![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
32 year-old female
Abnormal uterine bleeding Endometrial hyperplasia Adnexal mass Diagnosis Pathophys |
Endometrial hyperplasia due to hyperestrogenemic state
Ovarian neoplasm likely cause--GRANULOSA CELL TUMOR |
|
|
Estrogen-secreting ovarian tumor
|
Granulosa cell tumor
|
|
|
Mucin-secreting ovarian tumor
|
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Thyroid hormone-secreting ovarian tumor
|
Teratoma (dermoid cyst)
|
|
|
CD marker for neutrophils
|
CD15
|
|
|
CD marker for NKCs
|
CD16
|
|
|
What equation can predict probability of having a disease for a given test?
|
PPV = TP/(TP+FP)
|
|
|
Swelling
Pain Morning stiffness in multiple joints |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Acute vs Chronic relief of symptoms (treatment) |
Acute: Prednisone (only given for a short time bc of side effects)
Chronic: MTX (takes weeks to achieve effect) |
|
|
Graft Rejection:
Acute vs Chronic histologic findings |
Acute: cell-mediated process; expect to see mononuclear lymphocytic infiltrate with cardiac myocyte damage
Chronic: Scant inflammatory cells and interstitial fibrosis; mediated by T and B cells as well as Ab's; occurs months to years post-transplantation |
|
|
56 year-old female
Vertebral compression fracture |
Osteoporosis
|
|
|
What is the effect of estrogen on thyroid function?
|
Estrogen increases thyroid binding globulin (TBG) levels (because slows catabolism of TBG)
Inc'd TBG-->inc'd T4 and total T3 However, level of free thyroid hormones remains normal, so pts are euthyroid |
|
|
Patient receives several units of packed RBCs
Complains of tingling in toes and fingers Pathophys |
Packed RBCs mixed with citrate anticoagulant
Infused citrate can chelate serum calcium, cause hypocalcemia, and subsequently result in parasthesias. Note: Citrate can also chelate magnesium. |
|
|
Which diuretics are potassium sparing?
|
Sprinolactone
Amiloride Thiazide |
|
|
Label and list drugs by site of action.
|
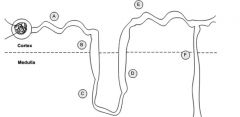
A) Proximal Convoluted Tubule--Acetazolamide (Carbonic anyhydrase inhibitor)
B) Blank C) Descending limb of LOH (no drugs act here) D) Thick ascending LOH--LOOP diuretics act here (furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid) E) Distal Convoluted Tubule--Thiazides work here (beware of hypokalemia)--HCTZ, furosemide F) Collecting duct--K+-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, amiloride, triamterene) |
|
|
Draw and label arteries of arm and forearm.
|
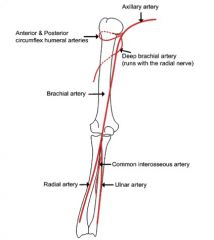
|
|
|
This artery runs with the radial nerve.
|
Deep brachial artery
|
|
|
What is the specific effect of statins on hepatic cholesterol synthesis?
|
Statins inhibit HMG CoA reductase and thus decrease cholesterol synthesis.
|
|
|
What reaction does HMG CoA reductase catalyze?
|
HMG CoA-->Mevalonic acid
|
|
|
What is the effect of bile acid-binding resins on hepatic cholesterol synthesis?
|
Bile acid-binding resins bind bile acids in GI tract, interfere with their reuptake, and result in excretion.
This results in hepatic synthesis of new bile acids (consumes liver cholesterol stores). This in turn results in increased hepatic cholesterol synthesis. This can be blocked with the addition of a statin drug. |
|
|
What agents increase hepatic cholesterol synthesis?
|
Fibrates
Bile-acid binding agents |
|
|
Initial jerking resistance to passive extension followed by sudden release of resistance.
