![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cause of erosion |
Caused by the intake of sediment load contained in the flow |
|
|
Relationship between flow velocity and erosion |
Not true that fast flows are erosional |
|
|
Flow capacity |
The amount of sediment that a flow can carry |
|
|
Flow competence |
The ability of a flow to carry larger particles |
|
|
What is a beform |
Morphological element due to local changes in deposition and erosion in response to a flowing current |
|
|
Difference vetween sed structure and bedform? |
Sed structures are the preserved structures of bedforms seen in the rock record |
|
|
Variables effecting bedforms |
Flow velocity Flow duration Flow depth |
|
|
Relationship between VSL thickness and grain size with regards to bedform |
When particle diameter exceeds thickness flows will become hydraulically rough and the mode of transport will change: If flow velocity is fast= Dunes If flow velocity is slow= Low plane bed |
|
|
Bedorms produced in sediment: Greater than 0.5mm Less than 0.7mm |
>0.5mm Lower plane bed <0.7mm ripples |
|
|
Ripple grain size field |
Less than 0.7mm |
|
|
Lower plane bed grain size range |
Greater than 0.5mm |
|
|
Grain size range for upper plane bed and transport mode |
Any grain size Suspension |
|
|
Relationship between ripple geometry and grain size |
Ripples get larger with grain size |
|
|
Relarionship between ripples geometry and flow depth |
None |
|
|
Dune relationship with flow depth |
Dunes scale with flow depth 0.2-0.3 times flow depth |
|
|
Antidune relationship with flow depth |
Require supercritical flows and so a greater flow depth requires a greater flow velocity |
|
|
Are ripples dunes |
No they are not continusously related but there is a grain size range of 0.2-0.5mm where they can coexist together |
|
|
Rippl evolution is due to and what does a 2d ripple indicate |
Flow duration Epheral flow |
|
|
Parting lineations are associated with |
Upper plane bed |
|
|
Define effective wave base |
Depth at which water motion ceases and thus sediment transport ceases |
|
|
How are orbitals related to the waves that made them |
Related to the height and length of the waves that made them |
|
|
Describe sediment motion at the ocean floor |
Moves back and forth moving by rolling and saltation |
|
|
Under oscillatory flows sediment motion is initiated when... |
Orbital velocity near bed> Threshold of entrainment for a grain size |
|
|
Describe the equation for orbital velocity |
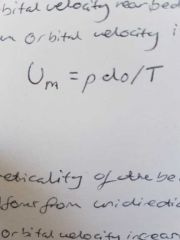
Where: Um=Orbital velocity p= fluid density do= Size of the orbital T= Wave period |
|
|
Size and spacing of oscillatory ripples increases with |
Orbital velocity |
|
|
Cause of hummocky x strat |
Orbital velocity increase |
|
|
Cause of climbing ripple formation |
Where aggradation outpaces migration |
|
|
Trough CB is caused by |
3d ripples or dunes |
|
|
Planar x strat is caused by |
2d ripples or dunes |
|
|
Key conditions for aeolian transport |
Supply of loose sediment Little vegetation Wind |
|
|
Mode of transport in wind flows |
Saltation and rolling/sliding |
|
|
Difference between wind transport and water transport |
Wind trasnport has: Lower viscosity and density Therefore: Greater shear stress is required to move grains |
|
|
How to identify wind transported grains |
Frosted, abraded look due to saltation and wind transport |
|
|
Wind ripple wavelength increases with |
Grain size Decreased sorting |
|
|
How to identify wind ripples in the record |
Show coarsening on the lee slope and therefore inverse grading due to saltation and settling |

