![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Contributions to sciatic nerve:
Pudendal nerve: leaves pelvis through ______, between __________. contribution to superior gluteal nerve: leaves pelvis superior to ______. |
L4,5,S1-3
S2-4 leaves through greater sciatic foramen, between piriformis, coccygeus L4,5,S1 piriformis |
|
|
Rectal veins:
Superior drains into: Middle drains into: Inferior drains into: Clinical important in cancer, because they connect with _________. |
Superior - inferior mesenteric
Middle - internal iliac --> IVC Inferior - internal pudendal --> internal iliac internal vertebral venous plexus |
|
|
Which nerve emerges medial to psoas major and goes through the obturator foramen?
Contributions to femoral nerve? What provides PNS fibers to foregut/midgut? PNS fibers to hindgut? |
obturator nerve
L2-3-4 Vagus Pelvic splanchnic - S2-4 |
|
|
What is abnormal dropping of kidney... how is this distinguished from a congenital misplaced kidney?
What causes pain associated with it? |
Nephroptosis
Distinguished from a congenital misplaced Kidney by a normal length of Ureter. Pain derived from stretching Renal vasculature. Suprarenal |
|
|
Inflamation to the kidney could cause what kind of pain?
|
Inflamation of the Kidneys or Pararenal Fossae can be
exacerbated by extension of the Lower Extremity at the Hip due to the proximity of the Kidneys to the Psoas Major Muscle |
|
|
Describe the following external features of the kidney and what each entails...
a. anterior surface b. posterior surface |
a. (rounded, convex surface variably covered
with Peritoneum, on Right Kidney contacts the Liver, Duodenum and Right Colic Flexure, on Left Kidney contacts the Stomach, Tail of the Pancreas, Spleen and Left Colic Flexure) b. (less rounded than the Anterior Surface, contacts the Thoracic Diaphragm) |
|
|
Describe the following external features of the kidney and what each entails...
a. lateral margin b. medial margin |
a. Lateral Margin (convex lateral edge of the Kidney)
b. Medial Margin (location of the Renal Hilum) 1. Renal Hilum (vertical Cleft on the concave, medial margin of the Kidney, transmits the Renal A., Renal V. and Renal Pelvis) a. Renal Pelvis (formed by the union of 2 or 3 Major Calices, funnel shaped region, exits at the Renal Hilum, taper into the Ureter) |
|
|
Describe the following external features of the kidney and what each entails...
a. superior pole b. inferior pole c. renal capsule |
e. Superior Pole (directed superiorly)
f. Inferior Pole (directed inferiorly) g. Renal Capsule (tough, fibrous outer coating of the Kidney) |
|
|
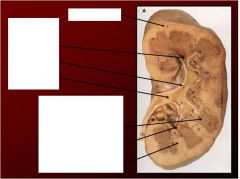
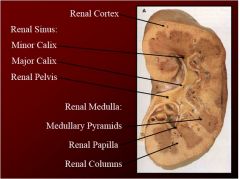
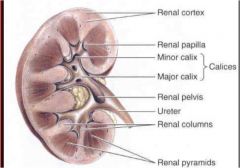
What are the four main features of the internal kidney structures?
|
1. renal sinus
2. renal medulla 3. renal cortex 4. renal pyramid |
|
|
How do you distiinguish between minor and major calix?
What is more than one major calix empty into? |
more than one minor calix is major and more than one major = renal pelvis
|
|
|
Describe the renal sinus structure and location...
The major and minor calix Where do they drain? |
Renal Sinus (internal hollow portion of the Kidney filled with Perinephric Fat and the urinary collecting system of the Kidneys, Major and Minor Calices)
1. Major Calix (formed by the union of 2 or 3 Minor Calices, empties into the Renal Pelvis) 2. Minor Calix (drains the Renal Papilla, combines with other Minor Calices to form the Major Calices) |
|
|
Describe the Renal medulla
Medullary pyramids Renal columns |
Renal Medulla (deep internal solid portion of the Kidney, contains the Medullary Pyramids and Renal Columns)
1. Medullary Pyramids (striated appearance, Medullary component of the Renal Pyramid, drains into the Renal Papillae) a. Renal Papilla (apex of a Renal Pyramid, empties into Minor Calices) 2. Renal Columns (course, granular appearance, supportive tissue between Medullary Pyramids) |
|
|
|
|
|
What is continuous with the fat on the posterior abdominal wall?
