![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
contraindications to surgery
|
absolute: Diabetic Coma, DKA
poor nutrition: albumin <3, transferrin <200, weight loss>20% severe liver failure: bili>2, PT>16, ammonia>150, or encephalopathy smoker: stop smoking 8wks prior to surgery |
|
|
Goldman's Index
|
greatest risks for surgery
1) CHF, then MI w/i 6mo, arrythmia, age>70, emergent surgery, AS |
|
|
meds to stop:
|
aspirin, NSAIDs, vit E (2wks)
warfarin (5d) - drop INR to < 1.5 (can use vitK) take 1/2 morning dose of insulin, if diabetic CKD on dialysis: dialysis 24 hrs pre-op |
|
|
BUN>100
|
increased risk of post op bleeding 2/2 uremic platelet dysfunction -> nl platelets but prolonged bleeding time
|
|
|
vent settings: assist control, pressure support, CPAP, PEEP
|
assist control: set TV and rate but if pt takes a breath, vent gives the volume
pressure support: patient rules rate but a boost of pressure is given (8-20) -> important for weaning CPAP: pt must breathe on own but + pressure given all the time PEEP: pressure given at the end of cycle to keep alveoli open (5-20) |
|
|
non-gap metabolic acidosis
|
diarrhea, diuretic, RTA
|
|
|
metabolic alkalosis - > next step?
|
check urine Cl
if <20, vomiting/NG, antacids, diuretics if >20, Conn's, bartter's, gittelmans |
|
|
sodium abnormalities
|

|
|
|
signs of Ca and K abnormalities
|
decreased Ca: numbness, AMS, prolonged QT interval, Chovstek's sign
increased Ca: stones, bones, psychiatric moans decreased K: paralysis, ileus, U waves (give K, max 40meq/hr) increased K: seizures, cardiac instability, prolonged QRS and PR (CBBIGKDDrop) |
|
|
Fluids and Nutrition
|
maintenance IVFs -> D5 1/2NS + 20KCl
up to 10kg -> 100ml/kg/d next 10kg -> 50ml/kg/d all above 20 -> 20ml/kg/d enteral feeds are best: keeps gut mucosa intact and prevents bacterial translocation TPN: indicated if gut can't absorb nutrients 2/2 physical or functional loss - risks = acalculus cholecystitis, hyperglycemia, liver dysfunction, zinc deficiency, other lyte problems |
|
|
pt coming out of burning house with confusion, headache, and cherry red skin
|
check carboxyhemoglobin (pulse ox is worthless)
treat with 100% O2; hyperbaric if CO-Hb is highly elevated |
|
|
Clotting and bleeding
|

|
|
|
burn w/u and tx
|

|
|
|
electrical burn - 1st step?
|
EKG, if abnl or +LOC, 48hrs of telemetry
|
|
|
burn -> what to check?
|
urine dipstick, if positive, but microscopic exam negative for RBC -> myoglobinuria, ATN
K+ (cells break) compartment syndrome -> criteria = 5Ps or compartment pressure > 30mmHg ---> may require fasciotomy at bedside |
|
|
shock: type, causes, PE, swan ganz, tx
|
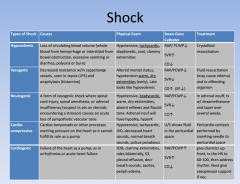
|
|
|
neck trauma according to zones
|
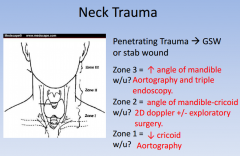
|
|
|
tx for extraperitoneal extravasation
|
best rest + foley
|
|
|
Which ortho trauma fractures go directly to the OR?
|
depressed skull fx
severely displaced or angulated fx any open fx (sticking out bone needs cleaning w/in 6hrs) femoral neck or intertrochanteric fx |
|
|
common fx
shoulder pain s/p seizure or electrical shock arm outwardly rotated & numbness over deltoid old lady FOOSH, distal radius displaced young person FOOSH, anatomic snuff box tender "I swear I punched a wall" clavicle most commonly broken where? |
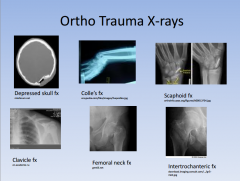
shoulder pain s/p seizure or electrical shock: posterior shoulder dislocation
arm outwardly rotated & numbness over deltoid: anterior shoulder dislocation old lady FOOSH, distal radius displaced: colle's fracture young person FOOSH, anatomic snuff box tender: scaphoid fx "I swear I punched a wall": metacarpal neck fx "boxer's fx". may need K wire clavicle most commonly broken where? between middle and distal 1/3s; needs figure of 8 device |
|
|
ortho tx
posterior shoulder dislocation anterior shoulder dislocation colle's fx scaphoid fx metacarpal neck fx "boxer's fx" may need k wire |
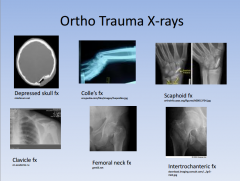
shoulder pain s/p seizure or electrical shock
arm outwardly rotated & numbness over deltoid old lady FOOSH, distal radius displaced young person FOOSH, anatomic snuff box tender "I swear I punched a wall" clavicle most commonly broken where? |
|
|
pressure ulcers caused by what?
