOST IMPORTANT prognostic factor for this patient?
|
presence of lymph node metastases
(if there is no spread to lymph nodes, 10 yr survival is almost 80%; it decreases to 35-40% with 1-3 positive nodes and 15% with more than 10 positive nodes) |
|
|
Patients with BRCA1 gene mutation have a high incidence of which type of breast cancer?
|
medullary carcinomas that are poorly differentiated, do not express HER2/neu protein, and are neg for estrogen/progesterone receptors
|

