![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Green Lead |
Ground |
|
|
Bipolar Leads |
I, II, III |
|
|
VF |
Left foot |
|
|
VR |
Right arm |
|
|
VL |
Left arm |
|
|
V1 |
4th intercostal space, right of sternum |
|
|
V2 |
4th intercostal space, left of sternum |
|
|
V4 |
5th intercostal space, midclavicular line |
|
|
V3 |
Halfway between V2 and V4 |
|
|
V5 |
5th intercostal space, left anterior axillary line |
|
|
V6 |
5th intercostal space, left midaxillary line |
|
|
Flat part of the ECG tracing |
Isoelectric line |
|
|
A deflection that is above and below the baseline? |
Biphasic |
|
|
How many mm per second does the ECG paper move? |
25mm |
|
|
Each small box is? |
1 mm square |
|
|
Each large box has how many small boxes? |
5 |
|
|
Each large box represents how many seconds? |
0.20 seconds |
|
|
Each small box represents how many seconds? |
0.04 seconds |
|
|
How many large boxes make up 1 second? |
5 |
|
|
15 large boxes make up how many seconds? |
3 |
|
|
Sequence Method |
Find QRS complex that is on a heavy line. 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 |
|

|
Sinus Bradycardia HR <60 |
|

|
Sinus Tachycardia HR >100 |
|
|
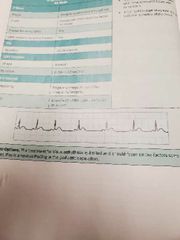
Sinus Arrhythmia |
|

|
Sinus Arrest and Sick Sinus Syndrome |
|

|
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker HR 60-100 3 Different P Wave Morphologies
|
|

|
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia HR >100 PR Interval Variations 3 Different P Wave Morphologies |
|

|
Atrial Flutter |
|

|
Atrial Fibrillation |
|

|
Supraventricular Tachycardia HR>150 |
|

|
Junctional HR 40-60 P Wave Absent or Inverted |
|

|
Accelerated Junctional HR 60-100 P Wave Absent or Inverted |
|

|
Junctional Tachycardia HR > 100 P Wave Absent or Inverted |
|

|
First Degree AV block PR Interval >1 big box |
|

|
Second Degree AV Block, Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach Increasing PR Interval w/ QRS dropped |
|

|
Second Degree AV Block, Mobitz Type II Same PR Interval |
|

|
Third Degree AV Block Decreasing PR Interval
|
|

|
Idioventricular HR 20-40 |
|

|
Accelerated Idioventricular HR 40-100 |
|

|
Ventricular Tachycardia HR 100-250 |
|

|
Ventricular Fibrillation |
|

|
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia |
|

|
Asystole |
|

|
Ventricular Artificial Pacemaker Trace |
|

|
AV Sequential Artificial Pacemaker Trace |
|

|
Premature Atrial Contraction |
|

|
Premature Junctional Contraction |
|

|
Unifocal Premature Ventricular Contractions |
|

|
Multifocal PVCs in a Bigeminy Pattern |
|

|
Unifocal PVCs in a Trigeminy Pattern |
|
|
Interiors of heart muscle cells are: |
Negative at rest (polarized) |
|
|
When depolarized, the interiors become: |
Positive and myocytes contract. |
|
|
The cell to cell conduction of depolarization through the myocardium is initiated by: |
Fast moving sodium Na+ ions |
|
|
The electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles? |
AV Node |
|
|
Depolarization conducts slowly through the AV node since it is carried by: |
Ca+ ions |
|
|
For the conduction of depolarization, purkinje fibers use: |
Fast moving Na+ ions |
|
|
Repolarization is accomplished by: |
Potassium K+ ions leaving the myocytes. |
|
|
Cause myocyte contraction: |
Calcium Ca++ ions |
|
|
Outflow causes repolarization of myocytes: |
Potassium K+ ions |
|
|
Movement produces cell-to-cell conduction of depolarization of the heart: |
Sodium Na+ ions |
|
|
Atrial Foci |
60-80 bpm |
|
|
Junctional foci |
40-60 bpm |
|
|
Ventricular foci |
20-40 bpm |
|
|
II, III, AVF |
RCA |
|
|
V1, V2, V3, V4 |
LAD |
|
|
I, AVL, V5, V6 |
LCA |
|
|
Location I |
Lateral |
|
|
Location II, III |
Inferior |
|
|
Location AVL |
Lateral |
|
|
Location AVF |
Inferior |
|
|
Location V1-V6 |
By twos Septal, Anterior, Lateral |