Pathophys |
Upper MN lesion to one of many areas:
-Corticospinal tracts of SC -Medulla pons, midbrain -Internal capsule -Precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex) |
|
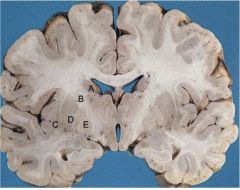
Label
|
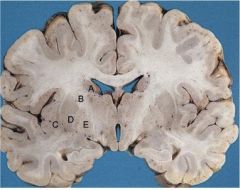
A) Caudate nucleus (affected by HD)
B) Internal capsule (lesion here and results in Upper MN lesion-->spastic paresis, hyperreflexia, positive Babinski) C) Insular Cortex (limbic system--emotion) D) Putamen E) Globus Pallidus |
|
|
Difficulty releasing doorknob
Cataracts Frontal baldness Gonadal atrophy Diagnosis Pathophys |
Myotonic dystrophy
Inherited AD trait Abnormal CTG expansion (undergoes anticipation) on myotonia-protein kinase gene Affects Type 1 fibers |
|
|
Molecular effects of natriuretic peptides.
|
Activate guanylate cyclase-->inc'd intracell cGMP
-->Vasodilation, diuresis, natriuresis, dec'd BP |
|
|
Effects of endothelin.
|
Vasoconstriction (increase afterload)
|
|
|
What is the effect of saline administration in a hypovolemic patient?
|
IV saline increases intravascular volume.
This increases preload-->inc'd ventricular myocardial sarcomere length-->inc'd stroke volume and cardiac output |
|
|
Effect of fluid resuscitation in hypovolemic patient on:
-Pulse Why? |
Pulse will decrease
In hypovolemia patient, sympathetic system is active-->inc'd total peripheral resistance and contraction velocity Fluids will reduce sympathetic activation and decrease total peripheral resistance and pulse |
|
|
14 year-old
Irregular menses lasting 7 to 10 days Pathophys |
In first five to seven years after menarche and last 10 years before menopause, menstrual cycle variability is common.
Anovulation is the cause. |
|
|
21 year-old
Unprovoked syncope Congenital QT prolongation Diagnosis Pathophys |
Romano-Ward syndrome (no neurosensory deafness)
Lange-Nielsen (neurosensory deafness) Due to mutation in K+ channel protein that contributes to delayed rectifier current of cardiac action potential Both predispose to Torsades de Pointes |
|
|
Severe dyspnea
PaO2 = 62 mmHg PAO2 = 71 mmHg Causes |
Normal PAO2 (alveoli) = 104 mmHg
Incoming PaO2 (venous) = 40 Should exit around 104 Since A-a = 71-62 = 9, there's no abnormal A-a gradient (should be 10-15) Liekly due to hypoventilation (suppressed respiratory drive, as in sedative OD, sleep apnea) or pts with dec'd inspiratory capacity (obesity, myasthenia gravis) |
|
|
Causes of acute otitis media
|
Step pneumo
H flu |
|
|
3-year old male
Otitis media with H. influenzae Immunizations up-to-date Pathophys |
Nontypable H. flu infection
Vaccine only confers immunity to H flu type B (with polysaccharide capsule) This nontypable must not have a capsule |
|
|
Molecular effect of:
Growing E. coli in lactose-rich environment Growing E. coli in lactose and glucose-rich environment |
In lactose-rich environment, lactose binds repressor protein-->conformational change-->releases lac operator-->uses lactose for energy
Glucose-containing media (with or without lactose)-->Glucose decreases adenylyl cyclase activity-->dec'd intracell cAMP -->dec'd expression of catabolite activator protein (CAP) CAP normally binds cAMP-->cAMP-CAP complex binds lac-operon and positively regulates it But without cAMP, there is no positive regulation of lac operon, so glucose is used for energy. |
|
|
Where is norepinephrine produced?
|
Peripheral and central NS
|
|
|
Where is epinephrine produced?
|
Mostly in adrenals
|
|
|
Describe the production of epinephrine.
