![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
speed of all EM waves |
3.0 x 10^8
|
|
|
3 types of mechanical waves
|
transverse, longitudinal, torsion
|
|
|
mechanical waves...
|
require a medium
|
|
|
free end reflection
|
wave reflected on the same side
|
|
|
when two waves meet from opposite sides
|
they cancel out
|
|
|
Universal Wave Equation
|
velocity= fλ |
|
|
when 2 waves meet on the same side
|
they double in amplitude
|
|
|
period
|
time over number of cycles
|
|
|
frequency
|
= number of cycles over time
|
|
|
crest
|
occurs when an object vibrates perpendicularly to its axis
|
|
|
nodal point
|
point of destructive interference that remains at rest
|
|
|
rarefraction
|
region in a LONGITUDINAL wave where particles = farther apart than normal
|
|
|
Fixed-end reflection
|
reflected pulse = inverted
|
|
|
cycle
|
1 complete back & forth motion/oscillation/vibration
|
|
|
loop
|

crest meets crest
|
|
|
giga
|
10^9
|
|
|
mega
|
10^6
|
|
|
kilo
|
10^3
|
|
|
centi
|
10^-2
|
|
|
milli
|
10^-3
|
|
|
micro
|
10^-6
|
|
|
nano
|
10^-9
|
|
|
period
|
time over cycle
|
|
|
frequency
|
# of cycles over time or 1 over period
|
|
|
Transverse Waves
|
particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave motion
mechanical |
|
|
wave motion
|
-----> or <--------
|
|
|
particle motion
|
^
| | V |
|
|
longitudinal waves
|
particles vibrate parallel to the direction of wave motion
mechanical |
|
|
torsion waves
|
twisting motion (bridge)
mechanical |
|
|
phase
|
position of crest or trough at any part of the wave at any time
|
|
|
relative of phase
|
relationship of 2 waves
|
|
|
difference of waves
|
difference of 2 waves
|
|
|
CONSTRUCTIVE Interference
|
2 waves join together and the sum of their amps= amplitude of new wave
|
|
|
DESTRUCTIVE Interference
|
trough of one wave @ same time as a crest of another... waves cancel out
|
|
|
Principle of Superposition
|
2 waves @ 1 place; amp= sum of amps
|
|
|
sound waves
|
LONGITUDINAL
motion of air particles= parallel to direction of sound travels faster in solids/liquids high pitch= high f loud noise= large amp |
|
|
Universal Wave Equation
|
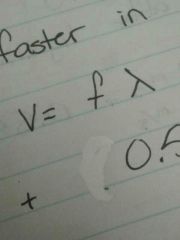
|
|
|
v=
|
332m/s + 0.59 (T°C)
|
|
|
wavelength
|
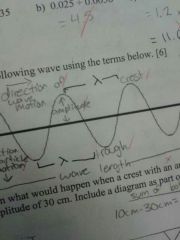
crest to crest or trough to trough
|
|
|
f(beats)=
|
| f2 - f1 |
|
|
|
Doppler Effect
|
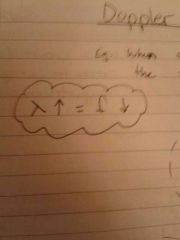
|
|
|
Doppler Effect Equation
|

|
|
|
v of sound
|
340m/s
|
|
|
All oscillating objects have a... |
natural frequency which they will vibrate @. |
|
|
Resonance |
Vibration caused when a periodic force is applied at the same frequency as the natural frequency
Ex: Child on a swing, trampoline |
|
|
Resonance in strings + springs |
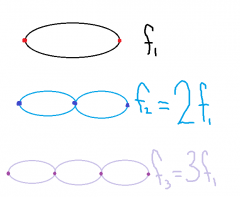
|
|
|
Open Air Columns |
Starts at L=1/2 (λ), increases by 1/2 |
|
|
Closed Air Columns |
Starts at L=1/4(λ), increases by 2/4 |
|
|
Frequency vs. Tension Equation |
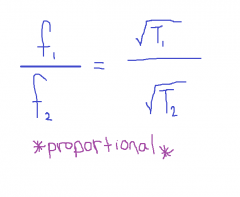
|
|
|
Frequency vs. Length Equation |
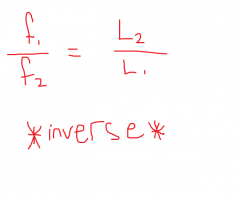
|
|
|
Frequency vs. Diameter Equation |
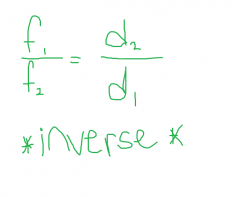
|
|
|
Frequency vs. Diameter Equation |
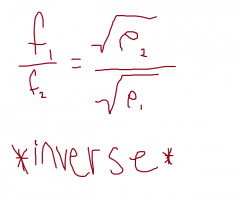
|

