![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the moment of a force(or torque)? |
The moment of a force(or torque) is the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the pivot to the line of action of the force. |
|
|
State the formula of the moment of a force. |
Moment of a force = F × d(in m) |
|
|
What is the SI unit of the moment of a force? |
The SI unit of the moment of a force is the newton metre (Nm). |
|
|
Why the moment of a force is a vector? |
The moment of a force is a vector as it has both magnitude and direction (clockwise or anticlockwise about the pivot). |
|
|
Why is it easier to open a lid with a spoon than a coin? |
A spoon has a greater torque as compared to a coin. 𝑅⃗ ∙ 𝐹 vector for a spoon is larger than that of a coin. the handle of a spoon is also longer making the 𝑅⃗ vector large, hence the torque is also increased, making it easy to open the lid. A coin is small, round in shape and hence offers minimum torque. |
|
|
State the Principle of moments. |
The principle of moments state that when a body is in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about a pivot is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about the same pivot. |
|
|
Explain an experiment to verify the principle of moments. |
Apparatus: uniform metre rule, various weights W1 and W2, cotton loops, knife edge, retort stand. Procedure: 1)set up the apparatus as shown with the knife edge at the 50 cm. 2)Hang W1= 0.5N and W2=0.4 N on opposite side of the pivot with the cotton loops. 3)Balance the system by adjusting the distances d1 and d2.Record the values of d1 and d2. 4)Repeat the experiment for another three sets of W1 and W2. 5)Record the values of d1 and d2. 6)Calculate the anticlockwise moment(W1×d1) and the clockwise moment(W2×d2). Observations: The clockwise moment is equal to the anticlockwise moment,thus verifying the Principle of Moments. |
|
|
Give 2 conditions that an object must satisfy for equilibrium. |
Conditions that an object must satisfy for equilibrium: 1)All forces acting on it are balanced (I.e resultant force is zero) 2)The resultant moment about the pivot is zero.(I.e the principle of moment must apply). |
|
|
Give 4 examples of levers. |
1)scissors 2) bottle openers 3)the wheelbarrow 4)the arm |
|
|
Why most levers help us to do work more easily? |
Most levers help us to do work more easily as a small effort enables us to lift and move larger loads. |
|
|
Why the metre rule only balances when the pivot is at the 50 cm mark? |
The metre rule only balances when the pivot is at the 50 cm mark because the moment of W about the pivot is zero. This is because the perpendicular distance between the pivot and the line of action of the weight W is zero. |
|
|
What is the centre of gravity of an object? |
Centre of gravity of an object is defined as the point through which its whole weight appears to act on any orientation of the object. |
|
|
How to find the centre of gravity of regular objects? Draw the centre of gravity for : 1.circle, 2.square, 3.rectangle, 4.triangle.
|
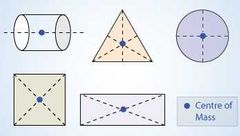
The centre of gravity of regular objects are at their geometrical centre. |
|
|
Explain an experiment to find the centre of gravity of irregular objects?(Apparatus,procedure,precautions) |
Experiment to find the centre of gravity of irregular objects: Apparatus: 1)retort stand,plumb line,cork,pin and a lamina. Procedure: 1)Make 3 small holes near the edge of the lamina.The holes should be as far apart from one another. 2) Suspend the lamina through one of the holes using a pin. 3) Hang a plumb line on the pin in front of the lamina. 4) When the plumb line is steady, draw a line on the lamina over the plumb line. 5)Repeat for the 2 holes. 6) The point of intersection of the 3 lines is the position of the centre of gravity. Precautions: 1)The holes must be small but not too much of the lamina is removed. 2) The lamina should be free to swing about its point of suspension. It will swing about the pin and finally come to a stop. |
|
|
What is stability? |
Stability refers to the ability of an object to return to it's original position after it has been slightly tilted. |
|
|
State the 3 cases of equilibrium. |
3 cases of equilibrium: 1)Stable equilibrium 2)Unstable equilibrium 3)Neutral equilibrium. |
|
|
What is stable equilibrium? |
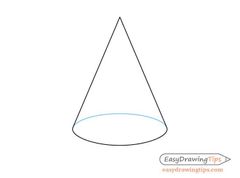
Stable equilibrium refers when an object is tilted slightly,it returns to its original position without toppling. |
|
|
What happens when tilting an object that is in stable equilibrium? (3) |
When tilting an object that is in stable equilibrium; 1)Its centre of gravity rises and then falls back again. 2)The line of action of its weight,W lies inside the object's base area. 3)The anticlockwise moment of its weight W about the point of contact C causes the cone to return to its original position.
|
|
|
What happens when tilting an object that is in the unstable equilibrium? |
When tilting an object that is in unstable equilibrium; 1)Its centre of gravity falls and continues to fall further. 2)The line of action of its weight,W lies outside the object's base area. 3)The clockwise moment of its weight W about the point of contact C causes the cone to topple. |
|
|
What is neutral equilibrium? |
An object is in the neutral equilibrium because if it is slightly displaced or rolled,it will stay in it's new position. |
|
|
What happens to an object that is in the neutral equilibrium? |
When an object is in the neutral equilibrium: 1)Its centre of gravity neither rises or falls ,it remains at the save level above the surface supporting it. 2)The line of action the two forces W and R always coincide. 3)There is no moment provided by its weight W about the point of contact C to turn the object. |
|
|
State 2 ways how to increase the stability of an object. |
to increase the stability of an object: 1)Its centre of gravity should be low as possible 2)the area of its base is as wide as possible. |
|
|
Why are cars made more stable? |
The more stable a car, the faster it can go. |
|
|
What is unstable equilibrium? |
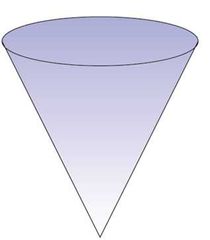
When an object is tilted slightly, it topples over. |