|
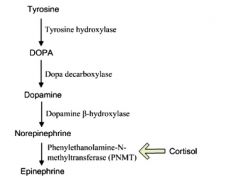
|
|
|
24 year-old male
Chronic headaches, visual changes Calcified mass on MRI Diagnosis Pathophys/Pathologic Findings |
Craniopharyngioma
Derived from remnants of Rathke's pouch (ectoderm)-->forms cyst filled with yellow, viscous fluid rich in cholesterol crystals |
|
|
34 year-old woman
Acute sinusitis 1 week ago Vulvar pruritis Vaginal discharge Diagnosis Pathophys |
Rhinitis/sinusitis probably resulted in Abx use-->suppression of normal bacterial vaginal flora--->Candida overgrowth
|
|
|
What bacteria comprise normal vaginal flora?
|
Gram positive lactobacilli
Corynebacterium Candida Group B Strep E coli |
|
|
What is reaction formation?
|
When person does opposite of what he/she feels or desires, ex: homosexual having a number of heterosexual affairs and publicly criticizing homosexuals in order to relieve inward anxiety about his/her homosexual desires
|
|
|
What is repression?
|
Unconscious removal of disturbing psychologic material from conscious awareness
Ex: adult who was abused as child lacking awareness of abuse until he/she sees movie featuring child abuse |
|
|
What is suppression?
|
Voluntary withholding of unpleasant thoughts or feelings from one's mind.
Ex: Student choosing not to worry about upcoming examination. |
|
|
What is displacement?
|
Transfer of impulse or desire toward safer and less distressful object
Ex: husband yelling at dog after argument with his wife |
|
|
In DNA replication, one strand is constructed 5'-->3' while the other in 3'-->5', although DNA polymerization occurs only in the 5'-->3' direction.
What is the main difference in synthesis of these two strands? |
Lagging strand (synthesized 3'-->5') synthesized discontinously and is composed of short stretches of RNA primer plus newly synthesized DNA segments called Okazaki fragments.
THUS, lagging strand requires repetitive action of DNA PRIMASE and DNA LIGASE. |
|
|
Blotchy red muscle fibers on Gomori trichome stain
|
AKA RAGGED RED FIBERS
Mitochondrial myopathy (maternal inheritance only!) Can't get from dad! |
|
|
Ragged red fibers
|
Mitochondrial myopathy
|
|
|
45 year-old man
States people are trying to harm him Wife denies threats or enduring harm Maintains a job Diagnosis Reasoning |
Delusional disorder, not schizophrenia paranoid type.
Delusional disorder exhibits non-bizarre delusions (delusions may be situations that are unlikely, but possible) Patient with schizophrenia would have bizarre delusions (such as covert alien activity), and wouldn't be able to maintain a marriage or a job |
|
|
56 year-old female
Begins treatment for severe joint pain, swelling Later reports cough, hemoptysis Sputum reveals acid-fast bacilli Pathophys |
Patient likely treated with TNF-alpha inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis (TNF-alpha inhibitors include infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab)
These drugs decrease macrophage function and may cause reactivation of latent tuberculosis |
|
|
beta-1 receptor:
Effects |
Inc'd cardiac output
Inc'd renin release |
|
|
Which region of the cochlea responds to high frequency sounds?
|
Cochlear base (neareast the oval/round windows)
|
|
|
Which region of the cochlea responds to low frequency sounds?
|
Helicotrema (furthest from oval/round windows)
|
|
|
8 year-old male from Asia
Throat pain, difficulty breathing Dies of heart failure Diagnosis Pathophys |
Corynebacterium diphtheria-->spread by respiratory droplets
-->AB exotoxin: B binds, A is active Since patient is from outside the US, never received immunization, and lacked IgG against exotoxin B subunit A exotoxin then penetrated cells, inhibiting ribosome function and resulting in neural/cardiac toxicity |
|
|
Describe the histologic changes in respiratory tract lining as it progresses distally.
