![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Security act 1933 |
Regulated new issues in the primary market. |
Regulations |
|
|
Security exchange act of 1934 |
Which created the sec and regulated the trading of existing securities in the secondary market. |
|
|
|
Securities & exchange commission (SEC) |
Functions as the ultimate enforcer of federal securities laws and is responsible for protecting U.S. investors. |
|
|
|
Division of enforcement (DOE) |
Is the branch of the SEC that investigates and takes civil action against those violating federal securities laws. |
|
|
|
Self regulatory organization (SRO) |
The primary function of an SRO is to regulate the activities of its members through the creation and enforcement of industry rules. |
|
|
|
Financial industry regulatory authority (FINRA) |
Is the leading SRO in the United states, regulating broker-dealers and registered representatives in the securities industry. |
|
|
|
Chicago board options exchange (CBOE) |
Is the examining authority for broker-dealers engaging in the options market. |
|
|
|
Municipal securities rulemaking board (MSRB) |
Is the SRO that governs the broker-dealers and banks that engage in the municipal securities business. The MSRB oversees activities such as underwriting, trading and selling tax exempt bonds, municipal securities, and 529 college savings plans. |
|
|
|
Federal deposit insurance corporation (FDIC) |
Is an independent federal agency protecting bank account deposits in the U.S. banks from bankruptcy. The FDIC is the primary regulator of banks and provides each depositor insurance protection of up to $250,000. The FDIC does not insure securities, mutual funds, insurance products, or other investments. |
|
|
|
FED |
Acts as the central bank of the United States. The FED is governed by the federal reserve board. (FRB) |
|
|
|
Federal reserve board (FRB) |
Has the responsibility to regulate the short-term supply money and credit in the United States. It has several important functions, including supervising and regulating banking institutions, and maintaining the stability of the financial system. Most importantly it is responsible for the nations monetary policy. |
|
|
|
Treasury department |
Is the executive agency responsible for promoting economic prosperity and ensuring the financial security of the United States. |
|
|
|
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) |
Is the agency under the treasury department that is responsible for collecting taxes and enforcing tax laws. |
|
|
|
Uniform securities Act |
Is a set of securities laws used to establish uniform securities registration standards and laws at the state level. It serves as model law that provides state administrators with a template or guide to create regulations for securities registrations and transactions in their own state. In the others each state can interpret the Act as it impacts the state. |
|
|
|
North American Securities Administrators Association (NASAA) |
Is a representative body made up of security regulators from the fifty states and the territories of the United States. They are responsible for creating , updating, and maintaining the state licensing exams. |
|
|
|
Blue sky laws |
State securities laws |
|
|
|
A person |
Defined as a natural individual or legal entity that can transact securities business. Market participants are included under the definition of a person. |
|
|
|
Security |
Is an investment contract offered through a legal entity managing the efforts for an expected profit. Common examples of security include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. |
|
|
|
Securities exchanges |
Are auction markets where listed securities are bought and sold. |
|
|
|
Over the counter market (OTC) |
Is negotiated market where unlisted securities are traded. |
|
|
|
Retail investor |
Is an individual that purchases securities for their own account. A retail investor is part of the general public. |
|
|
|
Accredited investor |
An individual with net worth of $1 million. An individual with an annual income of $200,000 for the past 2 years or a couple with joint income of $300,000 that expects that income level to remain. Any bank, investment company, and insurance company, regardless of assests. Am officer or director of issuer, or a non-profit institution, trust, partnership, ERISA qualified retirement plan, or corporation with assets over $5 millon. |
|
|
|
Institutional investor |
Is an entity that makes security transactions on a large scale for their own accounts or for institutional clients, such as Insurance or investments companies, trust, broker-dealers, investment advisers banks, savings, institutions, government agencies or employee benefit plans. |
|
|
|
Qualified institutional buyer (QIB) |
Is an institutional investor that owns and invest a minimum of $100 million in securities on a discretionary basis. An individual cannot qualify as a QIB. |
|
|
|
Issuer |
Is a legal entity, including a corporation, municipality, or the federal government, offering securities to the public to raise capital. Issuers may sell equity (stocks) or debt (bonds) securities to raise money. |
|
|
|
Underwriter or investment banker |