|
Paranephric Fat (Pararenal Fat Body; outside of the Renal Fascia, posterior to the Kidneys)
|
|
|
Of the following renal fat and fascia describe what it is derived from and what do they cover?
a. perinephric fat b. paranephric fat c. renal fascia |
a. Perinephric Fat (Perirenal Fat Capsule; derived from Extraperitoneal Fat, surrounds the Kidneys and Suprarenal Glands, is continuous with the Fat of the Renal Sinus)
b. Paranephric Fat (Pararenal Fat Body; outside of the Renal Fascia, posterior to the Kidneys) c. Renal Fascia (membranous layer of connective tissue that surrounds the Kidneys, Suprarenal Glands and Perinephric Fat, forms an anterior and poster lamina that that is open medially and inferiorly, continuous laterally with Transversalis Fascia) |
|
|
Renal Fascia will typically disallow spread of pus from one side to the other. Puss or blood from and injury can however spread inferiorly into the Pelvis this causes?
|
perinephric abscess
|
|
|
Describe where the kidney is removed during transplantation and where the transplanted one is placed?
How are they sutured? |
The Kidney is removed posteriorly leaving the Suprarenal Gland in place. The transplanted Kidney is placed into the Iliac Fossa and the Vessels and Ureters are sutured together
|
|
|
When the kidney fails to ascend during embryological period...
When inferior poles of the kidneys are joined... |
ectopic kidney
horseshoe kidney |
|
|
describe the trigone...
how it is formed Describe the folds involved... |
(formed by the two Ureteric Orifices and Internal Urethral Orifice)
a. Ureteric Orifices (openings for the Ureters into the Urinary Bladder) b. Internal Urethral Orifice (Opening for the Urethra in the Neck of the Urinary Bladder) c. Iterureteric Fold (superior limit of the Trigone, joins the two Ureteric openings) d. Uvula of the Urinary Bladder (swelling in the posterior wall of Urinary Bladder at the Internal Urethral Orifice) |
|
|
What are the "7" main parts of the urinary bladder?
|
1. trigone
2. apex 3. body 4. fundus 5. neck 6. detrusor 7. vesical fascia |
|
|
|
|
|
Describe the three aspects of the suprarenal gland
|
1. Hilum (exit point for Suprarenal Vs. and lymphatic drainage)
2. Cortex (derived from mesoderm, secretes Corticosteroids and Androgens) 3. Medulla (mass of neural tissue derived from Nerual Crest cells, secretes Catecholamines (Epinephrine), contains Chromaffin Cells) a. Chromaffin Cells |
|
|
Where are the suprarenal glands located?
|
positioned superomedially on the Kidneys, surrounded by and attached to the Thoracic Diaphragm by Renal Fascia, separated from the Kidneys by Renal Fascia, embedded in Perirenal Fat, Right Suprarenal Gland is more Pyramidal in shape, Left Suprarenal Gland is more crescent-shaped)
|
|
|
Describe the uniqueness of the the chromaffin cells in the suprarenal glands
|
act as Postsynaptic Sympathetic Cells bodies that receive a Presynaptic fiber from the Sympathetic Division of the Autonomic Nervous system to release Catecholamines)
|
|
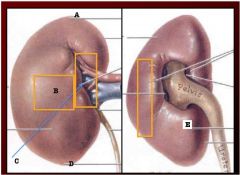
Label
|
A. Superior pole
b. Anterior surface c. Renal hilum of medial margin d. Inferior pole E. Posterior surface |
|
|
|
|
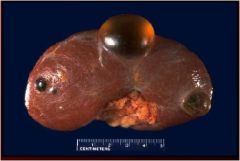
What do we have here?
What does this result in? |
Renal cyst
- result of polysystic disease of kidney can result in Renal Failure |
|
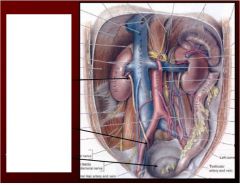
Name the three and label ureteric constrictions?