|
impaired blood flow -> ischemia
don't cx -> bheck CBC and blood cx can do tissue bx to r/o marjolin's ulcer (ulcerated squamous cell CA) best prevention is turning q2hrs |
|
|
pleural effusions: differentiating between transudative and exudative
|
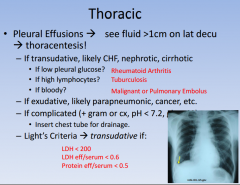
|
|
|
lung abscess
|
usually 2/2 aspiration (drunk, elderly, enteral feesd)
- most often in posterior upper or superior lower lobes - tx initially w/ antibx -> IV PCN or clinda - indications for surgery = abx fail, abscess >6cm, or if empyema present |
|
|
characteristics of benign nodules
|
popcorn calcifications -> hamartoma (most common)
concentric calcifications -> old granuloma age<40, well circumscribed, <3cm CXR and CT q2mo to look for growth |
|
|
characteristics of malignant nodules
|
risk factors (smoker, old), eccentric calcifications, >3cm
remove nodule (with bronch if central, open lung resection if peripheral) |
|
|
ARDS dx
|
bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on CXR
PCWP < 18 (excludes cardiac source) P/F < 200 (P/F < 300 indicates acute lung injury) tx: mechanical ventilation with PEEP |
|
|
more lung findings
|
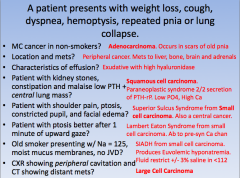
|
|

murmur buzzwords
|

|
|
|
dysphagia with hot/cold liquids and CP feeling like an MI + no regurg
|
esophageal spasm
|
|
|
gastric varices: how to manage hypovolemic shock vs stable
|
stable: treat with nonselective beta blocker (propranolol)
hypovolemic shock: endscopic sclerotherapy or banding, balloon tamponade, octreotide/somatostatin |
|
|
gastric ulcers: w/u and tx
|
w/u: double contrast barium swallow to identify any punched out ulcers, endoscopy with bx to identify H. pylori, benign vs malignant
surgery if lesion persists after 12wks tx |
|
|
gastric CA+ different metastases
|
adeno most common (particularly in Japan)
Krukenberg: ovaries Sister Mary Joseph: umbilical Virchow: L supraclavicular lymphoma MALT-lymphoma (h. pylori) blummer's shelf: mets felt on DRE |
|
|
duodenal ulcers: dx and tx
if ulcer doesn't resolve, then what? |
<45yo can do trial of H2 or PPI
dx: blood, stool or breath test for H. pylori, best test is EGD bc can also evaluate CA H.pylori tx: clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole, PPI if ulcer doesn't resolve, think of zollinger ellison -> secretin stimulation test looking for inappropriately elevated gastrin tx: surgical resection of tumor (if part of MEN1) |
|
|
pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
usually don't have sx until advanced.
if in head of pancreas, coursevoir's sign -> large, nontender gallbadder, itching, jaundice trousseu's sign -> migratory thrombophlebitis |
|
|
Insulinoma: sx + labs
|
sx (sweat, tremor, hunger, seizures), blood glucose < 45, responds to glucagon administration
labs: increase insulin, c-peptide, and pro-insulin |
|
|
Glucagonoma: sx?
