![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bacteruiria
|
Bacteria in urinalysis
|
|
|
Pyuria
|
White blood cells in urinarlysis from anywhere
|
|
|
"Significant" bacteriuria
|
More than 10^3 colony count in urine culture
>10^5 is documented true UTI Multiple organisms = false + contaminated specimen Lots of squamous cells = contamination |
|
|
Dysuria
|
Discomfort when voiding, burning
|
|
|
Lower urinary tract infection
|
Does not involve pelvis
|
|
|
Urethritis
|
Just urethra involved
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis
|
Infection in the medulla
|
|
|
Acute urethral syndrome
|
Burning, frequency, irriatation when voiding, all inflammatory response restricted to urethra
|
|
|
What is the leading cause of dysuria?
2nd most common? 3rd most? Causes of acute urethral syndrome? |
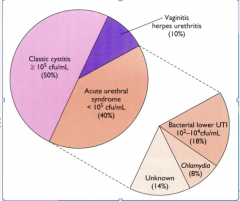
Cystitis = inflamed bladder, organisms adhering to wall causing inflammation
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of bacterial infections? Where do most come from? Which one is the most common? 2 other common ones?
|
Causative Bacteria
95% from G.I. tract E. coli – most common Staph. saprophyticus Other “niche” organisms |
|
|
What are age and sex differences in UTIs?
Infants? Years 3-50? What is seen in elderly (>65 yrs old) |
Infants: males > females
Years 3-50: females >>>males Elders (>65 years old) Increased Bacteriuria Multiple factors |
|
|
Is there an increase in UTIs in pregnancy?
Sex? |
Pregnancy
Bacteriuria in 4-10% Twice the expected rate 25% progression Sex is a risk factor for UTI. |
|
|
Which contraceptives show the highest incidence of bacteruria? Lowest bacteruria?
|
Highest = diaphragm-spermicide user
Lowest = oral contraceptive |
|
|
What are the two types of route of infection? Majority?
What can cause ascending route infection? Who might get hematogenous infections? Where will bacterial be? |
Route of Infection
Ascending route 95+% Urethral trauma Intercourse Instrumentation Diaphragm use Hematogenous route <5% = endocarditis or central lines, renal cortex localization |
|
|
By what mechanisms do UTIs occur?
|
Adhesion
Colonization Invasion Phase variation |
|
|
What are bacterial factors?
What are two types of adhesions on fimbriae? |
Bacterial factors:
Uropathogenic E. coli Virulence factors Adhesions on fimbriae Type I fimbriae P- fimbriae |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of bacteria/host cell interactions?
|
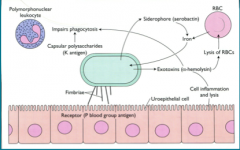
|
|
|
What are some host defense mechanisms to UTIs?
|
Bacterial growth inhibition
Urine flow Epithelial cell turnover Antibodies |
|
|
What are some predisposing host factors?
|
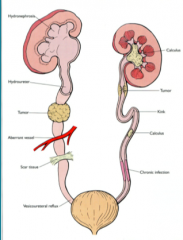
Urine flow obstruction
Female factors Abnormal urine flow Urethral trauma Vesiculo-ureteral reflux Instrumentation General health |
|
|
What are some clinical manifestations of lower urinary tract infections?
|
Frequency of urination
Dysuria - painful urination Turbid urine Suprapubic discomfort Hematuria Asymptomatic cystitis |
|
|
What are clinical manifestations of upper tract infections?
|
Fever
Chills Flank pain and “CVAT” Asymptomatic pyelonephritis |
|
|
How do you diagnose UTI?
|
Microscopic urinalysis
Gram stain of urine Urine culture Blood cultures (PRN) Screening tests |
|
|
What are some complications of UTI?
|
Gram negative sepsis
Intrarenal or extrarenal abscess Chronic renal insufficiency Struvite renal calculi Recurrent infection |
|
|
How do you prevent UTIs?
|
Proper use of urinary catheterization
Correction of anatomic abnormalities Prophylactic antibiotics - RARELY |
|
|
How long does it take to treat a lower tract infection? Males and females?
When can it take longer? |
Males: 1 week
Females: 1-3 days Longer if complicated UTI |
|
|
How long does it take to treat an upper tract infection?
How do you treat it? |
1-6 weeks
IV vs oral thearpy |
|
|
How do you treat asymptomatic bacteriuria?
|
Not treated in elderly (and others)
|
|
|
What seems to have the best efficacy for uncomplicated UTIs?
Complicated? |
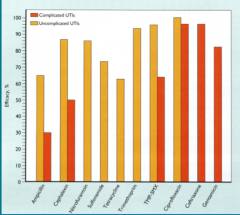
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone |
|
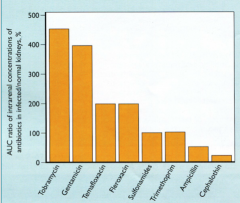
What is this?
|
Wall didn't know either.
Possibly aminoglycosides at the far left has the highest level of intrarenal concentration --> proximal tubule interstitial damage |

