![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Relative size magnification |
Increasing the size of an object makes it subtend a larger angle at the eye nodal point resulting in a larger retinal image |
|
|
Relative distance magnification |
Moving the object closer makes it subtend a larger angle at the eyes nodal point resulting in a larger retinal image |
|
|
How is an astronomical telescope adapted to form a terrestrial telescope? |
Porro prism or roof prism |
|
|
Define Terrestrial telescope |
It is a astronomical telescope that has been fitted with an erecting system |
|
|
Define a distance cap |
Is a negative lens fitted to the objective lens of a near vision telescope to adapt it for distance use |
|
|
Define a reading cap |
Is a positive lens fitted to the objective lens to adapt it for near |
|
|
Define a telemicroscope |
Is a telescope with a cap |
|
|
Free working distance |
Is measured from the objective lens to the task |
|
|
Exit image vergence |
Is the vergence of light exiting the back of the telescope |
|
|
Define the term activity limitation |
Difficulties a person may have in executing activities |
|
|
Define the term participant restrictions |
Problems an individual may experience in involvement in life situations |
|
|
Performance qualifier |
This describes what an individual does in their current environment. The lived experience of the individual, includes societal context, including assistive devices / personal assistance. |
|
|
Capacity qualifier |
This describes an individual's ability to execute a task or action i.e. the highest probable level of functioning of a person as a given moment in time |
|
|
The definition of low vision given by Low Vision Consensus group (1999) |
A person with low vision is someone who has impairment of visual function for whom full remediation is not possible by conventional spectacles, contact lenses or medical intervention and which causes restrictions in that person's everyday life. (Focus on patients function but there is no legal definition of 'low vision' in the UK) |
|
|
What 6 things at minimum should we consider for visual function |
Contrast sensitive Glare/ photophobia Scotoma Colour perception Duplicity theory (cones and rods) Binocularity |
|
|
Which act provides us with the definition/guidelines for blind and partially sighted? |
National assistance Act 1948 |
|
|
Blind (severely sight impaired) |
So blind as to be unable to perform any work for which eyesight is essential |
|
|
Partially sighted (Sight impaired) |
There is no legal definition of partial sight provided by the National Assistance Act (1948). It does give us the guidance of: 'substantially and permanently handicapped by defective vision caused by congenital defect or illness or injury' |
|
|
What can avoid at least half of the sight loss in the UK? |
Regular sight test Smoking cessation Health diet and exercise UV protection Eye safety can significantly reduce the risk of eye disease |
|
|
The leading causes of sight loss in the UK in order of prevalence are: |
1. Uncorrected refractive error (39%) 2. Age -related macular Degeneration (23%) 3. Cataract (19%) 4. Glaucoma (7%) 5. Diabetic Retinopathy (5%) |
|
|
Community Care Act (1948) |
Ensures that local authorities must provide specific service based on a person's need and not their registration status |
|
|
Group 1 of Severely sight impaired |
Visual acuity below 3/60 A patient who is 1/18 cannot be certified in group 1 |
|
|
Group 2 for SSI registrants |
Visual acuity between 3/60 and 6/60 and a contracted field of vision |
|
|
Group 3 for SSI registrants |
Visual acuity is better than 6/60 and have a severely contracted field of vision, especially if the contraction is in the inferior field or bi- temporal hemianopia |
|
|
The cosine law |
The greater the angle between the light source and the task, the lower the illumination. |
|
|
Luminous intensity (I) |
The power/strength of a light source in a given direction Measured in candela (cd) A source of 1 candela radiates 1 lumen of flux into one steradian Lumens/solid angles(steradian) |
|
|
Mean spherical intensity |
The average intensity of a real world source considered as though it was a point source MSI = Lumen / steradian in a sphere (4 pie) |
|
|
'objective' lens (telescopes) |
This lens is nearer the object It is the 'entrance pupil' for the telescope It's diameter controls field of view |
|
|
'Eyepiece' lens system (telescope) |
This lens is nearer the patient It is always the highest power lens Sometimes a series of lenses which help control aberrations Its position controls FOV |
|
|
Benefits and limitations of distance telescopes |
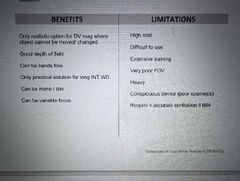
|
|
|
Types of telescopes |

|
|
|
What do theses marking mean 8x20x7.5 on a telescope? |
8 = magnification 20 = objective diameter 7.5 = Field of view in degrees |
|
|
What is a terrestrial telescope? |
An astronomical telescope can be modified to create an upright image using an erecting lens: Porro prism Roof ' pechan - schmit' prism This makes the device longer, heavier and more expensive |
|
|
Benefits and limitations of an astronomical (keplerian) telescope? |
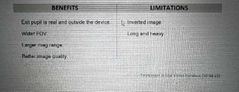
|
|
|
Benefits and limitations of a Galilean telescope? |
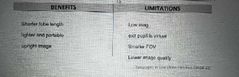
|
|
|
Reverse Galilean telescope (field expander) |
A Galilean system can be turned around (reversed) for patients with gross peripheral field defects For example retinal pigmentosa and glaucoma This mini does the image on the macula Increase their Field of view It would reduce acuity |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of high reading addition in low vision |
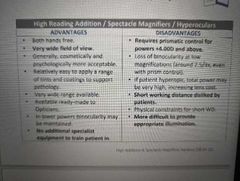
|
|
|
What is the rule of thumb for practice for high additions? |

|
|
|
Group 1 of sight impaired |
3/60 - 6/60 with a full field of view |
|
|
Group 2 of sight impaired |
6/60 - 6/24 moderate field loss, opacities, patchy |
|
|
Group 3 of sight impaired |
Larger or equal to 6/18 with marked field loss |

