![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw beta-alanine?
|
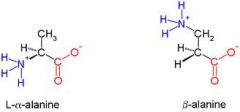
|
|
|
Beta-peptides cannot be degraded by ____________?
|
mammilian peptidases
|
|
|
What is a peptidase?
|
A protease (also termed peptidase or proteinase) is any enzyme that conducts proteolysis, that is, begins protein catabolism by hydrolysis of the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in the polypeptide chain forming the protein.
|
|
|
In protein concentration determination by UV/vis T is ________ and I is _________?
|
transmittance, intensity of light
|
|
|
T=
|
I
---- Io |
|
|
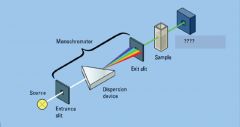
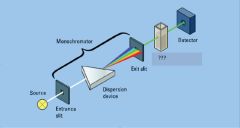
entrance slit, exit slit
|
|
|
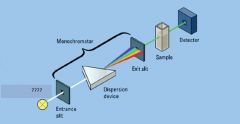
Light Detector
|
|
|
light source
|
|
|
sample in cuvette
|
|
|
What is the normal pathlength on a standard cuvette?
|
1cm
|
|

A = ?????
|
solute's absorbance
|
|

Io = ???????
|
intensity of the incident light at a given wavelength
|
|

I = ???????
|
intensity of the light after passing through the solute at a give wavelength
|
|

ɛ =
|
extinction coefficient
(varies with wavelength) |
|

c = ?????
|
solute concentration
|
|
|
Polypeptides absorb in the UV spectrum wavelength of__________ nm and do not absorb visible light which has a wavelength of ________nm?
|
200-400 , 400-800
|
|
|
What part of a polypeptide absorbs UV light at 214nm?
|
peptide bond
|
|
|
What part of a polypeptide absorbs UV light at 254nm?
|
Phe
|
|
|
What part of a polypeptide absorbs UV light at 278nm?
|
Trp
|
|
|
What part of a polypeptide absorbs UV light at 280nm?
|
Tyr
disulfide bonds absorb a little at 280nm also |
|
|
What is the extinction coefficent of Trp at 278nm?
|
5500 M-1 cm-1
|
|
|
What is the extinction coefficent of Tyr at 280nm?
|
1490 M-1 cm-1
|
|
|
For a protein at absorbance 280nm what is the formula for the extinction coefficient?
|
ɛ = (# of Trp residues X 5500) + (# of Tyr residues X 1490)
|
|
|
1. salting in
2. salting out |
|
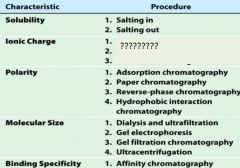
|
1. ion exchange chromatography
2. electrophoresis 3. isoelectric focusing |
|
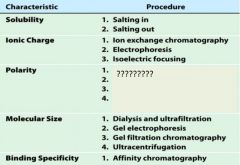
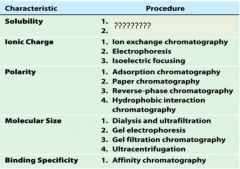
|
1. adsorption chromatography
2. paper chromatography 3. reverse-phase chromatography 4. hydrophobic interaction chromatography |
|
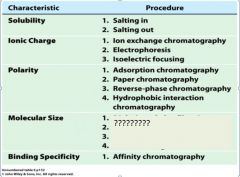
|
1. dialysis and ultrfiltration
2. gel electrophoresis 3. gel filtration or size exclusion chromatography 4. ultracentrifugation |
|
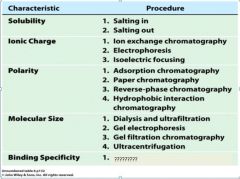
|
1. affinity chromatography
|
|
|
In the procedure of salting in, protein __________ at low ionic onentrations _________ as salt is added.
|
solubility, increases
|
|
|
What happens in the salting in procedure?
|
The additional ions shield the protein's multiple charges and prevent aggregation.
|
|
|
What is a common salt for salting out?
|
NH4SO4
ammonium sulfate |
|
|
How does the salting out procedure work?
|

