![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PSYCHOANALYSIS |
— Progenitor of all theories — Present behavior is heavily influenced by our past experiences (especially childhood experiences) (sometimes traumatic experiences) |
|
|
LEVELS OF MENTAL LIFE |
- Analyzes the Psyche - Region of Life - Container - Kung saan napupunta ang mga info na nakuha natin from externally |
|
|
What are 3 Levels of Mental Life? |
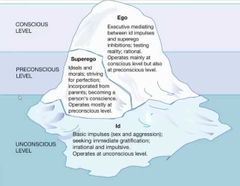
1. Conscious 2. Preconscious 3. Unconscious |
|
|
UNCONSCIOUS (Explain) |
- The very bottom part among the 3 levels - "Bottom of the well" - Not aware - Source of drives, urges & instincts - Fears, Unacceptable sexual desires, violent motives, immoral urges, selfish needs, irrational wishes, shameful experiences - Can be argued as Primal part - We don't know what's in it unless we deep dive - Pero hindi natin agad makukuha |
|
|
CONSCIOUS (Explain) |
- Is what we are aware - Basically kung ano yung nakikita natin - Mediator between the mind & reality • PERCEPTUAL CONSCIOUS SYSTEM - Which is turned towards the outerworld & acts as a medium for the perception of external stimuli - Nagdidirect sa mind natin kung saan tayo nagp-pay attention - A medium of perception that decides what to store |
|
|
PROVINCES OF THE MIND |
- If there's a container, then there should be content, so what are the things that goes into our mental life structure? 1. Id 2. Ego 3. Superego |
|
|
ID (Explain) |
- Pleasure principle - Completely unconscious - No contact with reality - Illogical, chaotic, instinctual - According to Freud, this is who we are, core of personality - Satisfies urges, desires, impulses, if not magwawala siya :> - It exists to avoid hardships & sufferings - Eventually as we grow, we need to get into contact with reality to satisfy our Id because no one can do it for you. |
|
|
Superego (Explain) |
- Above the ego - Morality & Idealistic principle - Represents the moral & ideal aspects of personality Conscience - What we should not do Ego Ideal - What we should do |
|
|
Why one must have strong ego? |
A healthy individual mist have a strong ego that can deal with the demands of Id & Superego & at the same time reality of life
Kung mapadala siya ng Id, Superego or ng reality, madidisintigrate si EGO & that is when it manifests symptoms of Psychopathology |
|
|
Dynamics of the 3 |
ID — CHILD Superego — ADULT Ego — YOU
ID & SUPEREGO are in demands but opposite: Id - Wants satisfaction Superego - Wants suffering
How about Ego ? - Must build with reality - Distributes equally to the demands of Id & Superego
|
|
|
Dynamics (The Movement) - The Battle of ID, Ego, Superego |
• Can manifest as someting as a movement in the Personality • Manifestation of ID, Ego, Superego Conflict are distincts |
|
|
DRIVES |
Operates as a constant motivational force from within even without stimulus, they're still there |
|
|
DRIVES |
Operates as a constant motivational force from within even without stimulus, they're still there |
|
|
Drives: Sexual Drive |
• Libido • ID centric • Source is always internal • Can be expressed via narcissim, love sadism & masochism |
|
|
Drives: Agression |
• ID centric • Destructive drive • Tendency to destroy things • To return the organism to an inorganic state • Suicidal thoughts are given because of agression drive • Can be expressed via learning, gossip, sarcasm, humiliation, humor & enjoyment Thanatos - Death Drive |
|
|
ANXIETY |
• Worry • Everywhere can be from Id, ego, superego • unpleasant state accompanied by physical sensation that warns the person of impending danger Kinds: • Neurotic Anxiety • Moral Anxiety • Realistic Anxiety |
|
|
NEUROTIC ANXIETY |
Apprehension about an unknown danger; during childhood. These feelings of hostility are often accompanied by fear of punishment & this fear becomes generalized into unconscious neurotic anxiety. • Originates from ID • Results fear of punishment or authority destructive feelings towards them. • You're not doing something, fear of punishment is mapupunta sa id unconscious eventually old, biglang lumalabas randomly. |
|
|
MORAL ANXIETY |
• Stems from the conflict between the ego & the superego (should or should nots) • Results from failure to do behave correctly • "Nasa isip lang ng tao dahil mataas ang moral standards niya" • You're thinking about " Tama ba ang ginawa ko?" |
|
|
REALISTIC ANXIETY |
• Originates from the outside world Resembles fear but does not involve specific feared objects; an unpleasant, nonspecific feeling involving a possible danger. - Is Ego preserving as it signals some dangers at hand - Is Self regulating as it precipitates repression which reduces the pain of anxiety |
|
|
❗❗❗ |
- Anxiety is only experienced by the Ego
