![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
134 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Identify the four skills of emotional intelligence |
Self Awareness Self Management Emotional Awareness Relationship Management |
M.A.M.A. |
|
|
Self Awareness |
Being able to understand what you are feeling |
Personal Competance/Emotional Intelligence |
|
|
Self Management |
Being able to handle your emotions |
Personal Competence/Emotional Intelligence |
|
|
Social Awareness |
Being able to understand other people's emotions |
Social Competence/Emotional Intelligence |
|
|
Relationship Management |
Being able to synthesize your emotions and others' emotions to manage interactions successfully |
Social Competence/Emotional Intelligence |
|
|
Identify the four common factors affecting individuals' preferences in the workplace |
Cognitive Styles Age/Generation Culture Household Situation |
Spirit Animals |
|
|
Cognitive Style |
What you bring to the table |
Spirit Animals |
|
|
Age/Generation |
"Multi-generational workplace" |
Baby Boomer and Millenials |
|
|
Household Situation |
Preferences based on family size/dynamics |
5 kids and a dog vs single partier |
|
|
Culture |
Preferences based on country or state (where you were raised) |
Diversity |
|
|
Group Structure |
Help us make sense of different relationships with team/organization. |
AF Organizational Chart |
|
|
Group Structure Characteristics |
Has an organizational structure, defined authority and can emerge over time |
AF Organization |
|
|
Group Norms |
Accepted standards or behaviors to regulate/guide a group's behavior |
Bringing donuts when late |
|
|
Group Norms Characteristics |
Typically performed at a subconscious level. Not written. Doing things with respect to where we are because we're used to something |
Unwritten |
|
|
Explicit Statement |
Statements or directives made by a group member (most often a formal/informal leader). Members accept directives as rules. |
0830 meetings established by authority |
|
|
Critical Event |
An event in the group's history that causes a group to reassess their existing rules, procedures, processes, or relationships |
Change the way we react about USB Drive |
|
|
Primacy |
The first behavior pattern to emerge in a group. Rules that aren't stated. Just the way it is |
Classroom seating after first day. PB&J |
|
|
Carryover behavior |
Norms that carry over the group members' experiences in other groups |
Old student bring donuts to a new study group when late and group accepts new norm |
|
|
Groupthink |
Mode of thinking when groups unity overrides motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action |
Overly cohesive team |
|
|
Identify Conflict resolution techniques |
Competing, Accommodating, Avoiding, Compromising, Collaborating |
CCCAA |
|
|
Competitive |
Position of power takes firm stand and know what they want. |
Conflict Resolution Technique CCCAA |
|
|
Useful in an emergency, unpopular decision,or defending against a selfish exploiter |
Competitive Conflict Resolution Technique |
CCCAA |
|
|
Collaborative |
Meets the needs of all people involved. |
Conflict Resolution Technique CCCAA |
|
|
Useful when you need to bring together a variety of viewpoints to get the best solution, when there's been previous conflicts in the group, or when the situation is too important for a simple tradeoff. |
Collaborative Conflict Resolution Technique |
CCCAA |
|
|
Compromising |
Partially satisfy everyone. Everyone gives up something |
Conflict Resolution Technique CCCAA |
|
|
Useful when the cost of conflict is higher than the cost of losing ground, when equal strength opponents are at a standstill and when a deadline is looming |
Compromising Conflict Resolution Technique |
CCCAA |
|
|
Accomodating |
Meets the needs of others at own expense. |
Conflict Resolution Technique CCCAA |
|
|
Appropriate when preserving harmony is more important, the issue is more important to the other party, or for a "favor" |
Accommodating Conflict Resolution Technique |
CCCAA |
|
|
Avoiding |
Evade the conflict entirely. |
Conflict Resolution Technique CCCAA |
|
|
Can be appropriate when victory is impossible, controversy is trivial. Or someone else is in a better position to resolve an issue |
Avoiding Conflict Resolution Technique |
CCCAA |
|
|
Identify the five principles of Interest Based Negotiations (I.B.N) |
1. Seperate people from the problem 2. Focus on interest, not positions 3. Invent options for mutual gain 4. Insist on objective criteria 5. Develop your BATNA
|
SFIID |
|
|
IBN |
Interest Based Negotiations |
A.K.A Principled Negotiations |
|
|
BATNA |
Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement |
Be willing to walk away |
|
|
