![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
T/F: Cardiac muscle cells are striated like skeletal muscle cells but are larger and contain multiple nuclei. |
False: cardiac muscle cells are significantly smaller than skeletal muscle cells and contain multiple nuclei |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle is also known as ___ muscle because of its microscopic appearance. |
Striated |
|
|
|
____ are fibrous bands that attach muscle to bone. |
Tendons |
|
|
|
When muscles contract, blood vessels ____. |
Constrict |
|
|
|
The most prominent aponeurosis is the ____, that runs length wise between the muscles of an animal's ventral midline. |
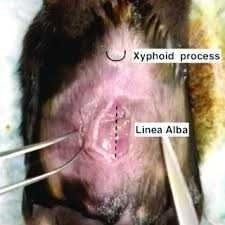
Linea alba/white line (connects the abdominal muscles) |
It is a common site for surgical entry. |
|
|
The neurotransmitter, ____, diffuses across the nerve fiber to the sarcolemma to trigger muscle contraction. |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
|
The binding of acetylcholine to receptors generates an electrical impulse leading to the release of ____ ions into the myofibrils. A. Ca2+ B. Na+ C. H+ |
Ca2+ (the increased calcium causes shortening of the sarcomere) |
|
|
|
___ is the movement of an extremity toward the medial plane while _____ is a movement away. |
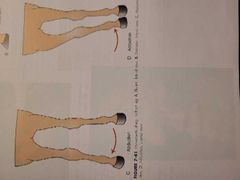
Adduction is towards, abduction is away. |
Addicts go towards drugs. Abductors take people away. |
|
|
Synovial joints can be classified into two types: |
Hinge (ginglymus joints) and gliding joints |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles working as ____ produce desired movement. A. Fixators B. Agonist |
Agonists |
|
|
|
The ____ of a muscle is the attachment site that has less movement/ more stability. A. Extension B. Insertion C. Origin
|
Origin |
|
|
|
The ___ of the muscle site undergoes the most movement during contraction. |
Insertion |
|
|
|
Muscle contractions vary in strength and range by controlling the number/force of the muscle fibers when contraction occurs |
Number |
|
|
|
___ (involuntary muscle) is found in the eyes, lungs, intestines, bladder, and reproductive tract. |
Smooth |
|
|
|
During longer periods of inactivity, muscles shift to an ____ metabolism; resulting in a buildup of ___ acid. |
Anaerobic, lactic acid |
|
|
|
The term ___, or "prime mover", describes a muscle group that directly produces a desired movement; directly opposed to these muscles are the ____. |
Agonists, antagonists |
|
|
|
The attachment sites between cardiac muscle cells that transmit impulses between cells. A. Myofibrils B. Myosin C. Intercalated discs |
Intercalated discs |
|
|
|
Nerve simulation from the ___ ___ system causes an increase in heart rate, while the ___ ___ system causes a decrease. |
Sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight system) , parasympathetic nervous system (rest/digest) |
|
|
|
____ muscle functions through large, rhythmic contractions such as peristalsis in the intestines. |
Visceral |
|
|
|
Muscle that is not under conscious control, such as cardiac muscle, is known as ___. |
Involuntary |
|
|
|
During prolonged periods of activity, muscles shift to _____ metabolism. This results in a buildup of ___ ____. |
Anaerobic, lactic acid |
|
|
|
Muscle contractions vary in strength and range by controlling the ____ of muscle fiber contractions stimulated. A. Number B. Strength |
Number |
|
|
|
Another name for a skeletal muscle cell is a ____. A. Fiber B. Myofibril C. Tubule |
Fiber |
|
|
|
Unlike tendons, ____ attach muscle to other muscle and are delicate/thin while tendon is tough/rope-like. A. Aponuerosis B. Epimysium C. Fascicles |
Aponuerosis |
|