|
|
|
Protein solubility depends on __________, __________, and ___________?
|
concentration of dissolved salts
pH temperature |
|
|
What pH buffer would you use to salt out your protein?
|
pH close to the pI
|
|
|
What are the two phases of chromatography?
|
mobile and stationary
|
|
|
Define ion exchange chromatography?
|
ions that are electrostatically bound to the insoluble and cheically inert matrix are reversibly replaced by ions in the solution
|
|
|
What type gradient would you use to elute off of an ion exchange column?
|
NaCl or salt
|
|
|
What type of ions can be purified with an anion exchange column?
|
anions
|
|
|
What type of ions can be purified with an cation exchange column?
|
cations
|
|
|
What is another name for gel filtration chromatography?
|
size exclusion chromatography
|
|
|
What is the most common substance used in an ion exchange column?
|
cellulose
|
|
|
Would a larger or smaller protein elute first on a size exclusion column?
|
larger
|
|
|
What range is an absorbance measurement reliable?
|
.2-1
|
|
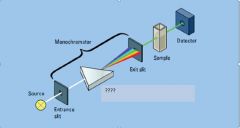
|
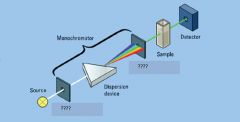
dispersion device
|
|
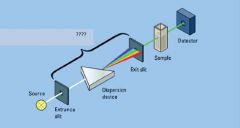
|
monochromator
|
|
|
Draw D-ribose?
|
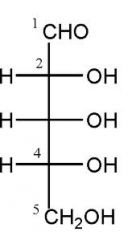
|
|
|
Draw D and L mannose?
|
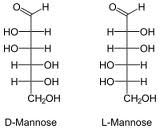
|
|
|
Draw D and L fructose?
|
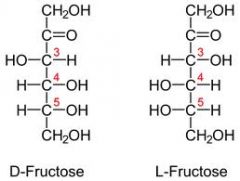
|
|
|
What are the three letter abbreviations for glucose, galactose, mannose, and fructose?
|
Glc, Gal, Man, Fru
|
|
|
What is the anomeric carbon?
|
The carbonyl carbon from the straight chain, now in cyclic form
|
|
|
What is the general form for a carbohydrate?
|
(C*H20)n
|
|
|
What is the photosynthesis reaction?
|
6CO2 + 6H2O >> C6H12O6 + 602
|
|
|
What is the most important function of carbohydrates?
|
source of energy
|
|
|
What are some other functions of carbohydrates besides energy source?
|
biochemical intermediates
associated with other entities - glycosides, vitamins and antibiotics form structural tissues in plants and microorganisms participate in biological transport |
|
|
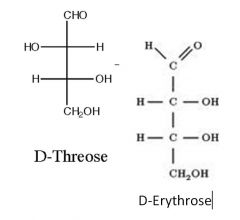
What is an epimer?
|
A molecule with one change to one stereocenter
|
|
|
What is an anomer?
|
Where the hydroxyl position changes on the anomeric carbon
|
|
|
Define the alpha anomer?
|
anomeric hydroxyl group trans to the terminal -CH2OH
|
|
|
Define the beta anomer?
|
anomeric hydroxyl group cis to the terminal -CH2OH
|
|
|
When drawing the cyclic form of L sugars which direction does the terminal - CH2OH go?
|
down
|
|
|
When drawing the cyclic form of D sugars which direction does the terminal - CH2OH go?
|
up
|
|
|
Define mutarotation?
|
Mutarotation is the change in the optical rotation that occurs by epimerization (that is the change in the equilibrium between two epimers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert). Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert
|
|
|
Draw a cyclic chair and label axial and equatorial positions?
|
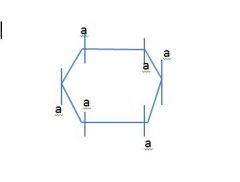
don't listen to tom
|
|
|
Draw a 6 member ring and label the axial and equatorial positions?
|
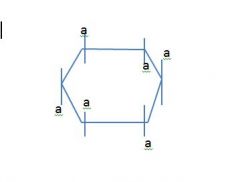
this slide is backwards fuck m,e
|
|
|
Draw Beta-D-2-Deoxyribopentose?
|
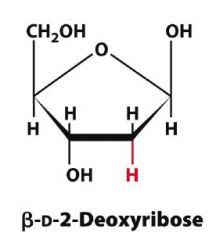
|
|
|
Draw alpha-6-deoxy-L-mannopyranose?
|
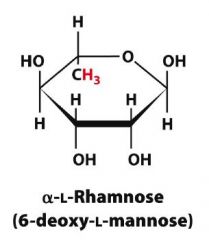
|
|

