![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
is the study of factors such as origin, occurrence, classification, type and effects of various secondary structures |
Structural Geology |
|
|
|
is the theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rock. |
Rock Mechanics |
|
|
|
is the use of elevation contour lines to show the shape of the Earth's surface. |
Topographic Map |
|
|
|
are imaginary lines connecting points having the same elevation on the surface of the land above or below a reference surface |
Elevation Contours |
|
|
|
make it possible to show the height and shape of mountains, the depths of the ocean bottom, and the steepness of slopes |
Contours |
|
|
|
represent the distribution of different types of rock and surficial deposits, as well as locations of geologic structures such as faults and folds |
Geologic Maps |
are the primary source of information for various aspects of land-use planning, including the siting of buildings and transportation systems |
|
|
It is the birds eye view of the earth surface |
Map View |
Also known as top view |
|
|
A geologic cross-section shows geologic features from the side view |
Cross-Sectional View |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: Q |
Quaternary |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: T |
Tertiary |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: K |
Cretaceous |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: J |
Jurassic |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: Tr |
Triassic |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: P |
Permian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: |P |
Pennsylvanian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: M |
Mississippian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: D |
Devonian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: S |
Silurian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: O |
Ordovician |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: -C |
Cambrian |
|
|
|
Geologic Age Symbol: p-C |
Pre-Cambrian |
|
|
|
Youngest to Oldest Geologic Time Period |
Quaternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Pennsylvanian Mississippian Devonian Silurian Ordovician Cambrian Pre-Cambrian |
|
|
|
these folds have the oldest beds in the middle, with beds dipping away from the axis |
Anticlines |
|
|
|
plunge towards the closed end of the V |
Plunging Anticlines |
|
|
|
these folds have the youngest beds in the middle, with beds dipping towards the axis |
Synclines |
|
|
|
plunge towards the open end of the V |
Plunging Synclines |
|
|
|
is a general term for the orientation of a line or plane. |
Attitude |
refers to the three dimensional orientation of a planar and linear features such as bed, a joint, a hornblende needle or a fold. |
|
|
The attitude of planar structure is defined by .. |
Strike and dip |
|
|
|
describe the orientation of a plane in a space. |
Strike and Dip |
|
|
|
is the azimuth direction line formed by the intersection of horizontal plane and the plane of interest. |
Strike |
|
|
|
is the inclination of the plane measured down. |
Dip |
is a vector—gives the direction and the amount of dip of the plane |
|
|
examples of planar structure |
bedding fault fold axial plane layering of lava cleavages schistosity |
|
|
|
The attitude of linear structure is defined by .. |
Trend and plunge |
|
|
|
is the bearing of the line |
Trend |
|
|
|
is the inclination of the line |
Plunge |
|
|
|
The acute angle between the line and strike of the plane on which the line lies. |
Pitch / Rake |
|
|
|
Examples of Linear Structures |
Fold axis hingeline intersection of two planes stretched pebbles other lineations |
|
|
|
In this method the compass dial is divided into four quadrants, namely NE, SE, SW, and NW. |
Quadrant Bearings |
|
|
|
Degrees North and south are at |
0° |
|
|
|
A compass direction of a line measured in degrees (0-360 degrees) clockwise from north |
Azimuth |
|
|
|
Brunton Compass properly known as .. |
Brunton Pocket Transit |
|
|
|
Essential tool for field geologists, environmental engineers, and surveyors |
Brunton Compass |
|
|
|
The compass was made by .. |
Brunton Inc. of Riverton, Wyoming |
|
|
|
The year and patent of compass |
David Brunton, 1987 |
|
|
|
Degrees of a Shallow Dip Angle |
0°-20° |
|
|
|
Degrees of a Moderate Dip Angle |
20°-50° |
|
|
|
Degrees of a Steep Dip Angle |
50°-90° |
|
|
|
Types of Dip |
True Dip Apparent Dip |
|
|
|
is the inclination of a plane measured in a plane that is not perpendicular to the strike |
Apparent Dip |
|
|
|
is the inclination of a plane measured in a plane trending perpendicular to the strike |
True Dip |
|
|
|
This rule is followed by most geologist in the world for consistency |
Right Hand Rule |
The azimuth direction of the strike is recorded such that true dip is inclined to the right of the observer. |
|
|
this method is similar to the method trend and plunge of in determining linear attitude. |
Dip-line Trend and Plunge |
This method relies on the implicit 90 degree angle between true dip azimuth and the strike. |
|
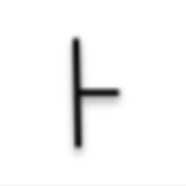
|
Strike and Dip |
|
|