Identify meeting attendee behaviors that contribute to effective meeting |
1. Do your homework: Research facts, present. case professionally, prepare for objections 2. Keep it short: Stick to the point, stick to the agenda, if you've got nothing to say, shut up! 3. Keep it cool and courteous: Questions, not contradictions, Listen & respect arguments, admit your weak points, & their strong ones |
HSC - video |
|
|
Five Meeting Menaces |
1. The Waffler 2. The Turf Warrior 3. Assassin 4. Dominator 5. Interrupter |
Double W.A.D.I peronalities |
|
|
Meandering method of discussion |
The Waffler |
Menaces |
|
|
How to handle the waffler |
1. Give them recognition 2. Take over the steering wheel 3. Don't stop the car |
Driving analogy |
|
|
Protective of their territory |
The Turf Warrior |
Menaces |
|
|
How to handle the Turf Warrior |
1. Respect their authority 2. Ask them for answers |
South Park Angie's desk |
|
|
Makes it a point to shoot down ideas |
The Assassin |
Menaces |
|
|
How to handle the Assassin |
1. Ask them for ideas 2. Push them 3. Keep Pushing |
And...And.... |
|
|
Their position is the right position |
The Dominator |
Menaces |
|
|
How to handle the Dominator |
1. Keep cool and stick to your guns 2. Respond to the arguments 3. Talk to the chair 4. Remember the stuck record |
Put yourself on repeat...4 items |
|
|
Interjects while others are talking |
Interrupter |
Menaces |
|
|
How to handle the Interrupter |
1. Ignore the Interrupter 2. Appeal to the chair 3. Use the "3-point" technique |
My point is...get up |
|
|
Define various methods of idea generation |
- Brainstorming and Electronic Brainstorming - Nominal Group Technique - Delphi Technique - Constructive Conflict |
Team decision making |
|
|
Requires team members to speak freely, avoid criticism, provide as many ideas as possible, and build on the ideas of others. And the electronic form thereof. |
Brainstorming |
Zombie |
|
|
Has participants write down ideas individually, describe these ideas in groups, then silently vote on these idea |
Nominal Group Technique |
Idea generation |
|
|
Systematically and anonymously pools the collective knowledge of experts on a particular subject without face to face meeting |
Delphi Technique |
Atomic Bomb |
|
|
Team members debate their different perceptions about an issue in a way that keeps the conflict focused on the task or process rather than people |
Constructive Conflict |
10th man concept |
|
|
Define various methods of decision making |
1. Authority Rule: military structure 2. Majority Rule: voting/polling 3. Compromise: everyone gives something 4. Consensus: Everyone agrees even if not idea |
Who made the group decision...4items |
|
|
Identify nine intellectual standards involved in critical thinking |
Clarity, Accuracy, Precision, Relevance, Depth, Breadth, Logicalness, Significance, Fairness |
Can All People Really Draw Backwards Looking Smiley Faces |
|
|
Clarity |
Is the problem/question clear, is it understandable |
Nine standards |
|
|
Accuracy |
Free from errors or distortion, true. Double check answers |
Nine standards |
|
|
Precision |
To the level of necessary detail. (Ex) "take a lil of the top" |
Nine standards |
|
|
Relevance |
Relates to the matter/issue at hand |
Nine standards |
|
|
Depth |
Understanding the underlying complexities |
Nine standards |
|
|
Breadth |
Encompassing multiple viewpoints |
Nine standards |
|
|
Logicalness |
Make sense together, no contradictions |
Nine standards |
|
|
Significance |
Focus on what's important |
Nine standards |
|
|
Fairness |
Unbiased, fair, not self-serving or one sided |
Nine standards |
|
|
Identify eight elements of reasoning involved in critical thinking |
1. Purpose of thinking: goal, objective 2. Question at Issue: problem 3. Information: data, facts, obs, experiences 4. Implications & Consequences: other systems 5. Concepts: theories, definitions, laws... 6. Points of View: frame of ref, perspective 7. Assumptions: know assumptions from facts 8. Inferences: know the outcome |
Elements of reasoning wheel |
|
|
Purpose of a Decision Point and Milestone |
To determine rather to cancel, change, or continue |
Points between phases |
|
|
Recognize the purpose of a phase |
Represents incremental work that develops a product to allow for better design/development decisions |
Refines the product |
|
|
Match the DOD decision support system to its function in product development |
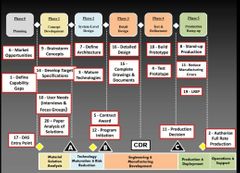
|
DAS to Industry alignment |
|
|
Sequence of the DAS |
1. Material Development Decision (DP) 2. Material Solution Analysis MSA (phase) 3. Milestone A (Milestone DP) 4. Technology Maturation & Risk Ruduction (Phase) 5. Development Request For Proposal (RFP) release (DP) 6. Milestone B (Milestone DP) 7. Engineering & Manufacturing Development (Phase) 8. Milestone C (Milestone DP) 9. Production & Development (phase) 10. Full Rate Production Decision Review FRPDR (DP) 11. Operations & Support (phase) |