|
hyperglycemia, diarrhea, weight loss
characteristic necrolytic migratory erythema |
|
|
VIPoma
|
watery diarrhea, hypoK, dehydration, flushing
looks like carcinoid syndrome octreotide to help sx |
|
|
Somatostatinoma
|
commonly malignant, observe steatorrhea, malabsorption from malfunctioning exocrine pancreas
|
|
|
shock liver labs
|
AST &ALT high s/p hemorrhage, surgery, or sepsis
|
|
|
TIPS
|
relieves portal HTN but worsens hepatic encephalopathy
tx with lactulose to help rid body of ammonia |
|
|
hepatocellular carcinoma risks + dx + tx
|
chronic hep B > hep C. cirrhosis for any reason, plus aflatoxin or carbon tetrachloride
dx with high AFP, CT/MRI tx: surgically remove solitary mass or use rads/cryoablation for palliation of multiple |
|
|
women on OCP with hemorrhagic shock
|
hepatic adenoma -> palpable abd mass or spontaneous rupture
dx with U/S or MRI tx: d/c OCPs; resect if large or pregnancy is desired |
|
|
RUQ pain, profuse sweating and rigors, palpable liver
|
entamoeba histolytica
tx: metronidazole -> don't drain! |
|
|
patient from mexico with RUQ pain and large liver cysts found on U/S
|
echinococcus
transmission: hydatic cyst parasite from dog feces lab findings: eosinophilia, + casoni skin test tx: albendazole and surgery to remove entire cyst rupture -> anaphylaxis |
|
|
vaccine ppx for post-splenectomy pts
|
S.pneumo, H. flu, and N. meningitidis
|
|
|
postop thrombocytosis post-splenectomy >1million
|
give aspirin
|
|
|
ITP
|
consider in isolated thrombocytopenia (bleeding gums, petechiae, nosebleeds)
decreased plt count, increased megakaryocytes in marroww NO splenomegaly tx with steroids 1st. if relapse, splenectomy |
|
|
hereditary spherocytosis
|
see sx of hemolytic anemia (jaundice, elevated indirect bilirubin, LDH, decreased haptoglobin, elevated retic count) + spherocytes on smear and + osmotic fragility test.
prone to gallstones tx with splenectomy (accessory spleen too) |
|
|
# site for carcinoid tumor
|
appendix
sx: diarrhea, wheezing happens when mets to liver (1st pass metabolism) if greater than two cm, at base of appendix, or with positive nodes => hemicolectomy, otherwise just appendectomy |
|
|
post op ileus
|
also consider if hypoK (make sure to replete), opiates
see dilated loops of small bowel with air-fluid levels do surgery for perforation. give lactulose/erythromycin |
|
|
umbilical hernia
|
in kids, close spontaneously by age 2; in adults, 2/2 obesity, ascites or pregnancy
|
|
|
smokers have higher risk for what? Crohns or UC
|
UC!
|
|
|
Crohns and UC tx
|
Crohn's: azathioprine, 6MP, and methotrexate
UC: ASA, sulfasalzine |
|
|
erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum, PSC, migratory polyarthritis
|
Crohn's: erythema nodosum, migratory polyarthritis
UC: pyoderma gangrenosum, PSC, anklosing spondylitis, uveitis |
|
|
diverticular dz
|
false diverticulae (only outpocketings of mucosa)
occur 2/2 low fiber diet in areas of weakness where blood vessels penetrate -> bleed complications are bleeding, obstruction, diverticulosis CT is best imaging to evaluate for abscess. no barium enema (bad if perforated) Tx with NPO, NG suction, IVF, broad spectrum abx, and pain management do colonoscopy 4-6 weeks later (need bleeding to be over) surgery indicated if: multiple episodes, age <50?, elective better than emergency (can do primary anastomosis) |
|
|
UC colonoscopy guidelines
|
needs colonoscopy 8-10yrs after dx
|
|
|
how to measure recurrence in colon cancer?
|
CEA
|
|
|
tx colorectal cancer
|
colon: remove affected segments and chemo if node positive
rectum: upper/middle 1/3 get a LAR (lower anterior resection), lower 1/3 gets an APR -> abdominoperineal resection (remove sphincter, permanent colostomy) |
|
|
AAA screening
|
men 65-75 who have smoked should get an abdominal U/S
if <5cm and asymptomatic, monitor growth surgery indicated if greater than 5cm or growing 4mm/yr |
|
|
AAA postop complications
|
#1 cause of death: MI
bloody diarrhea: ischemic colitis weakness, decreased pain with preserved vibration/proprioception: ASA syndrome 1-2yrs later if have brisk GI bleeding: aortoenteric fistula |
|
|
chronic mesenteric ischemia
|
slow progressing stenosis (required stenosis of 2.5 vessels) -> celiac, SMA and IMA
severe midepigastric (MEG) pain after eating, food fear, and weight loss "pain out of proportion to exam" dx: duplex or angiography tx: aortomesenteric bypass or transaortic mesenteric endarterectomy |
|
|
claudication peripheral artery dz
|
pain in butt, calf, thigh upon exertion
best test: ABI (nl >1) claudication and ulcers: 0.4-0.8 -> use medical mgmt limb ischemia -.2-0.4: surgery indicated gangrene: <0.2 may require amputation |
|
|
acute arterial occlusion: 5Ps -> no dopplerable pulses
|
tx: immediate heparin + prepare for surgery
surgery: (embolectomy or bypass) done w/in 6hrs to avoid loss thrombolytics may be possible if no surgery <2wks, hemorrhagic stroke complications: compartment syndrome during reperfusion period -> do fasciotomy watch for myoglobinuria |
|
|
DVT/PE
|
DVT: tx with heparin, then overlap with warfarin for 5d, then continue warfarin for 3-6mo
PE: if suspected, give heparin first. then w/u with V/Q scan, then spiral CT. pulm angio gold standard tx with heparin warfarin overlap. use thrombolytics if severe but NOT if s/p surgery or hemorrhagic stroke. surgical thrombectomy if life threatening. IVC filter if contraindications to chronic coagulation |
|
|
w/u thyroid nodule
|
picture
|
|
|
w/u adrenal nodule
|
picture
|
|
|
hypoparathyroidism labs
|
decreased calcium, increased phosphate, decreased PTH (phosphate thrashing hormone)
|
|
|
multiple endocrine neoplasias
|
1: diamond -> pituitary, parathyroid, pancreas
2a: square -> parathyroid, pheo 2b: triangle -> medullary thyroid, pheo |
|
|
breast cancer: what to do for DCIS, LCIS, infiltrating ductal/lobular CA, paget's, inflammatory
|
picture
|
|
|
sarcoma?