Securities broker-dealer that administers the public issuance and distribution of securities for a corporation or other issuing body. The underwriter works with the issuing entity to assist in determining the offering price and may buy the security from the issuer to sell to public investors through a distribution network. |
|
|
|
Custodian |
A firm such as a trust company, commercial bank, or similar financial institution, hired by the issuer to physically safeguard cash and securities for the buying public. |
|
|
|
Trustee |
A firm such as trust company, commercial bank, or similar financial institution, hired by bond issuers to protect the bondholders interest. |
|
|
|
Transfer agent |
A firm that performs all the record keeping and customer service functions, processes name and address changes and keeps track of the number of shares owned by each investor. Typically, the transfer agent will also act as the paying agent, distributing dividends and capital gains to investors. |
|
|
|
Broker-dealer |
Is a firm in the business of executing securities trades for compensation. |
|
|
|
Broker |
Is a firm acting as an agent, executing orders on behalf of customers, and gets paid commission. Brokers act in an agency capacity. |
|
|
|
Dealer |
Is a firm acting as a principal, trading for it's own account, and charges a mark up on purchases or Mark down on sales, instead of being paid commission. Dealers act in principle capacity. |
|
|
|
Investment banking |
The department of broker-dealer that negotiates with issuers when selling securities to the public. |
|
|
|
Research |
The department of broker-dealer that investigates issuers and the merits of their securities to make buy and sell recommendations. |
|
|
|
Trading |
The department of broker-dealer that handles trade executions for clients and the firm. |
|
|
|
Operations |
The department or a broker-dealer that ensures accurate record keeping within the firm. |
|
|
|
Clearing broker-dealer |
Is a firm that handles trades, both buy and sell. They are responsible for all the paperwork associated with the execution of the transaction and maintain custody of client assets and securities which must be segregated appropriately. |
|
|
|
Introducing broker-dealer |
Is a firm that introduces customer accounts to a clearing broker-dealer through a clearing agreement, which dictates each partys responsibilities. An introductory broker dealer does not maintain custody of client assets and securities. |
|
|
|
Prime broker |
Is a firm typically used by hedge funds to handle its complex needs. The hedge fund may use multiple executing brokers to handle trades, preventing a single firm from seeing the activities and duplicating the funds strategies. All trades are then settled through the prime broker. |
|
|
|
Market maker |
Is a dealer always ready to buy and sell securities by maintaining a quote of buy and sell prices. |
|
|
|
Trader |
Is a person in the firms trading department who effects securities transactions at the market-makers quote. |
|
|
|
Registered representative |
Is an individual who is registered with a broker-dealer and solicits or conducts securities business. |
|
|
|
Associated person |
Is any partner, officer, director, branch manager, person under common control or employee of a broker or dealer. A registered representative is considered an associated person. |
|
|
|
Investment advisor (IA) |
Is a firm in the business of providing advice on securities for compensation. |
|
|
|
Municipal Advisor |
Is a firm that provides advice to or on behalf of a municipal entity. The firm may also give advice regarding municipal financial products or the issuance of municipal securities, including advice with respect to the structure, timing, terms, and other similar matters concerning such financial products or issues, or solicitation of a municipal entity. |
|
|
|
Depository trust & clearing corporation |
Is a trade financial services company providing institutional trade processing, clearing and settlement services. |
|
|
|
Options clearing corporation |
Is the clearing agency through which transactions for all listed options are completed. The OCC is the obligor, the guarantor, and the issuer of options. |
|
|
|
Primary offering |
The sale of new securities by an issuer. |
|
|
|
Initial public offering (IPO) |
The first time a corporation sells its stock to the public, the primary offering. |
|
|
|
Underwriting spread |
A negotiated amount that is retained by the investment banker and is considered underwriting compensation for their role in the sale of the issue. Is the difference in price between ehah the public pays and what the issuer receives. |
|
|
|
Public offering price |
Is determined by the underwriter and issuer and includes the total amount needed to compensate the underwriter in addition to the amount required by the issuer. |
|
|
|
Market-out clause |
Releases the underwriting firm from the agreement if there are material adverse circumstances that affect the issuer or market disruptions that make marketing the issue difficult or impossible. |
|
|
|
Market-out clause |
Releases the underwriting firm from the agreement if there are material adverse circumstances that affect the issuer or market disruptions that make marketing the issue difficult or impossible. |
|
|
|
Syndicate desk, syndicate team |
Focuses on building an order book and allocating the stock. Members are liable for any shares that remain unsold at the end of the offering. |