- Source ng Id & source ng real world = No feelings
• ID - impulses, drives, ails • Superego - Parent, "Ito dapat ginawa mo hindi ganyan" - Anxiety si Ego ang nagsusuffer, siya yung nagtatrabaho so it needs to protect itself at the same time the 2 If not protect itself, how to protect the 2
- Anxiety energy naninira sa Ego
- Para magawa ng maayos para hindi ma disintegrate si ego due to anxiety
Forced with the Technique: Defense Mechanisms |
|
|
DEFENSE MECHANISMS |
• Avoid dealing w/ instinctual demands & to defend the ego against anxiety that accompanies the demands • As good as they are, they have limitations because everything has a cause: Psychic energy
• If Ego naubusan ng Psychic energy sa kaka defense mechanism, nagsusumabog si ego, need ng therapy - Psychopathology |
|
|
PRIMITIVE DEFENSE MECHANISMS |
1. Fixation 2. Regression 3. Projection 4. Introjection 5. Acting out 6. Denial 7. Reaction Formation 8. Dissociation |
|
|
PDM: Fixation |
- Permanent; remaining at the present more comfortable stage of developmentEx. Psychological Fixations - Oral Fixations Smoking Gum-chewing Nail-biting - Anal Fixations Orderliness Obsessiveness Rigidity - Phallic Fixations Vanity Exhibitionism Pride |
|
|
PDM: Regression |
- Temporary, reverting to an earlier stage of development which has lesser stress - Kung nagkakaroon ng psychological downtime like sadness, suffering we have the tendency to regress to our childhood experience. Because childhood is safe. |
|
|
PDM: Projection |
- Attributing unwanted internal impulse to an external object/person; see in others unacceptable feelings or tendencies that resides in ourselves (Paranoia) - Transferring your negative, unacceptable, unwanted thoughts, feelings, motives to another person. |
|
|
PDM: Acting Out |
- Performing an extreme behavior to express thoughts or feelings the person is incapable of expressing (self-harm) |
|
|
PDM: Denial |
- Refusal to accept reality as if the painful event or thought did not exist while being apparent to others (most primitive) - Straight up deny kasi hindi mo kaya |
|
|
PDM: Reaction Formation |
- Doing the opposite in an exaggerated, compulsive, obsessive way, form a reaction that it acceptable to society/others; limited to a single objects |
|
|
PDM: Dissociation |
- Breaking part of memory, consciousness or perception of self or the environment to avoid unbearable thought feelings & memories (DID) |
|
|
LESS PRIMITIVE DEFENSE MECHANISMS |
1. Repression 2. Undoing 3. Isolation 4. Displacement 5. Compartmentalization 6. Intellectualization 7. Rationalization |
|
|
LPDM: Repression |
- Threatening feelings into the unconscious; impulses may remain unconscious, creates more anxiety or expressed in disguised form such as physical symptoms - Most important that ego uses - You can't act out from impulses pipigilan niya lang - Because it is threatening to the ego |
|
|
LPDM: Undoing |
- Look away or dowl away w/ unpleasant experiences & consequences by making it dissapear through repetitive & ceremonial acts (compulsion) |
|
|
LPDM: Isolation |
- Uses obsessive thoughts to block out any feelings that follows an unwanted experience & severe associations (Obsession) |
|
|
LPDM: Displacement |
- Redirecting unacceptable urges onto different people - Displacing unwanted feelings to a much safer target |
|
|
LPDM: Compartmentalization |
- Lesser form of dissociation - Separate parts of self from awareness of other parts & behaving as if one has separate sets of values |
|
|
LPDM: Intellectualization |
- Dealing with stressors by excessive use of abstract thinking or complex explanations to control disturbing feelings |
|
|
LPDM: Rationalization |
- Giving another interpretation to a situation in the face of changing reality - Sour grape |
|
|
MATURE DEFENSE MECHANISMS |
1. Compensation 2. Sublimation 3. Altruism 4. Assertiveness |
|
|
MDM: Compensation |
- Counterbalancing perceived weaknesses by emphasizing strength in other areas |
|
|
MDM: Sublimation |
- Beneficial to self & society - Repression of genital aim onto cultural or social aim - Most healthy way - Satisfying an impulse, emotions, thoughts by substituting it in a more acceptable way Humor - channeling unacceptable impulses or thoughts into a light-hearted story or joke
Fantasy - channeling of unacceptable or unattainable desires into imaginations |
|
|
MDM: Altruism |
- Getting pleasure from giving to others what people would themselves like to receive |
|
|
PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT |
1. Oral Stage (0-1) 2. Anal Stage (1-3) 3. Phallic Stage (3-6) 4. Latency Stage (6-Puberty) 5. Genital Stage (12+ Puberty-on) |
|
|
❗❗❗ |