|
pic
|
|
|
w/u neck mass:
|
rule of 7s: 7 days = inflammatory, 7 mo = cancer, 7 yrs = congenital
MC reactive node so first check teeth, tonsils, etc for inflammatory lesion; if persists > 2wks, FNA! if node if firm, rubbery and B sx present, think lymphoma if midline: thryoglossal duct cyst, move tongue and mass will move -> remove surgically if anterior to SCM: brachial cleft cyst if spongy, diffuse and lateral to SCM, cystic hygroma (think Turners, downs, klinefelters) |
|
|
oral CA tx
|
most frequently squamous cell; in smokers and drinkers
tx with XRT or radical dissection of jaw/neck |
|
|
baby born with respiratory distress, scaphoid abdomen and CXR concerning for diaphragmatic hernia
biggest concern? tx? |
pulmonary hypoplasia
if dx prenatally, plan delivery at place with ECMO. let lungs mature 3-4d, then do surgery |
|
|
baby born with respiratory distress and excessive drooling
|
TE-fistula
best diagnostic test: place feeding tube, take CXR, see it coiled in thorax |
|
|
umbilical hernia a/w what?
|
congenital hypothyroidism (look for big tongue)
repair not needed unless persists past age 2 or 3 |
|
|
2wk old infant with bilious vomiting with pregnancy c/b polyhydramnios
|
intestinal atresia or annular pancreas (i guess malrotation/volvulus too?!)
a/w down syndrome (especially duodenal atresia) |
|
|
3d newborn not passed meconium. DDx?
|
meconium ileus -> consider CF if +FH, gastrograffin enema is dx and tx
hirschprung's -> DRE -> explosion of poo; bx showing no ganglia is gold standard |
|
|
5 day old former premie develops bloody diarrhea
|
necrotizing enterocolitis
XRAY: air in the wall Tx: NPO, TPN, abx and resection of necrotic bowel risk factors: premature gut, introduction of feeds, formula |
|
|
2mo old baby with colicky abd pain and currant jelly stools with sausage shaped mass in RUQ
|
intussusception
- barium enema is dx and tx |
|
|
BPH tx
|
medical: tamsulosin, finasteride
surgical tx: TURP |
|
|
prostate CA tx
|
look at bone scan for blastic lesions
tx with surgery, radiation, leuprolide or flutamide |
|
|
kidney stones guidelines
|
if stone < 5mm, hydrate and let it pass
if stone >5mm, do shock wave lithotripsy surgical removal if >2cm |
|
|
avascular necrosis
|
kids: leg-calve-perthe's dz in 4-5yo with a painless limp and SCFE in 12-13yo with knee pain or sickle cell pts
adults: steroid use, s/p femur fx |
|
|
osteosarcoma
|
seen in distal femur, proximal tibia @metaphysis around the knee
codman's triangle and sunray apperance |
|
|
ewing's sarcoma
|
- seen at diaphysis of long bones, night pain, fever and elevated ESR
- lytic bone lesions, onion skinning - neuroendocrine (small blue) tumor |
|
|
hyperacute, acute, chronic rejection tx
|
picture
|
|
|
lidocaine -> why administer with epinephrine?
|
to prevent systemic absorption -> numb tongue, seizures, hypotension, brady, arrythmias
no epi on the fingers, nose, penis, or toes! |
|
|
General anesthesia: meperidine, succinylcholine, rocuronium, halothane
|
meperidine: can lower seizure threshold esp in pts with renal failure
succ: can cause malignant hyperthermia, hyperK (not for burn or crush victim) rocuronium: sometimes allergic rxn in asthmatics halothane: can cause malignant hyperthermia, liver toxicity |
|
|
epidural (local + opioid)
|
if high block -> blocks heart's SNS nerves and phrenic nerve
|
|
|
spinal-subarachnoid (bupivicaine, etc)
|
for people who can't be intubated. can't give if increased ICP or hypotensive
|