|
|
|
Firm commitment underwriting |
The underwriter purchases all of the securities being sold by the issuer, and then resells them to thr investors at a slightly higher price. |
|
|
|
Standby underwriting |
The underwriter will standby to purchase any unsold new shares for it's own account and then attempt to sell those shares to the public. Any portion of the offering not sold to the public is retained by the underwriter. |
|
|
|
Best efforts underwriting |
The underwriter might agree to sell as many shares to investors as it can and than return any unsold shares to the issuer. |
|
|
|
All or none underwriting |
The underwriter attempts to sell all of the securities offered on a best efforts basis, but sales are contingent on successfully selling all of the shares. If all shares cannot be sold, the deal ke cancelled, and any funds previously collected from the investors are returned. |
|
|
|
Mini-max underwriting |
The underwriter has a specific amount of time to raise a minimum amount of capital for the issuer. If the underwriter cannot meet the minimum requirement by the specific date the underwriting is cancelled. The underwriter must sell the minimum required amount in the primary market, but they are afforded the ability to sell more based on the maximum amount stipulated in the underwriting agreement. |
|
|
|
Preliminary Prospectus (red herring) |
Contains material information about the offering, including an offering price range for the new issue. |
|
|
|
Free writing prospectus |
Is communication of an offer to sell or solicitation to buy that is provided by well known issuers before filing a registration statement. |
|
|
|
Omitting prospectus |
States that a security will soon be available to sell. |
|
|
|
Statutory prospectus |
Is the full prospectus and is an offer to sell an initial public offering ipo, a subsequent primary offering of securities, or mutual funds and variable insurance products, and can be circulated after the security is registered and approved for sale to the public. |
|
|
|
Statutory prospectus |
Is the full prospectus and is an offer to sell an initial public offering ipo, a subsequent primary offering of securities, or mutual funds and variable insurance products, and can be circulated after the security is registered and approved for sale to the public. |
|
|
|
Restricted stock |
Unregistered stock, acquired through private offerings or employee incentive plans, and is subject to mandatory holding periods before it can be sold. |
|
|
|
Control stock |
Is stock held by an officer, director, 10% shareholder, or an affiliated person of the corporation. |
|
|
|
Rule 144A |
Was created to allow qualified institutional buyers to trade unregistered securities with each other. These securities are usually private placements that normally cannot be traded without being registered. |
|
|
|
Regulation T |
Regulates the extension of credit from the broker-dealer to customers for margin accounts. Regulation T also sets payment dates on corporate securities as trade date plus 4 business days. |
|
|
|
Regulation U |
Regulates the extension of credit from banks to broker-dealer |
|
|
|
Maloney act of 1938 |
Amended the securities exchange act of 1934 and authorized the creation of a new SRO, the National Association of Securities Dealers, to regulate over the counter trading. |
|
|
|
NASDAQ |
Is the largest electronic trading exchange in the United States. |
|
|
|
NASDAQ Global select Market |
Lists securities of companies who can meet, and continue to Maintain the most rigorous initial listings standards for specific financial and liquidity requirements. |
|
|
|
NASDAQ Global Market |
Consists of OTC stocks of companies from around the world that meet one of the three sets of initial listing standards and must continue to maintain those standards. |
|
|
|
NASDAQ Capital Market |
Consists of stocks of smaller companies with less capitalization than required for the global market but which meet the minimum financial requirements for listing and must continue to meet those standards. |
|
|
|
NASDAQ Capital Market |
Consists of stocks of smaller companies with less capitalization than required for the global market but which meet the minimum financial requirements for listing and must continue to meet those standards. |
|
|
|
Dark pools |
Are private trading platforms where institutions can trade anonymously. Prices are not displayed publicly until after the trade is entered. |
|
|
|
Bid |
Is a price a customer receives upon sale of a security and the price the market maker is willing to pay to buy the security from the investor. A market maker will always display bid price and the number of shares it is willing to buy. |
|
|
|
Ask |
Is the price a customer pays when purchasing a security in the secondary market. The market maker will sell the security to the customer at the ask price. |
|
|
|
Interpositioning |
Is when a broker-dealer introduces a third party between the broker-dealer and the customer. |
|
|
|
Cost basis |
Is the original purchase price of a security, plus any costs associated with that purchase. It is used for calculating taxable gains or losses associated with the sale of a security or liquidations in certain types of accounts. |
|
|
|
Liquidation priority |
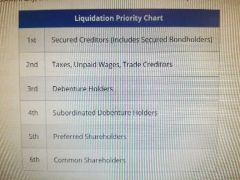
|
|