Draw?
|
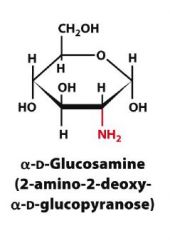
|
|
|
Take D-Glc and make D-Fru?
|
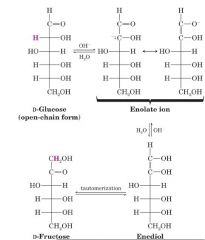
|
|
|
Take D-Glc and make D-Man?
|
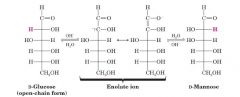
|
|
|
Take D-Glc and make D-Man?
|
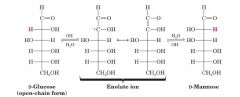
|
|
|
Name the two reducing agents used in class?
|
NaBH4, and H2,Ni
|
|
|
Draw D-glucitol and give another name for this molecule?
|
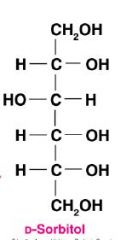
|
|
|
Draw D-Ribitol?
|
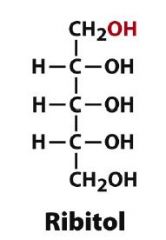
|
|
|
Draw D-glycerol?
|
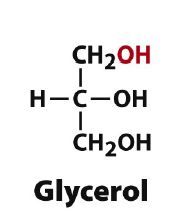
|
|
|
What is used to create an aldonic acid from a sugar?
|
Br2 and H2O
|
|
|
What is used to create an aldaric acid from a sugar?
|
HNO3
|
|
|
What is an aldonic acid?
|
when the aldehyde group of an aldose becomes oxidized to a carboxylic acid
|
|
|
What is an aldaric acid?
|
when the aldehyde and terminal CH2OH become oxidized to carboxylic acids
|
|
|
What is the general form for aldonic acid?
|
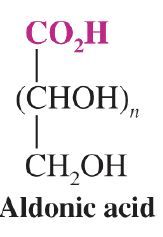
|
|
|
Turn D-Glc into D-Gluconic acid? What are the reagents?
|
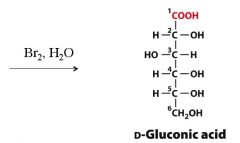
|
|
|
What is the general form of an aldaric acid?
|
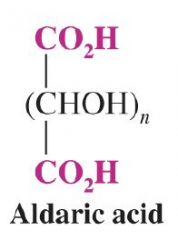
|
|
|
Turn D-Glc into D-glucaric acid? what are the reagent(s)?
|
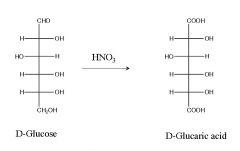
|
|
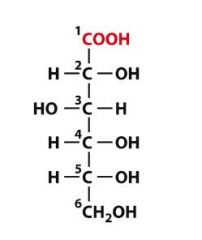
What is this molecule?
|
D-gluconic acid
|
|
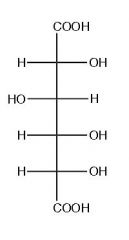
What is this molecule?
|
D-glucaric acid
|
|
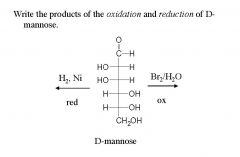
and name them?
|
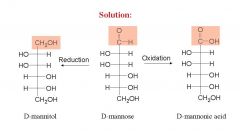
|
|
|
What defines a reducing sugar?
|
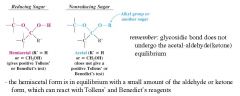
an OH group on the anomeric carbon
|
|
|
Name the three reagents used to test for reducing sugars?
|
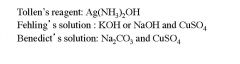
|
|
|
Tests for simple reducing sugars cannot distinguish between ________ and ________?
|
aldoses, ketoses
|
|
|
Define a Kiliani-Fisher synthesis?
|
> reaction of an aldose with HCN
> used to increase the chain length of monosaccharides > results in a cyanohydrin which is then hydrolyzed to an acid and reduced to the aldehyde > can prepare all monosaccharides from D-glyceraldehyde |
|
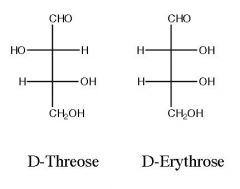
Draw and name the product)s)?
|
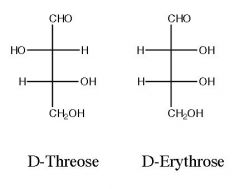
|
|
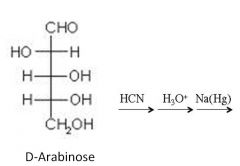
Draw and name the product(s)?
|
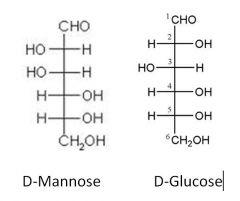
|
|
|
Define what happens in a Ruff degradation?
|
It shortens the chain of an aldose by removing the aldehyde carbon at the top of the Fischer projection
|
|
|
What are the reagent(s) for a Ruff degradation?
|
1) Br2, H2O
2) H2O2, Fe2(SO4)3 |
|
|
What is the by-product of Ruff degradation?
|
CO2
|
|