|
Bronchi: pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium, goblet cells, submucosal mucoserous glands, cartilage
Bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles lack goblet cells, glands, cartilage Terminal bronchioles: ciliated simple cuboidal Epithelial cilia persist up to end of respiratory bronchioles |
|
|
Cyanotic newborn
Apical displacement of tricuspid leaflets Atrialization of right ventricle Diagnosis Pathophys |
Ebstein's anomaly due to maternal ingestion of lithium (anti-manic medication) while pregnant
|
|
|
Branching hyphae
Round/cigar-shaped budding yeasts Fungus Epidemiology |
Sporothrix; assocd w/gardening (thorn prick)
|
|
|
Hyphae with doubly reflective wall
Forms spherules filled with endospores Fungus Epidemiology |
Coccidoides; Southwestern states (desert)
|
|
|
Branching hyphae
Oval yeast cells within macrophages Fungus Epidemiology |
Histoplasma
Ohio/Mississippi River valleys Bird, bad droppings (chicken coops, caves) |
|
|
Branching hyphae
Large, round yeasts with single bud Fungus Epidemiology |
Blastomyces
Ohio/Mississippi River valleys |
|
|
Multiple blastoconidia
Cells covered in budding blastoconidia Fungus Epidemiology |
Paracoccidoides
Central/South America |
|
|
This fungus forms a lung granuloma with calcifications.
|
histoplasma (looks similar to Tb!)
|
|
|
Scaly, erythematous lesions on sun-exposed skin
Diagnosis Risks |
Actinic keratoses (hperplasia of stratum corneum)
Small percent advance to invasic squamous cell carcinoma |
|
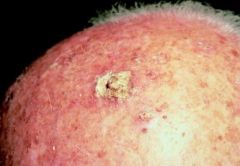
|
Actinic Keratoses (may advance to invasive squamous cell carinoma)
|
|
|
60 year-old woman
Diarrhea with mucoid material Cauliflower-like mass in sigmoid colon Hypokalemia Diagnosis Pathophys |
Villous adenoma (dysplastic epithelial cells form villi-like projections that extend from villous); tend to be large
Secretes large amounts of mucus-->secretory diarrhea If stool volume is large, diarrhea may cause hypovolemia and electrolyte imblanaces May also cause occult blood in stool |
|
|
Draw and label nerves of arm and forearm.
|
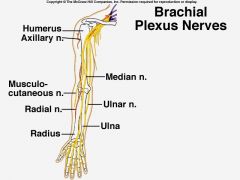
|
|
|
Draw the regions of the stomach.
Label where chief and parietal cells are located. What are their secretions? What region is colonized by H. pylori? What region is affected by penicious anemia? |
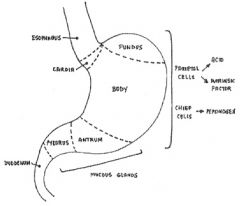
Antrum ("prepylorus") colonized by H pylori
Body affected by pernicious anemia |
|
|
How does M. tuberculosis result in tissue destruction?
|
Caseous necrosis-->
Delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction activates Th1 cells-->activates macs and CD8's Macs form Langhans giant cells, activate fibroblasts |
|
|
72 year-old female
Chronic renal insufficiency Takes diuretic Receives gentamicin for UTI Goes deaf Pathophys |
Patients with chronic renal insufficiency need high doses of diuretics to achieve maximal effect
Loop diuretics: furosemide, torsemide, bumetanide, ethacrynic acid can cause hypokalemia, hypo-Mg, hypo-Ca2+, and ototoxicity Ototoxicity exacerbated with gentamicin |
|
|
How does the 3' end of tRNA differ form the 5' end?
|
3' end = CCA (hydroxy terminal) which binds amino acids
5' end has a terminal phosphate residue |
|
|
What are causes of macrocytosis (RBCs)?
|
Folate deficiency
B12 deficiency CHRONIC EtOH |
|
|
What are the two most common causes of acute pancreatitis?
|
Alcohol abuse (will present with macrocytosis, elevated GGT)
Gallstones |