Why do we care about these? |
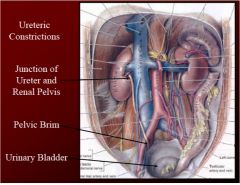
top to bottom-
1. junction of the ureter and renal pelvis 2. at the pelvic brim 3. as they enter the urinary bladder - If we concentrate urine too much causes kidney stone (ureteric Calculi)- pain is down ureter due to distension of ureter |
|
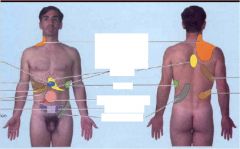
Pain distribution focus on kidney stone area
|
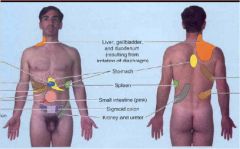
|
|
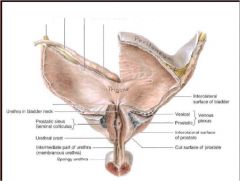
Name and label the four parts of the trigone...
What is the trigone exactly? |
Triangular shape of urinary bladder formed by two ureteric orifices and one internal urethral orifice
1. ureteric orifice 2. internal urethral orifice 3. iterureteric fold 4. uvula of urinary bladder |
|
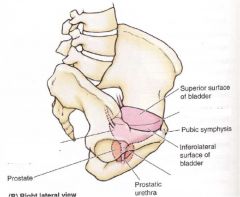
|
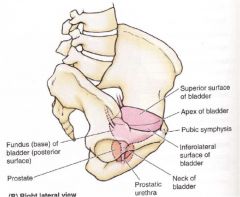
|
|
|
Why is urinary bladder not likely to be ruptured if you are punched in the lower abs?
|
it is surrounded by a thick muscle called the "detrusor muscle"
Contraction of the detrusor muscle causes urine to squirt out |
|
|
What is detrusor muscle surrounded by?
|
vesical fascia
|
|
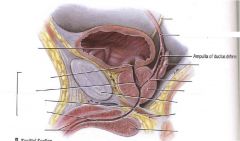
|
|
|
|
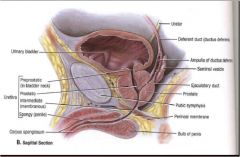
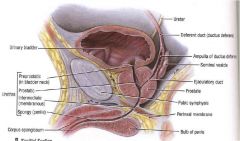
Describe the main parts of the male urethra and general location... Why is it more complicated than the females?
|
Due to prostate and penis it is more complicated that female
Main parts- a. preprostatic urethra- neck of urinary bladder b. prostatic urethra- prostate gland c. membranous- through external urethral sphincter d. spongy- inside corpus spongiosum of penis |
|
|
Describe the three parts of the spongy urethra.... Also describe the roles of each
|
a. intrabulbular fossa- in bulb of penis receives secretions of bulbourethral glands (opening for ducts of bulbourethral glands)
b. navicular fossa- in glans plenis c. urethral glands- mucus glands that dump into spongy urethra |
|
|
What are the 3 important parts within the prostatic urethra?
|
1. Seminal Colliculus- located in the urethral crest, rounded area with three slit-like openings
2. Prostatic sinus- bilateral space receives prostatic fluid from prostatic ductules 3. Urethral Crest- median ridge in the center of the prostate gland that contains Seminal Colliculus and is surrounded by Postatic sinuses |
|
|
Describe in detail the three holes located in the seminal colliculus and roles of each...
|
1. prostatic utricle- remnant of male vagina (uterovaginal canal)
2. Openings for ejaculatory ducts (2) |
|
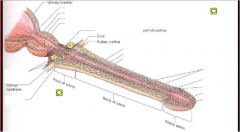
Space ship penis
|
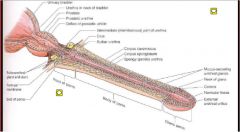
|
|
|
Name the path of the urethra from the urinary bladder of the female to the emptying...
|
goes into the vestibule of the vagina and goes out of the external urethral orifice
|
|
|
What is the name of the cells located in the Suprarenal glands related to sympathetic division that is directly innervated?
|
Chromaffin cells located in the medulla secrete catecholamines
- derived from neural crest cells |
|
|
What is the cortex of the suprarenal gland derived from and what does it secrete?
|
derived from mesoderm and secretes corticosteroids and androgens
|
|
|
25 yr old has fever, nausea, pain and itching in perineal region. Urologist diagnosis him with with infected bulbourethral glands. What structure is affected by infection?
|
External urethral sphincter-
|
|
|
WHich part of the prostate is most prone to cancer?
What artery supplies the glans penis? |
posterior part
- dorsal artery of the penis |