- The first 4 or 5 years of life (Infantile Stage) are the most crucial for personality fornation - Freud said, Anatomy is Destiny - Infantile - People are hesistant to accept that infants have sexual drive - However today, really all close observers accepts the idea |
|
|
1st: Oral Phase |
- Infants obtain life-sustaining nourishment through the oral cavity - Tendency to such their thumbs put everything in their mouth |
|
|
A. Oral-Receptive |
- Instant gratification receives everything through their mouth - Infants incorporate or receive int one's body the instinctual object-choice |
|
|
B. Oral-Sadistic |
- Infants respond through biting, cooing, sniling, crying, first auto-erotic experience is thumb sucking - Destroy everything to their mouth |
|
|
❗❗❗ |
People are given by their sexual urges & those urges have erogenous zone Body filled with sexual energy/ drive throughout the phase of development nalilipat ang erogenous zone |
|
|
2nd: Anal |
- Agressive Drive - Erogenous Zone: Anus |
|
|
Early Anal Phase |
- Sadistic drive is stronger than the erotic one - Children often behave agressively toward their parents for frustrating them with toilet training - Receive satisfaction by destroying or losing objects - Agression in Toilet training |
|
|
Late Anal Phase |
- Receives satisfaction by withholding & retention during Toilet training - Takes interest toward their feces - If children will be forced to withhold their feces, they may develop canal character Fixation (Orderliness, stinginess & Obstinacy) |
|
|
Toilet Training |
During this stage, the infants learn how to regulate the bodily impulses & delay immediate gratification to meet the demands of external environment |
|
|
Anal Retentive & Anal Explosive |
Anal Retentive - Too stingy who hold on to all kinds of objects, must specially to money, over controller, preoccupied with cleanliness & orderliness Anal Explosive - Manifest emotional outburst - Temper tabtrums - Rage - Unclean - Messy - Disorderly |
|
|
3rd: Phallic |
- A time when the genital area becomes the leading erogenous zone - Marked for the first time by a dicotonomy between male & female development - Anatomy is destiny different experiences by different process male & female then dito papasok ang oedipus complex |
|
|
Male Phallic Phase - Oedipus Complex |
- Sexual desire for mother/hostility for the father - Castration complex in the form of Castration - Maanxious ang bata - Merong mga impulses - Marerealize ng bata na may mali sa impulses - Nagkakaroon ng anxiety na mapuputulan ng penis - Identification with the father - Happens when you're presented in a situation wherein there's another figure or authority figure - You're afraid, because they're powerful, for the Ego to cope is to ifentify "I will be you, not me, so scary) - Resolves oedipus complex na triggering sa sexual drive - Can be remove - Can defend ego towards castration anxiety by doing that strong superego, child replaces the nearly completely dissolved
Anxiety shatters the oedipus complex Like your 1st problem is of course sexual drive, problems & anxiety will dissolved it & it will stay that way. The ego doesn't like anxiety, so defense mechanisms it is
: Uses father as role model, introjects authority into self & forms superego : Simple Oedipus Complex Starts w/ identification w/ father : Complete Oedipus Complex (affclection towards father; hostility towards mother (ambivalent condition) known as castration complex; castration anxiety : Once Oedipus complex is dissolved or repressed; incestous feelings are turned into feelings of love. He may identify with the father. |
|
|
Female Phallic Phase |
Castration complex in the form of penis envy - expressed as a wish to be a boy or desire to have a penis Oedipus Complex develops a desire for father & hostility for mother - Gradual realization that oedipal desires are useless or self-defeating, - Marerealize ng bata kasi never magkaroon ng penis - Identification w/ the mother - Replaces the dissolved Oedipal desire with weak superego |
|
|
LATENCY |
- Dormant psychosexual development (same-sex peer friendship) - Male & Female mingles with no problem - No tension, walang malisya - Subside ang sexual druve - Reinforced by suppresion by parents/teachers & by internal feelings of shame & guilt |
|
|
GENITAL |
- Puberty - Reawakening of sexual aim - Gives up auto-eroticism & directs sexual energy to another person instead of themselves - Synthesis of erogenous zones - Pleasure is gained through sexual intercourse w/ nonrelatives - Reproduction is already possible - Reawakening of sexual aim - Hormones magwawala |
|
|
APPLICATION OF PSYCHOANALYSIS |
Psychotherapy Psychoanalytic Theory - Uncover repressed memories through free association & dream analysis - Transforming what is unconscious into what is conscious |

