![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the function of the cardiovascular system?
|
To maintain blood pressure in the arteries and blood flow (perfusion) to the tissues, delivering oxygen, transporting hormonal messages and picking up waste products. The heart is the pump for this system.
|
|
|
What is the high pressure circulation system that delivers oxygenated blood to the body, returns deoxygenated blood to the heart?
|
Systemic Circulation
|
|
|
What is the low pressure circulation system, that delivers deoxygenated blood to lungs, returns oxygenated blood to the heart?
|
Pulmonary Circulation
|
|
|
What is the circulation system that is a separate blood supply system to the heart muscle itself?
|
Coronary Circulation.
|
|
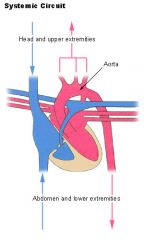
Take a look!
|
Systemic Circulation
|
|
|
What are vessels that carry blood to the heart?
|
Veins
|
|
|
What are vessels that carcy blood away from the heart?
|
Arteries
|
|
|
What are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood?
|
Pulmonary Arteries
|
|
|
What are the only veins that carry oxygenated blood?
|
Pulmonary Veins
|
|
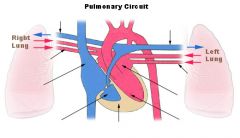
Take a look!
|
Pulmonary Circulation
|
|
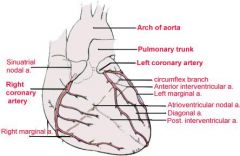
Take a look!
|
Coronary Circulation
|
|
|
What are the Cardiovascular functions?
|
Maintain normal blood pressure within arteries.
Maintain blood flow to tissues. Maintain normal blood pressure within capillaries and veins. Maintain these funections in rest and in work. |
|
|
What is Tissue Perfusion?
|
Delivery of O2 and nutrients to tissues.
Removal of waste products. Transport of hormonal messages from one part of the body to another. |
|
|
What is the force exerted by the blood against the inner walls of the blood vessels?
|
Blood Pressure
(Typically refers to systemic blood pressure) |
|
|
What is the maximum pressure achieved during ventricular contraction?
|
Systolic Blood Pressure
|
|
|
What is the lowest pressure that remains in the arteries when the ventricles are relaxing?
|
Diastolic Blood Pressure
|
|
|
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure called?
|
Pulse Pressure
|
|
|
What is the space between the two pleural cavities that contain the lungs - dividing the pleural spaces into left and right sides?
|
Mediastinum
|
|
|
What is the area on the right ventrolateral thorax where the heart makes contact with the chest wall? (elsewhere surrounded by lung)
|
Cardiac Notch
|
|
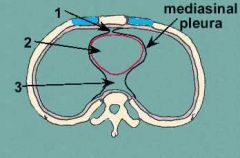
Take a look!
|
Mediastinum
|
|
|
What is the double walled connective tissue layer over the heart?
|
Pericardium
|
|
|
The out layer of the pericardium is called the?
|
Fibrous Pericardium
|
|
|
The inner layer of the pericardium is called the?
|
Serous Pericardium
|
|
|
The pericardium creates the potential space known as the?
|
Pericardial Space
|
|
|
What is the visceral layer of the serous pericardium of the covering the heart?
|
Epicardium
|
|
|
What is the word pertaining to the wall of an organ or cavity?
|
Perietal
|
|
|
What is the word pertaining to the soft internal organs?
|
Visceral
|
|
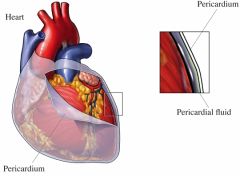
Take a look!
|
Pericardium
|
|
|
What is the heart muscle layer called?
|
Myocardium
|
|
|
What is the thin membranous lining layer of the inner chambers of the heart - the ventricles and atria are called?
|
Endocardium
|
|
|
The Fibrous Skeleton of the heart does what?
|
Seperates the heart into atrial and ventricular areas.
Tissue does not conduct electrical impulses. Serves as an anchor for the atrioventricular valves. |
|
|
What does auscultation mean?
|
Listening
|
|
|
If the fetal hole between the atria fails to close what is the defect called?
|
Atrial Septal Birth Defect
|
|
|
What delivers venous blood from the coronary circulatory system into the atrium?
|
Coronary Sinus
|
|
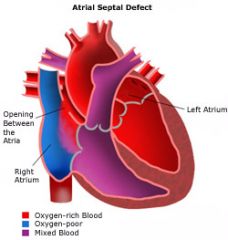
Take A Look!
|
Atrial Septal Birth Defect
|
|
|
Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into the?
|
low pressure pulmonary circulation.
|
|
|
What band runs from the interventricular septum to the free wall?
|
Moderator band
|
|
|
What prevents blood from flowing retrograde into the right atrium with ventricular contraction?
|
Tricuspid
Right Atrioventricular Valve (AV Valve) |
|
|
What prevents blood from flowing retrograde from pulmonary artery back into right ventricle?
|
Semilunar valve
(Pulmonic Valve) |
|
|
What prevents backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the atrium?
|
Mitral Valve
Left Atrioventricular Valve (AV Valve) |
|
|
Which ventricle is a high pressure system with walls 2 to 3 times thicker and no moderator band?
