![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is sound wave? |
A mechanical and longitudinal wave |
|
|
|
In what way does a sound travel? |
Straight line |
|
|
|
What does sound travel through? |
A medium |
|
|
|
Biologic effects |
The effect of the sound wave upon the biologic tissue through which it passes. |
Two tissue interactions: heating and cavitation |
|
|
What is the effects of the medium upon the sound wave called? |
Acoustic propagation properties |
|
|
|
What identifies sound waves? |
Acoustic Variables |
|
|
|
Name the Acoustic Variables and their units. |
Pressure (pascals Pa), Density (kg/cm^3), Distance (cm, mm), Temperature (K, °C, °F) |
|
|
|
Concentration of force in an area is called? |
Pressure |
|
|
|
Concentration of mass in a volume is called? |
Density |
|
|
|
Measure of particle motion is called? |
Distance |
|
|
|
What are the seven acoustic parameters? |
Period, Frequency, Amplitude, Power, Intensity, Wavelength, Propagation speed |
|
|
|
The particles move in a direction that is perpendicular (at right angle) to the direction that the wave propagates is called |
Transverse waves |
The wave is moving from left to right (black arrow); however, the particles in the wave are moving up and down (red arrow). |
|
|
Particles move in the same direction that the wave propagates are called |
Longitudinal Waves |
(The wave is moving from left to right)The particles in the wave are moving along in the same direction back and forth, from left to right and then from right to left. |
|

What type of wave is this? |
In-phase wave |
|
|

Name the wave |
Out-of-phase Wave |
|
|

Name the way |
Constructive interference: takes place with in-phase waves. |
|
|
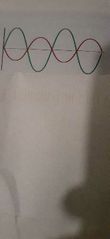
Name the way |
Out-of-phase wave |
|
|
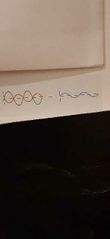
|
Destructive interference: takes place with out-of-phase waves |
takes place with out-of-phase waves |
|

Name the wave |
Out-of-phase waves of EQUAL amplitude may cancel eachother out. |
|