5 Phases, 3 Milestones, 3 Decision Points |
|
|
Sequence of Product Development Process |
Phase 0: Planning Decision Point Phase 1: Concept development Decision Point Phase 2: System level design Decision Point Phase 3: Detail Design Decision Point Phase 4: Test and Refinement Decision Point Phase 5: Production Ramp-up
|
6 phases 5 DP Paul cant stop doing the preacher |
|
|
JCIDS |
Joint Capabilities Integration & Development System |
|
|
|
DAS |
Defense Acquisitions System |
|
|
|
PPB&E |
Planning, Programming, Budgeting & Execution |
|
|
|
Determines Capability Gap |
Material Development Decision (Decision Point) |
|
|
|
Involves generating and evaluating (paper Analysis) multiple product concepts to fill the need |
Material Solution Analysis MSA (phase) |
|
|
|
Risk and Reduction Milestone |
Milestone A |
|
|
|
Reduce Technology, engineering, integration, and life cycle risk cost to contract for E.M.D phase is made with confidence. Involves developing a product architecture and defining system/subsystem performance requirements |
Technology Maturation & Risk Reduction (TMRR) phase |
|
|
|
DOD decides if we're ready to ask Industry if they're interested in developing our product |
The Development Request For Proposal RFP release (Decision Point) |
|
|
|
Selects a contractor and commits resources to develop a specific product. |
Milestone B |
|
|
|
Develop, build, and test a product to verify requirements have been met |
Engineering & Manufacturing Development: E.M.D phase of DAS |
|
|
|
Decision is made to move into production. |
Milestone C |
|
|
|
Produce and deliver requirements compliant products to users. Involves LRIP Low rate initial production |
Production & Development Phase |
|
|
|
When kinks are worked out and OT&E is successful final decision to enter full rate production |
Full rate production Decision review FRPDR (DP) |
|
|
|
After product Development. Operate and maintain the product until the end of its life |
Operations & Support phase |
|
|
|
Define project management |
A discipline of methods, theories, and techniques to manage projects that are temporary, unique, complex & uncertain |
|
|
|
Five project success factors |
1. Agreement on Goals 2. A Plan 3. Effective Communication 4. Controlled Scope 5. Management Support |
GAMES |
|
|
Done once, with a unique outcome, has a start and end |
Project |
|
|
|
The work performed over and over, repetitive, follow existing procedures |
On going operations |
|
|
|
Three over arching skills a PM must be knowledgeable of |
Technical Competence, Business Management, Project management |
|
|
|
Project success |
On time, on budget, high quality Schedule, Cost, Performance |
|
|
|
Trade Space |
Staying within the boundaries of schedule cost and performance triangle |
Triple constraint |
|
|
Typical Program/project office functional disciplines represented on a team |
Procuring Contracting Officer, Acquisition Logistics, Manufacturing, Quality Assurance, Configuration management, program/project manager, financial manager, system engineer, test & eval, data management |
PCO... |
|
|
WBS |
Work Breakdown Structure: identifies all the tasks in a project i.e. task list |
What does it do |
|
|
This is how W.B.S clarifies and provides necessary details for project management activities |
Project scope, monitor progress, create accurate cost & schedule estimates, build project teams |
|
|
|
Summary tasks |
Include several subordinate tasks Summarize subordinate work packages |
|
|
|
Work Packages |
The work done to complete a summary task |
Nothing under it |
|
|
How to determine work package size |
1. The 8/80 rule: no task smaller than 8hrs or larger than 80hrs 2. The reporting period rule: no task should be longer than status checkpoints 3. The if it's useful rule: break down tasks if task is easier to estimate, assign, or track |
Rules of thumb |
|
|
Describe the Critical Path Method CPM |
The longest path with 0 slack |
|
|
|
Program Evaluation & Review Technique (PERT) and Monte Carlo Simulations |
Stochastic scheduling techniques used to determine success probabilities (assigning confidence factors) |
Optimistic vs Pessimistic |
|
|
Planning Steps involved with developing a project schedule |
1. Build a WBS 2. ID task relationship/Sequence tasks (Gannt Chart) 3. Estimate work packages: time frame, ppl, and resources 4. Calculate initial schedule: find critical path 5. Assign & level resources: Affirm who's doing the work |
|
|
|
What's the importance of Slack |
When you have slack a work package can start late(depending on slack hrs) and the project can still finish on schedule |