Fill in the blanks.
|
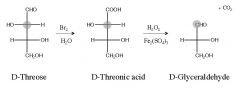
|
|
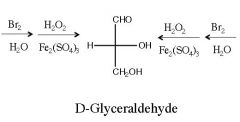
Name the starting sugars? what is this reaction?
|
|
|
|
What is a glycosidic bond?
|
In chemistry, a glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal group of a saccharide (or a molecule derived from a saccharide) and the hydroxyl group of some organic compound such as an alcohol. If the group attached to the carbohydrate residue is not another saccharide it is referred to as an aglycone. If it is another saccharide, the resulting units can be termed as being at the reducing end or the terminal end of the structure. This is a relative nomenclature where the reducing end of the di- or polysaccharide is towards the last anomeric carbon of the structure, and the terminal end is in the opposite direction. |
|
|
Define homopolysaccharide and heteropolysaccharide?
|
homo means one kind of subunit of sugar
heter means more than one kind of subunit of sugar |
|
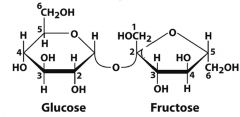
What is this molecule and what is the linkage?
|
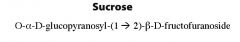
|
|
|
What are the monomers of sucrose and what is the linkage?
|
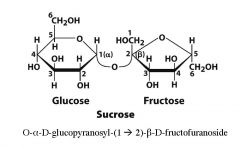
|
|
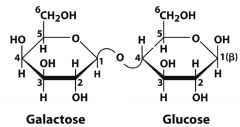
What is this molecule? what is the linkage?
|
|
|
|
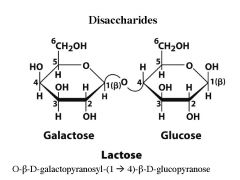
What are the monomers of Lactose? what is the linkage?
|
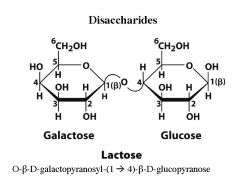
|
|
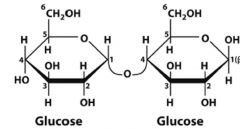
What is this disaccharide? what is the linkage?
|
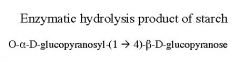
Maltose
|
|
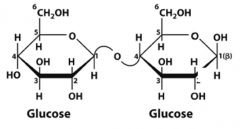
What is this disaccharide? what is the linkage?
|
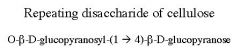
Cellobiose
|
|
|
People with the genetic disease phenylketonuria cannot breakdown ________, and should avoid the artificial sweetener ________?
|
phenylalanine, aspartame
|

