![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Menetrier's disease
|
Gastric hypertrophy with protein loss, parietal cell atrophy, and increase in mucus cells.
Precancerous Rugae of stomach are so hypertrophied that they look like brain gyri |
|
|
Meinier's dz
|
disorder of the inner ear that can affect hearing and balance to a varying degree.
Tinnitus ON AND OFF (as opposed to schwannoma) "Think of Reinier getting dizzy after drinking too much" |
|
|
Friedreich ataxia sx are mimicked by what deficiency?
|
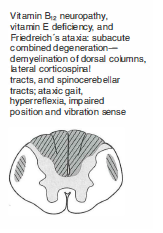
Vit B12 or Vit E
|
|
|
Anticholinergic sx
|
"Blind as a bat, mad as a hatter, red as a beet, hot as a hare, dry as a bone, the bowel and bladder lose their tone, and the heart runs alone."
|
|
|
stones, bones, abdominal groans, and psychiatric moans
|
primary hyperPTH
"Stones" refers to kidney stones, nephrocalcinosis, and diabetes insipidus (polyuria and polydipsia). These can ultimately lead to renal failure. "Bones" refers to bone-related complications. The classic bone disease in hyperparathyroidism is osteitis fibrosa cystica, which results in pain and sometimes pathological fractures. Other bone diseases associated with hyperparathyroidism are osteoporosis, osteomalacia, and arthritis. "Abdominal groans" refers to gastrointestinal symptoms of constipation, indigestion, nausea and vomiting. Hypercalcemia can lead to peptic ulcers and acute pancreatitis. The peptic ulcers can be an effect of increased gastric acid secretion by hypercalcemia,[4] but may also be part of a multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome of both hyperparathyroid neoplasia and a gastrinoma. "Psychiatric moans" refers to effects on the central nervous system. Symptoms include lethargy, fatigue, depression, memory loss, psychosis, ataxia, delirium, and coma. |
|
|
Elevated hCG is observed in what pathologic states?
|
hydatiform moles, choriocarcinoma, gestational trophoblastic tumors
|
|
|
Causes of increased AFP
|
"Increased Maternal Serum Alpha Feto Protein":
Intestinal obstruction Multiple gestation/ Miscalculation of gestational age/ Myeloschisis Spina bifida cystica Anencephaly/ Abdominal wall defect/Ataxia telangiectasia Fetal death Placental abruption Hepatocellular carcinoma non-seminoma germ cell tumor |
|
|
Causes of decreased AFP
|
Trisomy 21, Edwards (trisomy 18)
|
|
|
Branchial arch derivatives
|
When at the restaurant of the golden ARCHES, children tend to first CHEW (1), then SMILE (2), then SWALLOW STYLISHLY (3), or SIMPLY SWALLOW (4), and then SPEAK (6)
see pg 136 |
|
|
encapsulated bacteria
|

|
|
|
target cell associated pathology
|
HALT, said the hunter to its target
HbC, asplenia, liver disease, thalassemia |
|
|
Heinz bodies associated pathology
|
G6PD AND alpha thal
|
|
|
Howell-Jones bodies
|
basophilic nuclear remnants found in RBCs
seen in patients with functional hyposplenia or asplenia |
|
|
alternative to heparin in HIT
|
lepirudin, bivalirudin; directly inhibits thrombin
|
|
|
myelosuppression with MTX is reversible with what?
What about 5-FU myelosuppression? |
leucovorin
thymidine |
|
|
Antimetabolites and function
what phase do they work in? |
MTX, 5-FU, 6-MP, 6-TG, Cytarabine
S phase |
|
|
Which drug is used in child cancer?
|
Dactinomycin
|
|
|
distinguish multiple myeloma from waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
|
M spike = IgM (hyperviscosity sx); no lytic bone lesions
|
|
|
lipid lowering agents MOA
|
pic
|
|
|
Sx of TTP
|
"Follow Me To Real Nirvana"
fever, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal and neurologic problems (hint: predominant neuro problems=TTP; whereas predominant renal problems = HUS) |
|
|
carcinoma vs sarcoma
|
carcinoma: cancer of epithelial cell origin
sarcoma: mesenchymal cell origin |
|
|
schistocytes suggest what findings?
|
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (TTP, HUS, DIC, SLE, malignant hypertension) or mechanical damage (eg prosthetic valve)
|
|
|
CYP450 inducers and inhibitors
|
see pic
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis steps
|
see pic
|
|
|
HIV structure
|
see pic
|