|
|
|
Ways to balance a project at the project level |
Re-estimate project: run #s again Crash the schedule: shorten critical path Increase productivity: better tool, hire expert Reduce Performance: Max effort range |
Get back on schedule...4items |
|
|
Purpose of project cost estimating |
Provide the PM with the best possible estimate of the resources required to complete a project |
|
|
|
What are the various types of cost |
1. Fixed, Variable, or Semi-variable 2. Recurring or Nonrecurring 3. Direct or Indirect |
Can be multidisciplinary |
|
|
Fixed Cost |
Costs that do not change despite changes in cost driver |
|
|
|
Variable Cost |
Cost changes in total in proportion to cost driver |
|
|
|
Semi-variable Cost |
Contains both fixed and variable components |
Bill + fees |
|
|
Recurring Cost |
Repetitive, will continue as long as activity on project continues |
|
|
|
Non-recurring Cost |
Incurred once on the project and will not incur again regardless of project continuity |
|
|
|
Direct Cost |
Cost incurred directly as a result of executing the project |
|
|
|
Indirect Cost |
Indirectly incurred but MUST be incurred by all of the organization i.e. overhead or administrative costs |
|
|
|
Life Cycle |
Lust to Dust, Cradle to Grave |
|
|
|
Identify steps in cost estimating process |
1. Establish ground rules & assumptions: answer 4 W's 2. Collect data: ID similar projects, SME, raw data, filter 3. Select Methodolgy: Analogy, Parametric, Detailed estimator, Expert Opinion, Actual Cost 4. Make the estimate: sum the cost of the diff cost estimates 5. Check the estimate: verify your numbers 6. Review & report: put in format requested by stakeholder |
6 steps |
|
|
Analogy Methodology |
Cost estimation based on similar projects |
|
|
|
Parametric Methodolgy |
Estimates based on extrapolated cost by identifying cost drivers, specifying models, collect data, fit model, evaluate then apply |
Math |
|
|
Detailed Estimate Methodolgy aka Engineering Build up |
Cost estimation based on WBS projection of actual hours |
|
|
|
Expert Opinion Methodology |
Cost estimates based on SME opinions about cost, schedule, and technical data |
|
|
|
Actual Costs |
Cost estimation based on extrapolated costs from actual cost incurred early on the same project |
|
|
|
Identify stakeholders on a project |
Customers, Decision makers, vendors, employees, anyone impacted by project results, anyone who contributes to the project |
|
|
|
Ways to "lead" the stakeholder |
1. Control who is allowed to influence the project 2. Manage upwards: use the chain of command |
|
|
|
Purpose of Project Charter |
1. Announces a new project has begun 2. Demonstrates management support 3. Name and Purpose of Project 4. ID the project manager 5. Legitimate authority to PM 6. Statement of support from the user |
Planning Document |
|
|
Project Scope Statement a.k.a. Statement of Work |
Describes the major activities of the project 1. Goals and Objectives 2. Constraints 3. Success Criteria 4. Achievements |
Planning Document |
|
|
Communication Plan |
Gets the right info to the right people at the right time |
Planning Document |
|
|
Responsibility Matrix |
Shows who is responsible for what, decide and decide who does what 1. RACI: Responsible, Accountable, Consult, Informed 2. LIST major activities of project 3. List stakeholder groups 4. Code response 5. Incorporate the responsibility in the project |
Planning Document |
|
|
List the steps for building a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) Project Plan |
1. Define the work: create a WBS 2. Schedule the work 3. Allocate Budgets |
|
|
|
PMB |
Performance Measurement Baseline |
|
|
|
EVMS |
Earned Valued Management System |
Acronym |
|
|
BCWS |
Budgeted Cost for Work Scheduled (planned): A measure of how much work should be completed at a given time per the schedule Positive = ahead of schedule Negative = Behind on schedule |
|
|
|
BCWP |
Budgeted Cost for Work Performed: Earned value for work performed |
|
|
|
ACWP |
Actual Cost for Work Performed: How much the contractor spent |
|
|
|
BAC |
Budget at Completion: Sum of $ budgeted for each work package |
|
|
|
EAC |
Estimate at completion: New estimate (projection) for TOTAL cost of program. i.e. if you run out of funds and you get more |
|
|
|
SV |
Schedule Variance |
Acronyms |
|
|
SPI |
Scheduled Performance Index: Measure historical EFFICIENCY Fav > 1 Unfavorably < 1 Closer to 1 = goodness |
|
|
|
CPI |
Cost Performance Index: Measure historical EFFICIENCY Fav > 1 Unfavorably < 1 Closer to 1 = goodness |
|
|
|
TCPI |
To Complete Performance Index: Measure how efficient contractor need to be to get back on track |
|
|
|
CV |
Cost Variance: Positive = under budget Negative = Over budget |
|