|
Vertical Strata/Bedding |
|
|

|
Horizontal Strata/Bedding |
|
|

|
Anticline Axis |
|
|

|
Syncline Axis |
|
|

|
Plunging Anticlines |
|
|

|
Plunging Synclines |
|
|

|
Strike-Slip Fault |
|
|
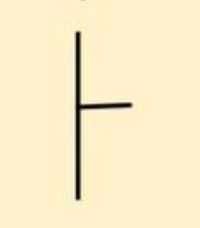
|
Inclined Bedding |
|
|
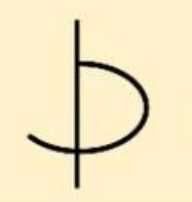
|
Overturned Bedding |
|
|
|
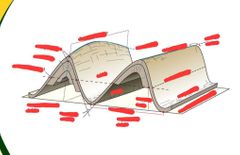
are most effectively displayed on 3D Block diagrams because they display the interpretation of the structure in the subsurface. |
Fold Structures |
|
|
|
a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. |
Fold |
|
|
|
Metamorphic fabrics |
Foliation Cleavage |
|
|
|
points of maximum curvature within a single folded surface. |
Hinge |
|
|
|
a line when moved parallel to itself “sweeps out” a folded surface. |
Axis |
The fold axis and fold hinge line have the same attitude. |
|
|
the plane or surface defined by connecting fold hinge lines in multiple folded surfaces |
Axial Plane/Surface |
|
|
|
the area of a folded surface between hinge points. |
Fold Limbs |
|
|
|
a point on a folded surface where the curvature changes direction. |
Inflection Point |
This is half the distance between hinge points. |
|
|
highest elevation point on a folded surface. |
Crest |
|
|
|
lowest elevation point on a folded surface. |
Trough |
|
|
|
Concave-down folds |
Antiforms |
|
|
|
Concave-up folds |
Synforms |
|
|
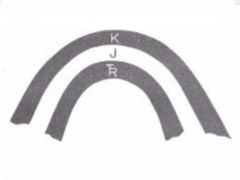
|
Anticline |
Oldest Middle |
|

|
Synformal Anticlines |
Oldest Middle |
|
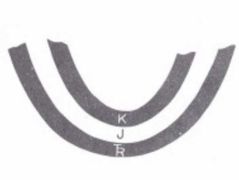
|
Syncline |
Youngest Middle |
|
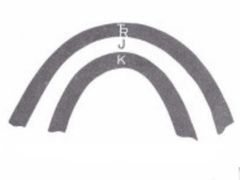
|
Antiformal Syncline |
Youngest Middle |
|
|
Axial Surface Hinge Line Hinge Zone Fold Axis Hinge Points Axial Trace Inflection Point Limb Inflection Line Amplitude Wavelength Non-cylindrical Fold Interlimb Angle Cylindrical Fold |
|
|
|
In the map view a non-plunging fold will have .. .. .. .. |
Straight, parallel, contact lines |
|
|
|
are produced by geologically significant intervals of time marked by uplift and erosion, or by non- deposition. |
Unconformable contacts |
|
|
|
contain oldest strata in the core (center) of the structure |
Domes |
Anticlines |
|
|
contain younger strata in the core of the structure |
Basins |
Synclines |
|
|
have one limb containing overturned strata- otherwise they follow the rules discussed above for anticlines and synclines. |
Overturned folds |
|
|
|
Overturned Synclines |
|
|

|
Overturned Anticlines |
|
|
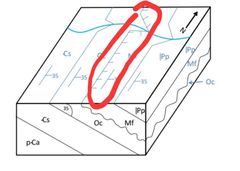
|
Unconformable Contact |
|
|
|
simply defined as an exposure of a solid rock on the surface of the earth. |
Outcrop |
|
|
|
commonly called stereonets, we are just concerned with orientations, alone |
Sterographic projections |
|
|
|
a diagrammatic representation of the earth's surface or part of it, showing the geographical distributions, positions, etc., of natural or artificial features such as roads, towns, relief, rainfall, etc. |
Map |
|
|
|
Should include concise information related to geographic information and theme of the map's content |
Title |
|
|
|
refers to the relationship (or ratio) between distance on a map ang a corresponding distance on the ground |
Scale |
|
|
|
Should include a north arrow and corner coordinates information |
Orientation |
|
|
|
Explanation of symbols used in a map including, colors, lines, icons, and symbols |
Legend |
|
|
|
Selected reference locations or features for orientation |
Reference features |
|
|
|
Authors, publisher, associated publications; complete bibliographic information |
Source information |
|
|
|
What was the base source of geographical information if a map, such as a USGS topographic map or satellite image? What was the map projection? |
Base map information |
|
|
|
What year was the map release? Is the data old or new data? |
Date published |
|
|
|
Is there a publication associated with this map? |
Written text |
|
|
|
preserves the same scale in every direction, locally, thus maintaining the correct shape of the features |
Conformal |
|
|
|
preserves the area throughout, but distorts the shape |
Equal Area |
|
|
|
depicts the correct distance between a point at the center of the projection and points in any direction away from the center |
Equidistant |
|
|
|
Shows true angles or bearings, locally |
Equal angles |
|
|

|
Normal fault |
|
|
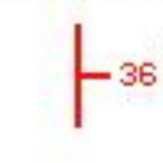
|
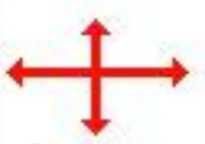
Strike and Dip Inclined Bedding Inclined at an Angle |
|
|
|
Dome |
|
|

|
Basin |
|
|

|
Reverse Fault Thrust Fault |
|
|
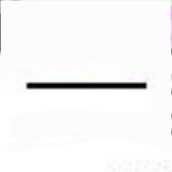
|
Contact Certain |
|
|

|
Contact Inferred |
|
|

|
Contacts Inferred Beneath Sedimentary Cover |
|