|
Left Ventricle
|
|
|
What valve prevents backflow into the left ventricle during diastole?
|
Aortic Valve
|
|
|
Know for Exam
Know the three cardiovascular systems Be able to label the 4 chambers and valves of the heart Which arteries carry deoxygenated blood? Trace the flow of blood through the heart and label each part |
Do I know these?
|
|
|
What creates the first S1 "Lub" sound?
|
Closure of the AV valves creates the first heart sound.
|
|
|
What is the term for the amount of blood leaving the heart?
|
Cardiac Output
|
|
|
What is the term for the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures of the expanding and contracting arterial walls?
|
Pulse Pressure
|
|
|
What is the specialized area of cardiac muscle in the right atrium (Pacemaker) that spontaneously depolarizes?
|
Sinoatrial (SA) node
|
|
|
When the Sinoatrial (SA) node spontaneously depolarizes a wave of depolarization takes two routes! What are they?
|
1. AV node via conductive fibers. (Highway Route)
2. Across Both Atrial Myocardium to Stimulate Arterial Contraction - Slower local route - Via cell to cell interaction - Stoped by the fibrous skeleton at the bottom of the atria. |
|

Depolarization Pathway
|
Depolarization Pathway
|
|
|
What is a diseased myocardium which spontanously depolarizes called?
|
Ectopic Pacemakers
|
|
|
What is a heart muscle cells contracting independently of each other and so coordinated pumping is lost called?
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
|
|
|
What is a large electrical current in attempt to repolarize all the cells at the same time called?
(Reset) |
Defirbrillator
|
|
|
Cardiac Ouput X Peripheral Resistance / Vessel Constriction Equals?
|
Blood Pressure = Cardiac Ouput X Peripheral Resistance / Vessel Constriction
|
|
|
Stroke volume X heart rate equals?
|
Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume X Heart Rate
|
|
|
What is the volume of blood in the ventricle right before it starts to contract called?
|
EDV - (End Diastolic Volume)
Preload |
|
|
Preload is?
|
EDV - (End Diastolic Volume)
|
|
|
What is the volume of blood left in the ventricle at the end of systole?
|
ESV - (End-Systolic Volume)
|
|
|
What is the S2 "Dub" sound from?
|
Semi-lunar valves (pulmonic: aoritc) close.
|
|
|
What is it called when all valves closed, ventricles relax and pressure inside the ventricle decreases?
|
Isovolumetric Relaxtion
|
|
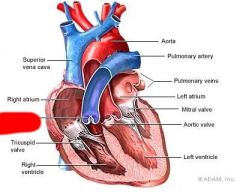
What valve is this?
|
Pulmonary Valve
|
|
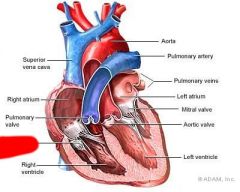
What valve is this?
|
Tricuspid Valve
|
|
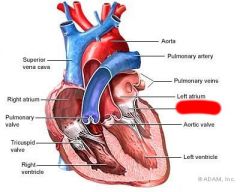
What valve is this?
|
Mitral Valve
|
|
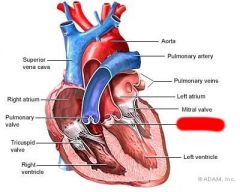
What valve is this?
|
Aortic Valve
|
|
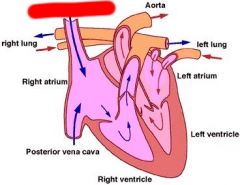
Label
|
Cranial Vena Cava
|
|
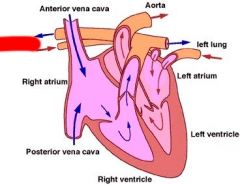
Label
|
Right Lung
|
|
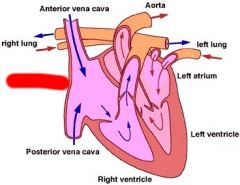
Label
|
Right Atrium
|
|
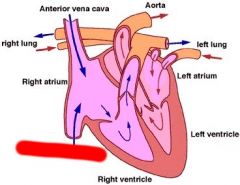
Label
|
Caudal Vena Cava
|
|
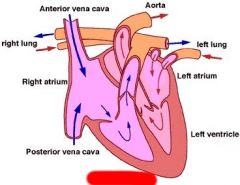
Label
|
Right Ventricle
|
|
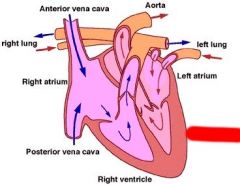
Label
|
Left Ventricle
|
|
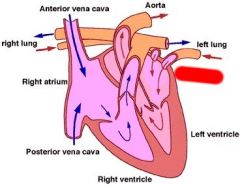
Label
|
Left Atrium
|
|
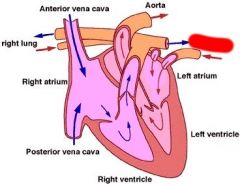
Label
|
Left Lung
|
|
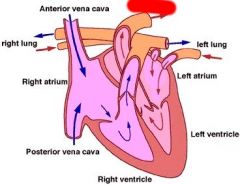
Label
|
Aorta
|

